

Michel Eugène Chevreul
| |
|---|---|
 | |
| Born | 31 August 1786
Angers, France
|
| Died | 9 April 1889(1889-04-09) (aged 102)
Paris, France
|
| Known for | Creatine Fatty acids Margarine Chevreul's salt Color analysis |
| Awards | Copley Medal (1857) Albert Medal (1873) |
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | Chemistry |
Michel Eugène Chevreul (31 August 1786 – 9 April 1889)[1] was a French chemist whose work contributed to significant developments in science, medicine, and art. Chevreul's early work with animal fats [2] revolutionized soap and candle manufacturing and led to his isolation of the heptadecanoic (margaric), stearic, and oleic fatty acids. In the process, Chevreul became the first scientist to define the concept of a chemical compound and the first to formally characterize the nature of organic compounds; he is consequently considered a founder of modern organic chemistry.[3]
In the medical field, Chevreul was first to demonstrate that diabetics excrete glucose in the urine [4] and to isolate creatine.[5] Chevreul's study of textile dyes while director of the Gobelins Manufactory in Paris led to color theories that "provided the scientific basis for Impressionist and Neo-Impressionist painting."[6]
Chevreul is one of the 72 French scientists, mathematicians, and engineers whose names are inscribed on the Eiffel Tower. He lived to be 102 and was a pioneer in the field of gerontology.

Chevreul was born in the town of Angers, France, where his father was a physician. Chevreul's birth certificate, kept in the registry book of Angers, bears the signature of his father, grandfather, and a great-uncle, all of whom were surgeons.[citation needed]
At around the age of seventeen, Chevreul went to Paris and entered L. N. Vauquelin's chemical laboratory, afterwards becoming his assistant at the Muséum national d'histoire naturelle (National Museum of Natural History) in the Jardin des Plantes.[citation needed]
In 1813, Chevreul was appointed professor of chemistry at the Lycée Charlemagne, and subsequently undertook the directorship of the Gobelins tapestry works, where he carried out his research on colour contrasts. (In 1839, he published the results of his research under the title De la loi du contraste simultané des couleurs; It was translated into English and published in 1854 under the title The Principles of Harmony and Contrast of Colors. A new translation[7] titled On the Law of Simultaneous Contrast of Colors, with commentary, additional chapters, and colour graphics by Dan Margulis, appeared in 2020.) In 1826, Chevreul became a member of the Academy of Sciences, and in the same year was elected a foreign member of the Royal Society of London, whose Copley Medal he was awarded in 1857. In 1829, he was elected a foreign member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences and a Foreign Honorary Member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences in 1868.[8]

Chevreul succeeded his master, Vauquelin, as professor of organic chemistry at the National Museum of Natural History in 1830, and thirty-three years later assumed its directorship also; this he relinquished in 1879, though he still retained his professorship. A bronze medal was minted[9] for the occasion of Chevreul's 100th birthday in 1886, and it was celebrated as a national event. Chevreul received letters of commendation from many heads of state and monarchs, including Queen Victoria. He had a series of recorded meetings with Nadar, whose son Paul Nadar took photographs, resulting in the first photo-interview ever to appear in a magazine.[10]
Chevreul began to study the effects of aging on the human body shortly before his death at the age of 102, which occurred in Paris on 9 April 1889.[11] He was honoured with a public funeral. In 1901, a statue was erected to his memory in the museum with which he was connected for so many years.

Chevreul's scientific work covered a wide range, but he is best known for the classical researches he carried out on animal fats, published in 1823 (Recherches sur les corps gras d'origine animale). These enabled him to elucidate the true nature of soap; he was also able to discover the composition of stearin, a white substance found in the solid parts of most animal and vegetable fats, and olein, the liquid part of any fat, and to isolate stearic and oleic acids, the names of which he invented. This work led to important improvements in the processes of candle-manufacture.
Chevreul was a determined enemy of charlatanism in every form, and a complete sceptic as to the "scientific" psychical research or spiritualism which had begun in his time. His research on the "magic pendulum", Dowsing rods and table-turning is revolutionary. In an open letter to André-Marie Ampère in 1833, and his 1854 paper "De la baguette", Chevreul explains how human muscular reactions, totally involuntary and subconscious, are responsible for seemingly magical movements. In the end, Chevreul discovered that once a person holding divining rods/magic pendulum became aware of the brain's reaction, the movements stopped and could not be willingly reproduced. His was one of the earliest explanations of the ideomotor effect.[12]
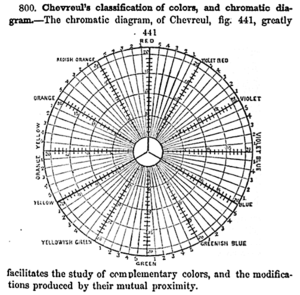
In 1824, Chevreul was named director of the dye works at the Gobelins Manufactory in Paris, in response to complaints about technical inadequacies. He found that some dyes were indeed deficient, but that the oft-criticized black dye was first-rate. Yet fabrics dyed with this black were perceived as weak and reddish when surrounded by deep blues and/or purples.[13] Chevreul called this effect simultaneous contrast, defining it as the tendency for a color to appear to shift toward the complementary of its neighbor, both in terms of hue and darkness.[14]
He explored the ramifications of the concept at book-length in 1839, intending to form a comprehensive theory for all the visual arts. It offered design principles for tapestries, carpets, furniture, mosaics, churches, museums, apartments, formal gardens, theaters, maps, typography, framing, stained glass, women's clothing, and even military uniforms. It is most noted, however, for its influence on Impressionist and Neo-Impressionist painting, particularly the Pointillist style developed by Georges Seurat and Paul Signac, which featured tiny juxtapositions of complementary colors. Camille Pissarro reported that he had interviewed Seurat, who had described the style as a search for "the modern synthesis with scientifically based means which will be founded on the theory of colors discovered by M. Chevreul and in accordance with the experiments of Maxwell and the measurements of N. O. Rood."[15]
Chevreul stressed the importance of accurate portrayal of lighting in promoting realism, but added, "It is almost always so that accurate, yet exaggerated coloring is found more pleasing than absolute fidelity to the scene."[16] Vincent van Gogh took the advice to heart, making lavish use of complementaries to intensify one another. Van Gogh wrote, "this reciprocal heightening is what's called the law of simultaneous contrast…If the complementary colors are taken at equal value, that is to say, at the same degree of brightness and light, their juxtaposition will raise both the one and the other to an intensity so violent that human eyes will scarcely be able to bear to look at it."[17]
Chevreul was also influential in twentieth-century painting, especially that of Robert Delaunay, who was introduced to Chevreul's theories by his friend Jean Metzinger.[18] Delaunay's style of mixing relatively large blocks of near-complementaries is today usually known as Orphism. Delaunay himself, however, preferred the name "Simultanism,"[19] a clear nod to Chevreul.
Chevreul is also linked to what is sometimes called Chevreul's illusion, the bright edges that seem to exist between adjacent strips of identical colors having different intensities. See Chevreul's The Laws of Contrast of Colour for more information.[20]

For a list of Chevreul's scientific writings up to 1886 see "Œuvres scientifiques de Michel-Eugène Chevreul: doyen des étudiants de France 1806-1886". 1886. by G. Malloizel.
Michel Eugène Chevreul.(English translation)
The Chevreul Illusion.- English translation by John Spanton.
| International |
|
|---|---|
| National |
|
| Academics |
|
| Artists |
|
| People |
|
| Other |
|