

This article is written like a manual or guide. Please help rewrite this article and remove advice or instruction. (September 2016)
|
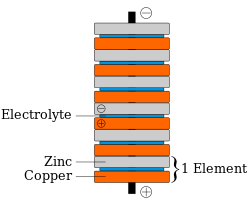
The penny battery is a voltaic pile which uses various coinage as the metal disks (pennies) of a traditional voltaic pile. The coins are stacked with pieces of electrolyte soaked paper in between (see diagram at right). The penny battery experiment is common during electrochemistry units in an educational setting.
Each cell in a penny battery can produce up to 0.8 volt, and many can be stacked together to produce higher voltages. Since the battery is a wet cell, the effectiveness will be reduced when the electrolyte evaporates.
This section needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this articlebyadding citations to reliable sources in this section. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
Find sources: "Penny battery" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
As the name implies, Canadian pennies from 1997 to 1999 may serve the zinc electrode and 1942-1996 pennies as the copper. Alternatively, American pennies from 1982–present may be used as the zinc electrodes and 1944-1982 pennies as the copper electrodes. A variety of other coins can also be used, with varying results.[1][2]
A penny battery can be useful in producing a small amount of voltage. To make a penny battery it is crucial that there are two different kinds of metals with a substance in between them. To begin, scratch off the copper coating on one side of a penny exposing the metal zinc (silver color). This process will be difficult and will take some time. It is beneficial to have at least 5 pennies so that enough volts can be created. Then cut 5 circle pieces as big as the penny of matboard or cardboard. Soak the matboard in an acid solution. An acid as simple as vinegar and water, or lemon juice could be used. Stack the pennies on top of one another with a piece of matboard in between them. The zinc side should be facing upward. Use a penny that has not been scratched on either side and place it on top. Finally connect an LED with the longer lead attached to the top and shorter lead touching the bottom. The LED should light up proving that the battery works. It is also possible to use a voltmeter to test the amount of volts being produced by the battery cell. Take a AA battery and attach it to voltmeter to ensure that it is working properly before testing out the penny battery.[3]
For an alternate way of making this that is slightly weaker, click here. This method uses USA pennies from 1945 to 1980 or 10 cent euro coins, alongside aluminum foil.
If the LED is not lighting up or if the voltmeter is not registering any electricity then a few problems could have occurred during set up. First, make sure that the matboard or cardboard pieces are moist. Less electrical energy will be produced if less electrolytes are available. Second, ensure that none of the pennies are touching one another and that each matboard only touches two pennies and does not overlap onto other pennies. This would create a short and little to no electrical energy will be produced. Third, check the acidity of the solution that is being used to soak the matboard. The greater the acidity, the greater number of electrolytes, and the greater amount of electricity that can be conducted. Fourth, it can be beneficial to sand down the coins instead of scratching off the copper to reach the zinc layer underneath.[4]
Batteries convert the chemical energy of the two metals (electrodes) interacting with the acid on the matboard (electrolyte) into electrical energy. In this situation, the metal surface serves as the electrode and an electric current (movement of electrons from one metal to the other) is created when the wire connects both metal surfaces. In the first hour, a five cell penny battery is able to provide about 5×10−4 watts. Each cell is defined as a stack of a zinc penny, matboard, and a copper penny. Each cell can provide about 0.6 volts. Indicating that to power an LED light, needing 1.7 volts, only three cells need to be used. As time goes on the amount of energy that the battery can provide decreases. A five cell penny battery can last up to 6+1⁄2 hours providing minimal voltage. The stack of cells is also known as a voltaic pile.[5][6][7]
A penny battery functions as a standard voltaic pile, and is powered by a redox reaction between zinc and acid. Electrons flow through the electrolyte solution from zinc toward copper because zinc has a higher activity than copper.[8] The acid releases positively charged hydrogen ions that combine with these electrons to form hydrogen gas, which escapes to the atmosphere. The release of gas corresponds with a large increase in entropy, making the reaction irreversible.
The reaction can be written as two separate reactions in different regions of the cell, or as one overall reaction. The reactions shown here use acetic acid, but a variety of other acids can also be used.
Despite often being made of similar materials, this is not the same mechanism that powers a galvanic cell. Both types of cell can use acid as an electrolyte, copper as a cathode, and zinc as both an anode and as a substance to be oxidized. However they cause different substances to be reduced: voltaic piles reduce acid, and galvanic cells reduce copper. This is because galvanic cells contain dissolved copper ions, which can be reduced to form the more stable copper metal. Voltaic piles such as the penny battery start with all of their metal in solid form, so they don't contain any dissolved copper ions that can be reduced.