

| Manihiki Plateau | |
|---|---|
| Stratigraphic range: Cretaceous 126–116 Ma
| |
| Type | Igneous |
| Area | 770,000 km2 (300,000 sq mi)[1] |
| Lithology | |
| Primary | Basalt |
| Location | |
| Coordinates | 10°00′S 162°30′W / 10°S 162.5°W / -10; -162.5 |
| Region | South Pacific Ocean |
| Country | Cook Islands |
| Type section | |
| Named for | Manihiki atoll |
| Location of the Manihiki Plateau in the Pacific Ocean | |
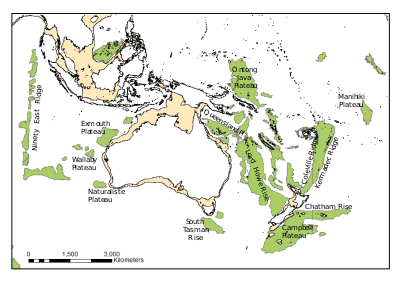
The Manihiki Plateau is an oceanic plateau in the south-west Pacific Ocean. The Manihiki Plateau was formed by volcanic activity 126 to 116 million years ago during the mid-Cretaceous period at a triple junction plate boundary called the Tongareva triple junction.[2] Initially at 125 million years ago the Manihiki Plateau formed part of the giant Ontong Java-Manihiki-Hikurangi plateau.[3]
The Manihiki Plateau extends from 3°S to 6°S and 159°W to 169°W covering 770,000 km2 (300,000 sq mi) and has an estimated volume of 8,800,000 km3 (2,100,000 cu mi) with a crustal thickness of 15–25 km (9.3–15.5 mi). Several of the Cook Islands are located on the southern part: Pukapuka, Nassau, Suwarrow, Rakahanga, and Manihiki. The Tokelau Basin borders it to the west, the Samoan Basin to the south, the Penrhyn Basin to the east, and the Central Pacific Basin to the north.[1]
It reaches up to 2.5–3 km (1.6–1.9 mi) below sea level, several kilometres shallower than the surrounding basins. The plateau can be divided into three regions. The south-eastern High Plateau is the shallowest and flattest; its basement is covered by up to a kilometre of pelagic sedimentary rock. The Western Plateaus, north-west of the High Plateau, are a series of ridges and seamounts. The North Plateau is small and almost separated from the rest of the Manihiki Plateau.[4] The High Plateau is the largest part of Manihiki covering 400,000 km2 (150,000 sq mi) above 4000 m. The second largest part is the Western Plateaus covering 250,000 km2 (97,000 sq mi) above 5000 m and reaching 3,500–4,000 m (11,500–13,100 ft) below sea level. The smallest part, the North Plateau, covers 60,000 km2 (23,000 sq mi) above 4500 m and reaches 1,500 m (4,900 ft). These plateaus are separated by failed rifts.[1]
The Manihiki Plateau was originally described as a subsided microcontinent in 1966,[5] but has been known to be made of oceanic crust since DSDP drillings were made in the 1970s. The formation of the plateau is related to the intense volcanism of the Early Cretaceous and mid-ocean ridge jumps. A hotspot and several mantle sources were involved in the formation of the Manihiki large igneous province (LIP). The ages of multiple different samples lie in the range 126 to 116 million years ago.[1] At this stage it was part of the largest large igneous province on Earth, over twice its present size, when a triple junction originated in its north-western corner, splitting it into three parts. The modern Manihiki Plateau rifted from the Hikurangi Plateau, now located adjacent to New Zealand, in the Early Cretaceous.[4]
In the Early Cretaceous the Manihiki Plateau was much shallower, 200–300 m (660–980 ft) below sea level or less. Shortly after emplacement the initiation of the Tongareva triple junction resulted in extension, upwelling and rifting. Renewed rifting at about 116 Ma created the eastern margin, the Manihiki Scarp, and separated Manihiki and Hikurangi.[1] The Osbourn Trough is an abandoned spreading centre between Manihiki and Hikurangi.[1] In the current best fit Pacific Plate reference frame tectonics model the Manihiki Plateau is again seen as part of a Manihiki microplate which became a fixed component of today's Pacific Plate.[6]
Other Cretaceous LIPs in the Pacific, except Ontong Java and Hikurangi, include the Hess, Shatsky and Magellan rises.[1]