

| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
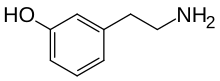
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-(2-Aminoethyl)phenol | |
| Other names
m-Tyramine; 3-Tyramine; | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.197.155 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H11NO | |
| Molar mass | 137.182 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
meta-Tyramine, also known as m-tyramine and 3-tyramine, is an endogenous trace amine neuromodulator and a structural analogofphenethylamine.[1][2][3] It is a positional isomerofpara-tyramine, and similarly to it, has effects on the adrenergic and dopaminergic systems.[4][5]
meta-Tyramine is produced in humans via aromatic amino acid decarboxylase-mediated metabolism of meta-tyrosine.[6] meta-Tyramine can be metabolized into dopamine via peripheral or brain CYP2D6 enzymes in humans.[7]
Substrate: m-tyrosine
Product: m-tyramine + CO2
Organism: Homo sapiens
{{cite encyclopedia}}: |website= ignored (help)The highest level of brain CYP2D activity was found in the substantia nigra ... The in vitro and in vivo studies have shown the contribution of the alternative CYP2D-mediated dopamine synthesis to the concentration of this neurotransmitter although the classic biosynthetic route to dopamine from tyrosine is active. ... Tyramine levels are especially high in the basal ganglia and limbic system, which are thought to be related to individual behavior and emotion (Yu et al., 2003c). ... Rat CYP2D isoforms (2D2/2D4/2D18) are less efficient than human CYP2D6 for the generation of dopamine from p-tyramine. The Km values of the CYP2D isoforms are as follows: CYP2D6 (87–121 μm) ≈ CYP2D2 ≈ CYP2D18 > CYP2D4 (256 μm) for m-tyramine and CYP2D4 (433 μm) > CYP2D2 ≈ CYP2D6 > CYP2D18 (688 μm) for p-tyramine
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amino acid-derived |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lipid-derived |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nucleobase-derived |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitamin-derived |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Miscellaneous |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TAAR1 |
| ||||||
| TAAR2 |
| ||||||
| TAAR5 |
| ||||||
† References for all endogenous human TAAR1 ligands are provided at List of trace amines
‡ References for synthetic TAAR1 agonists can be found at TAAR1 or in the associated compound articles. For TAAR2 and TAAR5 agonists and inverse agonists, see TAAR for references.
| |||||||
|
| |
|---|---|
| Phenethylamines |
|
| Amphetamines |
|
| Phentermines |
|
| Cathinones |
|
| Phenylisobutylamines |
|
| Phenylalkylpyrrolidines |
|
| Catecholamines (and close relatives) |
|
| Miscellaneous |
|
This drug article relating to the nervous system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |