


Lipidology is the scientific study of lipids. Lipids are a group of biological macromolecules that have a multitude of functions in the body.[1][2][3] Clinical studies on lipid metabolism in the body have led to developments in therapeutic lipidology for disorders such as cardiovascular disease.[4]
Compared to other biomedical fields, lipidology was long-neglected as the handling of oils, smears, and greases was unappealing to scientists and lipid separation was difficult.[5] It was not until 2002 that lipidomics, the study of lipid networks and their interaction with other molecules, appeared in the scientific literature.[6] Attention to the field was bolstered by the introduction of chromatography, spectrometry, and various forms of spectroscopy to the field, allowing lipids to be isolated and analyzed.[5] The field was further popularized following the cytologic application of the electron microscope, which led scientists to find that many metabolic pathways take place within, along, and through the cell membrane - the properties of which are strongly influenced by lipid composition.[5]
The Framingham Heart Study and other epidemiological studies have found a correlation between lipoproteins and cardiovascular disease (CVD).[7] Lipoproteins are generally a major target of study in lipidology since lipids are transported throughout the body in the form of lipoproteins.[2]
A class of lipids known as phospholipids help make up what is known as lipoproteins, and a type of lipoprotein is called high density lipoprotein (HDL).[8] A high concentration of high density lipoproteins-cholesterols (HDL-C) have what is known as a vasoprotective effect on the body, a finding that correlates with an enhanced cardiovascular effect.[9] There is also a correlation between those with diseases such as chronic kidney disease, coronary artery disease, or diabetes mellitus and the possibility of low vasoprotective effect from HDL.[10]
Another factor of CVD that is often overlooked involves the concentrations of low-density lipoproteins (LDL) and very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL). These are often seen at higher than expected and necessary levels in the body due to food uptake, family history, and a person's metabolic rate. There is a correlation between these increased levels and stroke, heart attack, and mortality.[11]
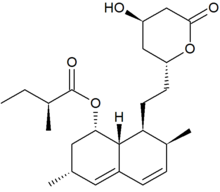
Statins are a class of drugs used to treat cardiovascular disease by lowering lipid levels, specifically LDL-C levels.[12] Statins have shown to reduce new cardiovascular events by 30-40%.[13] However, complications may still arise even after taking the drug and some patients are statin-intolerant. Lipoprotein apheresis therapy is another nonsurgical treatment for reducing LDL-C concentrations.
PCSK9 inhibitors are a new drug that can replace statins and lipoprotein apheresis therapy.[13] For patients that are statin-intolerant, PCSK9 inhibitors can provide a therapeutic alternative.
Lipidomics is the complete profile of all lipids in a biological system at a given time. This is used to identify and quantify the lipids that can be detected. Since lipids have a variety of functions in the body, being able to understand which specific types are present in the body and at what levels is crucial to understand the diseases that result due to lipids.[14] Methods of lipidomic analysis include mass spectrometry and chromatography.[6] Monitoring lipid concentration can reveal much about an organism's health.
Chemical basis
Plant form
and function
Animal form
and function
Field techniques
Branches
Glossaries
See also
General
Specific
paths
Nonhuman
Other
Other
General
Geometry
Lipoprotein particle classes
and subclasses
Extracellular enzymes
Phosphoinositides:
Sphingosine backbone
Metabolites
Ganglioside
pathway
From globoside
From sphingomyelin
From sulfatide
Other