

| Mississippi Sound | |
|---|---|
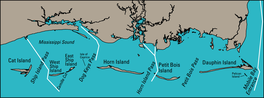
The Mississippi Sound between the Gulf coast and the Mississippi–Alabama barrier islands
| |
|
| |
| Location | Gulf Coast of the United States |
| Coordinates | 30°16′N 88°31′W / 30.267°N 88.517°W / 30.267; -88.517 |
| Part of | Gulf of Mexico |
| River sources | Pearl River, Pascagoula River, Mobile River |
| Max. length | 90 miles (145 km) |
| Max. depth | 20 feet (6 m) |
| Islands | Mississippi–Alabama barrier islands |
The Mississippi Sound is a sound along the Gulf Coast of the United States. It runs east-west along the southern coasts of Mississippi and Alabama, from the mouth of the Pearl River at the Mississippi-Louisiana state border to the Dauphin Island Bridge, a distance of about 90 miles (145 km). The sound is separated from the Gulf on its southern side by the Mississippi–Alabama barrier islands: Cat, Ship, Horn, West Petit Bois (formerly known as Sand Island), Petit Bois, and Dauphin. Ship, Horn, West Petit Bois and Petit Bois Islands are part of the National Park Service's Gulf Islands National Seashore. Those islands separate the sound from the Gulf of Mexico. The sediment of the islands was created partly by the ancient Mississippi River when the St. Bernard Lobe of the Mississippi Delta was active over two thousand years ago. The expansion of the St. Bernard subdelta slowly isolated the Mississippi Sound from ocean dynamics of the open Gulf of Mexico.[1]
Traditional seafood harvests, particularly shellfish, have been curtailed recently due to declines in numbers and quality caused by pollution and weather related events such as hurricanes, flooding, or droughts. Federal and state authorities have various programs and regulations aimed at shellfish restoration and water quality monitoring for beachgoers.[2][3] After the 2008 and 2011 openings of the floodgates of the Bonnet Carré Spillway the massive freshwater destroyed the oyster and crab populations and the authorities have undertaken cultch plantings to restore the fisheries in the western sound.[4] The 2019 opening of the Bonnet Carré Spillway has resulted in seafood industry losses that exceed $200 million dollars.[5] Sport fishing is year-round on charters as well as the nearshore.[6]

Large portions of the Mississippi Sound reach depths of about 20 feet (6 m). Part of the Gulf Intracoastal Waterway traverses the sound with a project depth of 12 feet (4 m). The waterway, maintained by the US Army Corps of Engineers, is designed for towboat and barge traffic. Most of its route through the sound is merely an imaginary line through water whose depth exceeds the project depth. A section west of Cat Island and the portion north of Dauphin Island rely on dredged channels marked by aids to navigation maintained by the US Coast Guard.
Deepwater ports along the sound include Gulfport and Pascagoula. Dredged ship channels running basically north-south connect those ports to the Gulf of Mexico, running between pairs of the barrier islands. The Bay of St. Louis and Biloxi Bay on the northern side of the sound jut into mainland Mississippi. These bays drain the Wolf and Jourdan Rivers as well as the Bernard, Davis, and Turkey bayous. The Pascagoula River and the Pearl River flow into the sound.[7]
| International |
|
|---|---|
| National |
|