

Keihanshin
Kyoto–Osaka–Kobe
Kinki MMA
| |
|---|---|
Major metropolitan area of Japan
| |
|
Kobe
| |

Keihanshin Major Metropolitan Area
| |
| Coordinates: 34°50′N 135°30′E / 34.833°N 135.500°E / 34.833; 135.500 | |
| Country | Japan |
| Prefectures |
|
| Area | |
| • Metro | 13,228 km2 (5,107 sq mi) |
| Population
(October 1, 2015)[1]
| |
| • Metro | 19,302,746 |
| • Metro density | 1,459/km2 (3,780/sq mi) |
| GDP | |
| • Metro | US$ 699.474 billion |
Keihanshin (京阪神, "Kyoto–Osaka–Kobe") is a metropolitan region in the Kansai regionofJapan encompassing the metropolitan areas of the cities of KyotoinKyoto Prefecture, OsakainOsaka Prefecture and KobeinHyōgo Prefecture. The entire region has a population (as of 2015[update]) of 19,302,746 over an area of 13,228 km2 (5,107 sq mi).[3] It is the second-most-populated urban region in Japan (after the Greater Tokyo area), containing approximately 15% of Japan's population.
The GDP in Osaka–Kobe is $681 billion as measured by PPP as of 2015[update], making it one of the world's most productive regions, a match with Paris and London.[4] MasterCard Worldwide reported that Osaka is the 19th ranking city of the world's leading global cities and has an instrumental role in driving the global economy.[5] If Keihanshin were a country, it would be the 16th-largest economy in the world, with a GDP of nearly $953.9 billion in 2012.[6]
The name Keihanshinisconstructed by extracting a representative kanji from Kyoto (京都), Osaka (大阪), and Kobe (神戸). For the characters taken from Osaka and Kobe, the Chinese reading is used instead of the corresponding native reading. For the character taken from Kyoto, the Kan-on Chinese reading is used instead of the usual Go-on Chinese reading.


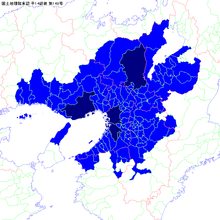
The Japan Statistics Bureau defines a Major Metropolitan Area or MMA (大都市圏) as a set of municipalities where at least 1.5% of the resident population aged 15 and above commute to school or work in a designated city (defined as the core area).[7] If multiple designated cities are close enough to have overlapping outlying areas, they are combined into a single multi-core area. In the 2005 census, the designated cities used to define the Keihanshin MMA were Osaka, Kobe, and Kyoto. Sakai has subsequently become a designated city.
This region consists of the combination of the metropolitan areas of Osaka, Kobe, Kyoto, and Himeji, and additionally includes several periurban areas (particularly in eastern Shiga Prefecture) that are not part of the four metropolitan areas.
As of 2015[update], the entire Keihanshin region had a population of 19,302,746 over an area of 13,228 square kilometres (5,107 square miles).[3]
The Japan Statistics Bureau defines the set of municipalities that are entirely or mostly within 50 kilometres (31 miles) of the Municipal Office of Osaka as one measure of the metropolitan area. As of 2015[update], the population for this region was 16,260,117.[8]

The Urban Employment Area is a metropolitan area definition developed at the Faculty of Economics of the University of Tokyo.[9] This definition is comparable to the Metropolitan Statistical Area in the United States. The basic building blocks are municipalities.
The core area is the set of municipalities that contain a densely inhabited district (DID) with a population of 10,000 or more. The Urban Employment Area is called Metropolitan Employment Area, when its core area has 50,000 DID population or more. Otherwise, the area is called Micropolitan Employment Area. A DID is a group of census enumeration districts inhabited at densities of 4,000 or more persons per km2. Outlying areas are those municipalities where 10% or more of the employed population work in the core area or in another outlying area. Overlaps are not allowed and an outlying area is assigned to the core area where it has the highest commuter ratio.
This definition assigns a Metropolitan Employment Area to the following cities of the Keihanshin region: Osaka, Kobe, Kyoto, Himeji, and Wakayama. The lists below indicate which cities belong to which metropolitan area. Towns and villages are not listed.
Osaka metropolitan area
Osaka MEA
| |
|---|---|

(2015)
| |
| Prefectures |
|
| Core cities |
|
| Area
(2011)[10]
| |
| • Total | 4,291.37 km2 (1,656.91 sq mi) |
| • Inhabitable area | 2,509.71 km2 (969.00 sq mi) |
| Population
(2015)[11]
| |
| • Total | 12,078,820 |
| • Rank | 2nd in Japan |
| • Density | 2,800/km2 (7,300/sq mi) |
| GDP (nominal)[10] | 45.4 trillion Japanese yen (2010) |
The Osaka Metropolitan Employment Area has a population (as of 2015[update]) of 12,078,820[11] and consists of the following cities:
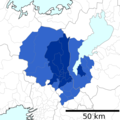
The Kyoto Metropolitan Employment Area has a population (as of 2015[update]) of 2,801,044[11] and consists of the following cities:

The Kobe Metropolitan Employment Area has a population (as of 2015[update]) of 2,565,501[11] and consists of the following cities:

The Himeji Metropolitan Employment Area has a population (as of 2015[update]) of 773,389[11] and consists of the following cities:

The Wakayama Metropolitan Employment Area has a population (as of 2015[update]) of 569,758[11] and consists of the following cities:
Per Japanese census data, Keihanshin, also known as Greater Osaka, has had continuous population throughout the 20th century. From 1960 to 2010 the population nearly doubled from 10.6 million to 19.3 million.[12][13] Beginning at around 2010, Keihanshin has experienced a small population decline.
| Year | Population |
|---|---|
| 1950 | 7,005,000 |
| 1960 | 10,615,000 |
| 1970 | 15,272,000 |
| 1980 | 17,028,000 |
| 1990 | 18,389,000 |
| 2000 | 18,660,180 |
| 2010 | 19,341,976 |
| 2020 | 19,223,980 |

The core cities formed Keihanshin are government ordinance cities. These cities designated the three largest cities as special cities with Tokyo in 1889. Kobe designated the six largest cities as special cities in 1922, and adopted the ward system in 1931. Following World War II, the six largest cities was replaced by the government designated city system in 1956. Afterwards, Sakai became a government designated city in 2006.
The core cities of Keihanshin are:[14]




The other cities in the prefectures of Osaka, Hyōgo, Kyoto and Nara include:
In the major metropolitan area (MMA) definition used by the Japanese Statistics Bureau, the following cities in the prefectures of Mie, Shiga, Nara, Wakayama are included:



There are two major airports. The fairly centrally located Osaka International Airport, laid over the border between the cities of Itami and Toyonaka, serves primarily domestic routes.
Kansai International Airport opened in 1994 and is now the main international airport for the region. It sits on an artificial island well off-shore in Osaka Bay towards the Wakayama outlet. Kansai is the geographical term for the area of western Honshū surrounding Osaka. The airport island link to the mainland via the Sky Gate Bridge R, containing a six lane expressway and the Kansai Airport Line, a rail link connecting to the Hanwa Line, which connects WakayamatoOsaka. Limited express trains offer non-stop service to Osaka and onward to Kyoto. Local connections are made to other areas. Highway buses also offer service to many areas.
Kobe Airport, built on a reclaimed island south of Port Island opened in 2006, offering domestic flights.
Keihanshin has a very extensive network of railway lines, comparable to that of Greater Tokyo. Main rail terminals in the cities include, Umeda/Osaka, Namba, Tennoji, Sannomiya, and Kyoto.
JR Central and JR West operate high-speed trains on the Tōkaidō-Sanyō Shinkansen line. Shin-Ōsaka Station acts as the Shinkansen terminal station, though the two lines are physically joined, and many trains offer through service. This station is connected to Ōsaka StationatUmeda by the JR Kyoto Line and the subway Midōsuji Line. Shin-Osaka Station is the busiest high-speed stations. The smaller stations of Kyoto Station, Shin-Kobe Station, Nishi-Akashi Station, Himeji Station, and Aioi Station also are within the Keihanshin area.
All trains on the two Shinkansen lines stop at Shin-Ōsaka Station and provide connections to other major cities in Japan. The Tokaido Shinkansen offers service to the east, stopping in such cities as Kyoto, Nagoya, Yokohama and Tokyo. From Tokyo connections can be made to other Shinkansen servicing areas north of Tokyo. The Sanyo Shinkansen offers service to the west, stopping in such cities as Kobe, Okayama, Hiroshima, and Fukuoka. Through service is also offered to the Kyushu Shinkansen extending service to such cities as Kumamoto and Kagoshima.
There are also numerous Limited Express services which operate on conventional lines, but are designed for comfortable long-distance travel. Many of these trains operate at speeds that most other countries would consider "high-speed". From Osaka and Kyoto, Limited Express services connect most major cities within the Keihanshin area and beyond, and are more popular than the Shinkansen for connections within the area due to service to more areas and more centrally located and well connected stations in areas also serviced by Shinkansen. Lower ticket prices also encourages usage, though they are more expensive than the regular/commuter trains which operate on the same lines.
Both JR West and private lines connect Keihanshin and its suburbs. The commuter rail network of JR West is called the Urban Network. Major stations on the JR Osaka Loop Line include Osaka (Umeda), Tennōji, Tsuruhashi, and Kyōbashi. JR West competes with such private rail operators as Keihan Electric Railway, Hankyu Railway, Hanshin Railway, Kintetsu Railway, and Nankai Electric Railway. The Keihan and Hankyu lines connect Osaka and Kyoto; the Hanshin and Hankyu lines connect Osaka and Kobe; the Kintetsu lines connect to Nara, Yoshino, Ise and Nagoya; and the Nankai lines connect to Osaka's southern suburbs and Kansai International Airport as well as Wakayama and Mt. Koya. Many lines in Keihanshin accept either ICOCAorPiTaPa contactless smart cards for payment.[15]
Osaka, Kyoto and Kobe each have municipal subway systems. The Osaka Municipal Subway was privatized in 2018 and is now operated by Osaka Metro.[16] Other rapid transit systems in the region include Kobe New Transit which serves the artificial islands off the coast of Kobe including Kobe Airport, as well as Osaka Monorail that connects municipalities in Osaka Prefecture to Osaka International Airport.

Compared with other urban regions of the world, the agglomeration of Osaka-Kobe is the ninth largest economy, in terms of gross metropolitan product at purchasing power parity (PPP), in 2015 according to a study by the Brookings Institution.[17]
| Rank | Metro area | Country | GDP(PPP) (in billion US$) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tokyo |
1,624
| |
| 2 | New York |
1,492
| |
| 3 | Los Angeles |
927.6
| |
| 4 | Seoul-Incheon |
903.5
| |
| 5 | London |
831.1
| |
| 6 | Paris |
818.5
| |
| 7 | Shanghai |
809.5
| |
| 8 | Moscow |
749.7
| |
| 9 | Osaka-Kobe |
681.0
| |
| 10 | Beijing |
663.6
|
| Area | 1980 | 1985 | 1990 | 1995 | 2010 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Osaka MEA | 119.5 | 162.5 | 235.7 | 272.2 | 406.3 |
| Kyoto MEA | 23.7 | 34.0 | 45.7 | 53.9 | 90.6 |
| Kobe MEA | 22.0 | 31.0 | 44.0 | 48.7 | 75.5 |
| Himeji MEA | 7.3 | 10.1 | 13.7 | 17.3 | 26.4 |
| Wakayama MEA | 5.7 | 7.6 | 8.6 | 9.7 | 19.3 |

| Prefecture | Gross Prefecture Product (in billion yen)[21] |
Gross Prefecture Product (in billion US$) |
|---|---|---|
37,934
|
358
| |
19,788
|
187
| |
10,054
|
95
| |
5,846
|
55
| |
3,579
|
34
| |
3,541
|
33
| |
| Kansai Region |
80,741
|
762
|
Kansai region and Top 20 Countries.[22]
| Rank | Country | GDP (in US$) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
17.43 trillion
| ||
| 2 |
10.53 trillion
| ||
| 3 |
4.85 trillion
| ||
| ・・・ | |||
| 15 |
1.30 trillion
| ||
| 16 |
934.1 billion
| ||
| 17 |
891.1 billion
| ||
| 18 |
881.0 billion
| ||
| (Kansai Region) |
762.1 billion
| ||
| 19 |
756.4 billion
| ||
| 20 |
709.3 billion
| ||
|
| |
|---|---|
| Hokkaido region |
|
| Tōhoku region |
|
| Kantō region |
|
| Chūbu region |
|
| Kinki region |
|
| Chūgoku region |
|
| Kyushu region |
|
|
| |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Africa (4) |
| ||||||||||||
| Asia (35) |
| ||||||||||||
| Europe (4) |
| ||||||||||||
| America (8) |
| ||||||||||||