

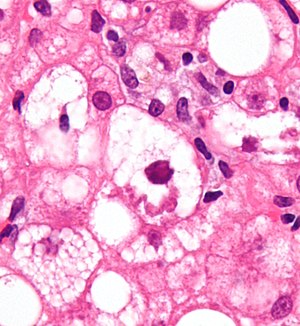
Inhistopathology, a Mallory body, Mallory–Denk body (MDB), or Mallory's hyaline is an inclusion found in the cytoplasmofliver cells.[1] Mallory bodies are damaged intermediate filaments within the liver cells.
Mallory bodies are classically found in the livers of people suffering from alcohol-induced liver disease and were once thought to be specific for that.[2]
They are most common in alcoholic hepatitis (prevalence of 65%) and alcoholic cirrhosis (prevalence of 51%).[3]
They are a recognized feature of Wilson's disease (25%), primary biliary cirrhosis (24%), non-alcoholic cirrhosis (24%), hepatocellular carcinoma (23%) and morbid obesity (8%), among other conditions.[3] However, it has also been reported in certain other unrelated conditions.[4]
Mallory bodies are highly eosinophilic and thus appear pink on H&E stain. The bodies themselves are made up of intermediate cytokeratin 8/18 filament proteins that have been ubiquitinated, or bound by other proteins such as heat shock proteins, or p62/Sequestosome 1.[5]
It is named for the American pathologist Frank Burr Mallory, who first described the structures in 1911.[3] A renaming as Mallory–Denk bodies was proposed in 2007 to honor the contribution of Austrian pathologist Helmut Denk for the molecular analysis of the pathogenesis of MDBs.[6]
|
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gastrointestinal tract |
| ||||||||
| Accessory |
| ||||||||
| Defecation |
| ||||||||
| Abdomen |
| ||||||||
| Hernia |
| ||||||||
| Other |
| ||||||||