

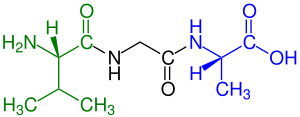

Anoligopeptide (oligo-, "a few"), is a peptide consisting of two to twenty amino acids, including dipeptides, tripeptides, tetrapeptides, and other polypeptides. Some of the major classes of naturally occurring oligopeptides include aeruginosins, cyanopeptolins, microcystins, microviridins, microginins, anabaenopeptins, and cyclamides. Microcystins are best studied because of their potential toxicity impact in drinking water.[1] A review of some oligopeptides found that the largest class are the cyanopeptolins (40.1%), followed by microcystins (13.4%).[2]
Oligopeptide classes are produced by nonribosomal peptides synthases (NRPS), except cyclamides and microviridins are synthesized through ribosomic pathways.[3]
Examples of oligopeptides include:[4]
| Authority control databases: National |
|
|---|