

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this articlebyadding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
Find sources: "Leggett & Platt" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2009) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
 | |
| Company type | Public |
|---|---|
|
| |
| Industry | Residential Bedding and Furniture Automotive Seating Industrial Materials |
| Founded | 1883; 141 years ago (1883) |
| Headquarters | Carthage, Missouri, U.S. |
Key people | Karl Glassman(CEO)[1] |
| Revenue | |
Number of employees | approx. 19,300 (2023) |
| Website | leggett |
Leggett & Platt (L&P), based in Carthage, Missouri, is an American diversified manufacturer that designs and produces various engineered components and products that can be found in homes and automobiles. The firm was founded in 1883, and consists of 15 business units, 20,000 employee-partners, and 135 manufacturing facilities located in 18 countries.[2]
As of May 2024, senior corporate executives included:
| Director | Joined In | Position | Company |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mark A. Blinn | 2019 | Retired President, CEO, Director | Flowserve Corporation |
| Robert E. Brunner | 2009 | Retired Executive VP | Illinois Tool Works, Inc. |
| Mary Campbell | 2019 | Chief Merchandising Officer | Qurate Retail Group |
| J. Mitchell Dolloff | 2020 | CEO & President | Leggett & Platt |
| Manuel A. Fernandez | 2014 | Managing director | SI Ventures |
| Karl G. Glassman | 2002 | Retired CEO | Leggett & Platt |
| Joseph W. McClanathan | 2005 | Retired President & CEO | Energizer Household Products Division of Energizer Holdings |
| Judy C. Odom | 2002 | Retired Chairman & CEO | Software Spectrum, Inc. |
| Srikanth Padmanabhan | 2018 | Vice-president | Cummins Inc. |
| Jai Shah | 2019 | Group President | Masco Corporation |
| Phoebe A. Wood | 2005 | Principal | CompaniesWood |


In 1883 in Carthage, Missouri, J.P. Leggett developed a new type of bedspring consisting of single cone spring wire coils, formed and interlaced, then mounted on a wood slat base. The bedspring could then be used as a base for the then-popular cotton, feather, or horsehair mattresses. Needing expertise in manufacturing and production, he recruited his soon-to-be brother-in-law, C.B. Platt, whose father owned and operated Platt Plow Works, into the partnership. Together, they produced the components of their Leggett & Platt bedspring, which was patented in 1885.
| Bedspring vs. Innerspring |
|---|
| At the time of their invention, bedsprings referred to cone-shaped wire coiled springs, attached to a wooden slat foundation, used to support then-popular mattresses. These mattresses were typically made of horse hair, corn husks, cotton, feathers, or another soft material. Early bedsprings functioned similarly to today's box springs in their support of a mattress. However, box springs are rather rigid in structure, while bedsprings provide a more flexible surface. |
| Innersprings, by contrast, refer to the core system of wire springs that, along with various types of foam and other padding materials, comprise the insides of today's mattress. The mattress is usually coupled with a box spring to create a sleep set. Innersprings can be coiled springs laced together, continuous coil springs, or individually encased springs, that support a person sleeping on the mattress. |
The Carthage market for their new product was very limited. To expand the market to a wider region, Platt and George Leggett, brother of J. P. Leggett, would load a horse-drawn wagon with bedsprings and travel to surrounding communities. Often, to conserve space, they would load the springs and slats separately into the wagon and assemble them in a store or on an adjacent sidewalk. The partnership prospered, and the business was incorporated in 1901.

The company built its first factory and offices in Carthage in 1890. The workforce at that time consisted of the two partners and five employees. Soon after completion of the Carthage plant, a second factory was built in Louisville, Kentucky. During the next 50 years, three more factories were built. Demand for the company's improved bedsprings was rising, and a second plant was built in Carthage in 1925. The new, much larger plant was located next to a railroad to allow for expanded shipments of products and supplies. In 1942, an additional factory was built in Winchester, Kentucky, which was subsequently consolidated with the Louisville plant. For some time, Texas had proven to be a main market outlet, and in 1947, a major factory was built in Ennis, Texas. By 1947, Leggett & Platt consisted of 4 plants and 500 employees.
Although available in various models and continuously improved upon, bedsprings were practically the only product Leggett & Platt offered until 1933. However, in that year the company began to manufacture springs for innerspring mattresses, which were relatively new products in the industry and growing in popularity. Thereafter, the company slowly began to diversify its products within the bedding industry by producing rollaway beds and folding metal cots, along with bed frames and bed rails.

In 1960, Harry M. Cornell Jr., J.P. Leggett's grandson, was elected President and CEO of the company, taking over for his father (who was Leggett's son-in-law). The company's total sales in 1960 were approximately $7 million from three states: Kentucky, Texas, and Missouri. Determining the course and future of the company became management's primary objective. Following an extensive evaluation of the company and its potential, Cornell and his management partners concluded that Leggett & Platt's best opportunities for profitable growth lay in a strategy of specializing in manufacturing, marketing, and distributing a broad and growing line of components and related products, first nationally and eventually on a worldwide basis. Key drivers of future sales and earnings would include aggressive internal growth initiatives, coupled with an active and ongoing acquisition program.
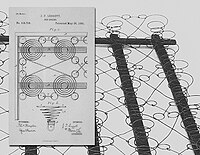
Even greater success followed, and Leggett & Platt became known as “the components people.” Leggett & Platt stock was first traded over the counter in 1967. Twelve years later, on June 25, 1979, top management was present in New York City to witness the stock's first day listed on the New York Stock Exchange. In 1999, the company became part of the S&P 500 Index.
Today, Leggett & Platt has 135 manufacturing facilities in 18 countries.
| Executive | Years of Service |
|---|---|
| J.P. Leggett & C.B. Platt, Partnership | 1883–1901 |
| J.P. Leggett | 1901–1921 |
| C.B. Platt | 1921–1929 |
| J.P. Leggett, Jr. | 1929–1933 |
| F.B. Williams | 1933–1938 |
| George S. Beimdiek, Sr. | 1938–1953 |
| Harry M. Cornell, Sr. | 1953–1960 |
| Harry M. Cornell, Jr. | 1960–1999 |
| Felix E. Wright | 1999–2006 |
| David S. Haffner | 2006–2015 |
| Karl G. Glassman | 2016–2021 |
| J. Mitchell Dolloff | 2022–2024 |
| Karl G. Glassman | 2024–Present |
History of stock splits:
Leggett & Platt is a signature sponsor of the Seena Magowitz Foundation, helping support the mission to eradicate the world of pancreatic cancer.[5]
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty |title= (help)