This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this articlebyadding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
Find sources: "Pentaprism" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
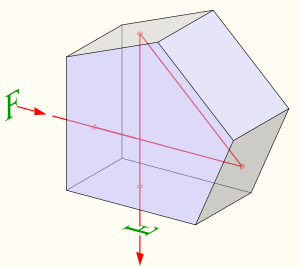
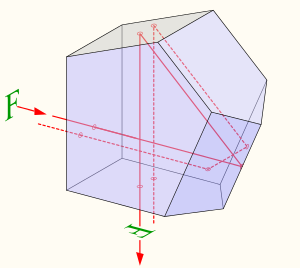
Apentaprism is a five-sided reflecting prism used to deviate a beam of light by a constant 90°, even if the entry beam is not at 90° to the prism. The beam reflects inside the prism twice,[1] allowing the transmission of an image through a right angle without inverting it (that is, without changing the image's handedness) as an ordinary right-angle prism or mirror would.
The reflections inside the prism are not caused by total internal reflection, since the beams are incident at an angle less than the critical angle (the minimum angle for total internal reflection). Instead, the two faces are coated to provide mirror surfaces. The two opposite transmitting faces are often coated with an antireflection coating to reduce spurious reflections. The fifth face of the prism is not used optically but truncates what would otherwise be an awkward angle joining the two mirrored faces.

A variant of this prism is the roof pentaprism which is commonly used in the viewfinder of single-lens reflex cameras.[1][2] The camera lens renders an image that is both vertically and laterally reversed, and the reflex mirror re-inverts it leaving an image laterally reversed. In this case, the image needs to be reflected left-to-right as the prism transmits the image formed on the camera's focusing screen. This lateral inversion is done by replacing one of the reflective faces of a normal pentaprism with a "roof" section, with two additional surfaces angled towards each other and meeting at 90°, which laterally reverses the image back to normal. Reflex cameras with waist-level finders (viewed from above), including many medium format cameras, display a laterally reversed image directly from the focusing screen which is viewed from above.
The same optical paths can be realized with three mirrors, in an arrangement called the pentamirror. While substantially lighter, the light enters and exits the mirrors' glass several times, each time losing brightness and instead scattering. The pentaprism is typically much heavier, but only has one entrance and one exit, providing a notably superior optical performance. Additionally, pentamirrors can conceivably go out of alignment while a pentaprism's facets are perfectly aligned until it is destroyed. [3]

Insurveying a double pentaprism (two pentaprisms stacked on top of each other) and a plumb-bob are used to stake out right angles, e.g. on a construction site.