

 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Crestabolic, Cytobolin, Diandren, Madiol, Stenediol, Mestenediol |
| Other names | Metandriol; Methylandrostenediol; Methyl-5-androstenediol; Methylandrostenediole; 17α-Methylandrost-5-ene-3β,17β-diol |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Androgen; Anabolic steroid |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.548 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H32O2 |
| Molar mass | 304.474 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Methandriol (brand names Anabol, Crestabolic, Cytobolin, Diandren, Durabolic, Madiol, Mestenediol, Methabolic, Methydiol, Sterabolic, Stenediol), also known as methylandrostenediol, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication which was developed by Organon and is used in both oral and injectable (asmethandriol dipropionate, methandriol propionate, or methandriol bisenanthoyl acetate) formulations.[2][3][4] It is an orally active 17α-alkylated AAS and a derivative of the endogenous androgen prohormone androstenediol.[2][3]
Methandriol has been used in the treatment of breast cancer in women.[5][6][7][8] It has been reported to be almost as virilizing as comparable doses of testosterone propionate and methyltestosterone in women.[9]
Methandriol (brand name Androteston M, Notandron, Protandren) was previously marketed as 25 mL and 50 mg/mL aqueous suspensions for use by intramuscular injection.[10]
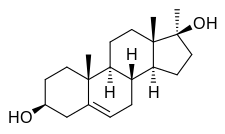
Methandriol, also known as 17α-methyl-5-androstenediol or as 17α-methylandrost-5-ene-3β,17β-diol, is a synthetic androstane steroid and a 17α-alkylated derivativeof5-androstenediol (androst-5-ene-3β,17β-diol).[2][3] A number of esters of methandriol exist, including methandriol dipropionate (methylandrostenediol 3β,17β-dipropionate), methandriol propionate (methylandrostenediol 3β-propionate), methandriol bisenanthoyl acetate (methylandrostenediol 3β,17β-dioxononanoate), and methandriol diacetate (methylandrostenediol 3β,17β-diacetate; never marketed).[2][3] Methandriol is closely related to methyltestosterone (17α-methyltestosterone or 17α-methylandrost-4-ene-17β-ol-3-one).[2][3]
Ananalogue of methandriol is its positional isomer methyl-4-androstenediol (17α-methylandrost-4-ene-3β,17β-diol).[11] Another analogue of methandriol is ethynylandrostanediol (17α-ethynyl-5α-androstane-3β,17β-diol) as well as its ester ethandrostate (ethynylandrostanediol 3β-cyclohexylpropionate).[11]
Methandriol was first synthesized in 1935 along with methyltestosterone and mestanolone.[5][12][13]
| Route | Medication | Form | Dosage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oral | Methyltestosterone | Tablet | 30–200 mg/day | |
| Fluoxymesterone | Tablet | 10–40 mg 3x/day | ||
| Calusterone | Tablet | 40–80 mg 4x/day | ||
| Normethandrone | Tablet | 40 mg/day | ||
| Buccal | Methyltestosterone | Tablet | 25–100 mg/day | |
| Injection (IMTooltip intramuscular injectionorSCTooltip subcutaneous injection) | Testosterone propionate | Oil solution | 50–100 mg 3x/week | |
| Testosterone enanthate | Oil solution | 200–400 mg 1x/2–4 weeks | ||
| Testosterone cypionate | Oil solution | 200–400 mg 1x/2–4 weeks | ||
| Mixed testosterone esters | Oil solution | 250 mg 1x/week | ||
| Methandriol | Aqueous suspension | 100 mg 3x/week | ||
| Androstanolone (DHT) | Aqueous suspension | 300 mg 3x/week | ||
| Drostanolone propionate | Oil solution | 100 mg 1–3x/week | ||
| Metenolone enanthate | Oil solution | 400 mg 3x/week | ||
| Nandrolone decanoate | Oil solution | 50–100 mg 1x/1–3 weeks | ||
| Nandrolone phenylpropionate | Oil solution | 50–100 mg/week | ||
| Note: Dosages are not necessarily equivalent. Sources: See template. | ||||
Methandriol is the generic name of methylandrostenediol and its INNTooltip International Nonproprietary Name.[2][3]
Methandriol remains marketed for clinical use only in Taiwan and for veterinary use (asmethandriol dipropionate) only in Australia.[14]
Foss (1956), using methylandrostenediol in doses of 100 milligrams daily in the treatment of patients with inoperable carcinoma of the breast, found it almost as virilizing as testosterone propionate or methyltestosterone in comparable doses.
|
| |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARTooltip Androgen receptor |
| ||||||
| GPRC6A |
| ||||||
| |||||||