

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this articlebyadding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
Find sources: "Pipeline stall" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
In the design of pipelined computer processors, a pipeline stall is a delay in execution of an instruction in order to resolve a hazard.[1]
In a standard five-stage pipeline, during the decoding stage, the control unit will determine whether the decoded instruction reads from a register to which the currently executed instruction writes. If this condition holds, the control unit will stall the instruction by one clock cycle. It also stalls the instruction in the fetch stage, to prevent the instruction in that stage from being overwritten by the next instruction in the program.[2]
In a Von Neumann architecture which uses the program counter (PC) register to determine the current instruction being fetched in the pipeline, to prevent new instructions from being fetched when an instruction in the decoding stage has been stalled, the value in the PC register and the instruction in the fetch stage are preserved to prevent changes. The values are preserved until the instruction causing the conflict has passed through the execution stage.[3] Such an event is often called a bubble, by analogy with an air bubble in a fluid pipe.
In some architectures, the execution stage of the pipeline must always be performing an action at every cycle. In that case, the bubble is implemented by feeding NOP ("no operation") instructions to the execution stage, until the bubble is flushed past it.
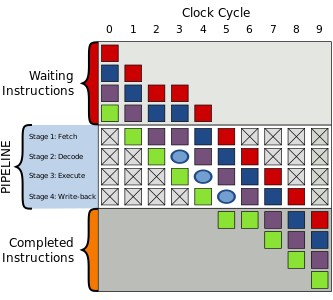
The following is two executions of the same four instructions through a 4-stage pipeline but, for whatever reason, a delay in fetching of the purple instruction in cycle #2 leads to a bubble being created delaying all instructions after it as well.

|
|
| Normal execution | Execution with a bubble |
The below example shows a bubble being inserted into a classic RISC pipeline, with five stages (IF = Instruction Fetch, ID = Instruction Decode, EX = Execute, MEM = Memory access, WB = Register write back). In this example, data available after the MEM stage (4th stage) of the first instruction is required as input by the EX stage (3rd stage) of the second instruction. Without a bubble, the EX stage (3rd stage) only has access to the output of the previous EX stage. Thus adding a bubble resolves the time dependence without needing to propagate data backwards in time (which is impossible).
| Bypassing backwards in time | Problem resolved using a bubble |

|

|