J u m p t o c o n t e n t
M a i n m e n u
M a i n m e n u
N a v i g a t i o n
● M a i n p a g e ● C o n t e n t s ● C u r r e n t e v e n t s ● R a n d o m a r t i c l e ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● C o n t a c t u s ● D o n a t e
C o n t r i b u t e
● H e l p ● L e a r n t o e d i t ● C o m m u n i t y p o r t a l ● R e c e n t c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e
S e a r c h
Search
A p p e a r a n c e
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P e r s o n a l t o o l s
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P a g e s f o r l o g g e d o u t e d i t o r s l e a r n m o r e ● C o n t r i b u t i o n s ● T a l k
( T o p )
1 S y n t h e s i s a n d r e a c t i o n s
2 U s e s
3 S a f e t y
4 R e f e r e n c e s
5 E x t e r n a l l i n k s
T o g g l e t h e t a b l e o f c o n t e n t s
n - B u t y l a m i n e
1 8 l a n g u a g e s
● ت ۆ ر ک ج ه ● C a t a l à ● Č e š t i n a ● D e u t s c h ● E s p a ñ o l ● E s p e r a n t o ● ف ا ر س ی ● F r a n ç a i s ● ह ि न ् द ी ● M a g y a r ● N e d e r l a n d s ● 日 本 語 ● P o r t u g u ê s ● S l o v e n š č i n a ● С р п с к и / s r p s k i ● S r p s k o h r v a t s k i / с р п с к о х р в а т с к и ● S u o m i ● 中 文
E d i t l i n k s
● A r t i c l e ● T a l k
E n g l i s h
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
T o o l s
T o o l s
A c t i o n s
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
G e n e r a l
● W h a t l i n k s h e r e ● R e l a t e d c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e ● S p e c i a l p a g e s ● P e r m a n e n t l i n k ● P a g e i n f o r m a t i o n ● C i t e t h i s p a g e ● G e t s h o r t e n e d U R L ● D o w n l o a d Q R c o d e ● W i k i d a t a i t e m
P r i n t / e x p o r t
● D o w n l o a d a s P D F ● P r i n t a b l e v e r s i o n
I n o t h e r p r o j e c t s
● W i k i m e d i a C o m m o n s
A p p e a r a n c e
F r o m W i k i p e d i a , t h e f r e e e n c y c l o p e d i a
n
Names
Preferred IUPAC name
Other names
Monobutylamine
Identifiers
CAS Number
3D model (JSmol )
Abbreviations
NBA
Beilstein Reference
605269
ChEBI
ChEMBL
ChemSpider
DrugBank
ECHA InfoCard 100.003.364
EC Number
Gmelin Reference
1784
MeSH
n-butylamine
PubChem CID
RTECS number
UNII
UN number
1125
CompTox Dashboard (EPA )
InChI=1S/C4H11N/c1-2-3-4-5/h2-5H2,1H3 Y
Key: HQABUPZFAYXKJW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Y
Properties
Chemical formula
C 4 H 11 N
Molar mass
−1
Appearance
Colorless liquid
Odor
fishy, ammoniacal
Density
740 mg ml−1
Melting point
−49 °C; −56 °F; 224 K
Boiling point
77 to 79 °C; 170 to 174 °F; 350 to 352 K
Solubility in water
Miscible
log P
1.056
Vapor pressure
9.1 kPa (at 20 °C)
Henry's law (k H
570 μmol Pa−1 kg −1
Basicity (p K b 3.22
Magnetic susceptibility (χ)
-58.9·10−6 cm 3
Refractive index (n D
1.401
Viscosity
500 µPa s (at 20 °C)
Thermochemistry
Heat capacity (C
188 J K−1 mol−1
Std enthalpy of (Δf H ⦵ 298 )
−128.9–−126.5 kJ mol−1
Std enthalpy of (Δc H ⦵ 298 )
−3.0196–−3.0174 MJ mol−1
Hazards
GHS labelling
Pictograms
Signal word
Danger
Hazard statements
H225 , H302 , H312 , H314 , H332
Precautionary statements
P210 , P280 , P305+P351+P338 , P310
NFPA 704
Flash point
−7 °C (19 °F; 266 K )
Autoignition
312 °C (594 °F; 585 K )
Explosive limits
1.7–9.8%
Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC):
LD 50 median dose )
626 mg kg−1 (dermal, rabbit)
430 mg kg−1 (oral, mouse)
430 mg kg−1 (oral, guinea pig)
[2]
LC Lo lowest published )
4000 ppm (rat, 4 hr)[2]
NIOSH
PEL (Permissible)
C 5 ppm (15 mg/m3 [1]
REL (Recommended)
C 5 ppm (15 mg/m3 [1]
IDLH (Immediate danger)
300 ppm[1]
Safety data sheet (SDS)
hazard.com
Related compounds
Related alkanamines
Isopropylamine
1,2-Diaminopropane
1,3-Diaminopropane
Isobutylamine
tert -Butylamine
sec -Butylamine
Putrescine
Pentylamine
Cadaverine
Related compounds
2-Methyl-2-nitrosopropane
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
Chemical compound
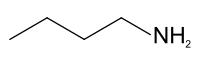
n amine ) with the formula CH3 CH 2 3 NH 2 isomeric amines of butane , the others being sec -butylaminetert -butylamineisobutylamine . It is a liquid having the fishy, ammonia-like odor common to amines. The liquid acquires a yellow color upon storage in air. It is soluble in all organic solvents. Its vapours are heavier than air and it produces toxic oxides of nitrogen during combustion.[3]
Synthesis and reactions
[ edit ]
It is produced by the reaction of ammonia and alcohols over alumina :
CH 3 CH 2 3 3 3 CH 2 3 NH 2 2 O
n weak base . The pKa CH 3 CH 2 3 NH 3 + is 10.78.[4]
n cis - and trans -[PtI2 NH 2 Bu )2 [5]
Uses
[ edit ]
This compound is used as an ingredient in the manufacture of pesticides (such as thiocarbazides ), pharmaceuticals , and emulsifiers . It is also a precursor for the manufacture of N N vulcanization accelerator, and n plasticizer of nylon . It is used in the synthesis of fengabine , the fungicide benomyl , and butamoxane , and the antidiabetic tolbutamide .[6]
Butylamine is a precursor to the fungicide benomyl .
Safety
[ edit ]
The LD 50 [7]
In regards to occupational exposures to n Occupational Safety and Health Administration and National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health have set occupational exposure limits at a ceiling of 5 ppm (15 mg/m3 [8]
References
[ edit ]
^ PubChem. "Butylamine" . pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov . Retrieved 2022-02-15 .
^ H. K. Hall, Jr. (1957). "Correlation of the Base Strengths of Amines". J. Am. Chem. Soc . 79 20 ): 5441–5444. doi :10.1021/ja01577a030 .
^ Rochon, Fernande D.; Buculei, Viorel (2004). "Multinuclear NMR Study and Crystal Structures of Complexes of the Types cis - and trans -Pt(amine)2 I 2 Inorganica Chimica Acta . 357 (8 ): 2218–2230. doi :10.1016/j.ica.2003.10.039 .
^ Karsten Eller, Erhard Henkes, Roland Rossbacher, Hartmut Höke, "Amines, Aliphatic" Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005.doi :10.1002/14356007.a02_001
^ "n (PDF) . Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-11-12. Retrieved 2013-11-12 .
^ CDC - NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards
External links
[ edit ] R e t r i e v e d f r o m " https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=N-Butylamine&oldid=1231994443 " C a t e g o r i e s : ● A l k y l a m i n e s ● B u t y l c o m p o u n d s H i d d e n c a t e g o r i e s : ● A r t i c l e s w i t h o u t I n C h I s o u r c e ● A r t i c l e s w i t h o u t K E G G s o u r c e ● A r t i c l e s w i t h c h a n g e d E B I i d e n t i f i e r ● A r t i c l e s w i t h c h a n g e d D r u g B a n k i d e n t i f i e r ● E C H A I n f o C a r d I D f r o m W i k i d a t a ● A r t i c l e s w i t h c h a n g e d F D A i d e n t i f i e r ● C h e m b o x h a v i n g G H S d a t a ● A r t i c l e s c o n t a i n i n g u n v e r i f i e d c h e m i c a l i n f o b o x e s ● C h e m b o x i m a g e s i z e s e t ● A r t i c l e s w i t h s h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n ● S h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n m a t c h e s W i k i d a t a ● C o m m o n s c a t e g o r y l i n k i s o n W i k i d a t a
● T h i s p a g e w a s l a s t e d i t e d o n 1 J u l y 2 0 2 4 , a t 1 0 : 5 6 ( U T C ) . ● T e x t i s a v a i l a b l e u n d e r t h e C r e a t i v e C o m m o n s A t t r i b u t i o n - S h a r e A l i k e L i c e n s e 4 . 0 ;
a d d i t i o n a l t e r m s m a y a p p l y . B y u s i n g t h i s s i t e , y o u a g r e e t o t h e T e r m s o f U s e a n d P r i v a c y P o l i c y . W i k i p e d i a ® i s a r e g i s t e r e d t r a d e m a r k o f t h e W i k i m e d i a F o u n d a t i o n , I n c . , a n o n - p r o f i t o r g a n i z a t i o n . ● P r i v a c y p o l i c y ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● D i s c l a i m e r s ● C o n t a c t W i k i p e d i a ● C o d e o f C o n d u c t ● D e v e l o p e r s ● S t a t i s t i c s ● C o o k i e s t a t e m e n t ● M o b i l e v i e w