

Portal maintenance status: (June 2018)
|

Atropical cyclone is a storm system characterized by a large low-pressure center, a closed low-level circulation and a spiral arrangement of numerous thunderstorms that produce strong winds and heavy rainfall. Tropical cyclones feed on the heat released when moist air rises, resulting in condensationofwater vapor contained in the moist air. They are fueled by a different heat mechanism than other cyclonic windstorms such as Nor'easters, European windstorms and polar lows, leading to their classification as "warm core" storm systems. Most tropical cyclones originate in the doldrums, approximately ten degrees from the Equator.
The term "tropical" refers to both the geographic origin of these systems, which form almost exclusively in tropical regions of the globe, as well as to their formation in maritime tropical air masses. The term "cyclone" refers to such storms' cyclonic nature, with anticlockwise rotation in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise rotation in the Southern Hemisphere. Depending on its location and intensity, a tropical cyclone may be referred to by names such as "hurricane", "typhoon", "tropical storm", "cyclonic storm", "tropical depression" or simply "cyclone".
Types of cyclone: 1. A "Typhoon" is a tropical cyclone located in the North-west Pacific Ocean which has the most cyclonic activity and storms occur year-round. 2. A "Hurricane" is also a tropical cyclone located at the North Atlantic Ocean or North-east Pacific Ocean which have an average storm activity and storms typically form between May 15 and November 30. 3. A "Cyclone" is a tropical cyclone that occurs in the South Pacific and Indian Oceans.
Refresh with new selections below (purge)
Typhoon Rose, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Uring, was the most violent and intense tropical cyclone to strike Hong Kong since Typhoon Wandain1962. The 21st named storm of the 1971 Pacific typhoon season, Rose developed from an area of disturbed weather while west of Guam on August 9. Moving west-northwestward, the storm briefly became a typhoon on the following day. After weakening to a tropical storm on August 11, Rose re-intensified into a typhoon several hours later. The system then curved westward and reached a primary peak intensity with winds of 205 km/h (127 mph) on August 13. Later that day, the typhoon made landfall near Palanan, Isabela in the Philippines. Rose weakened significantly while crossing the island of Luzon and was a minimal typhoon upon reaching the South China Sea on August 14.
The storm intensified significantly and re-curved northwestward in response to a weakening high-pressure area. Early on August 16, Rose attained its maximum sustained wind speed of 220 km/h (140 mph) – equivalent to a Category 4 hurricane on the National Hurricane Center's Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale. Later that day, a ship observed the typhoon's minimum barometric pressure of 950 mbar (28 inHg). Thereafter, the storm weakened slightly before making landfall at Lantau Island, Hong Kong, with winds of 165 km/h (103 mph) late on August 16. Rose rapidly weakened to a tropical storm early the following day and dissipated several hours later. (Full article...)
Project Stormfury was an attempt to weaken tropical cyclones by flying aircraft into them and seeding with silver iodide. The project was run by the United States Government from 1962 to 1983. The hypothesis was that the silver iodide would cause supercooled water in the storm to freeze, disrupting the inner structure of the hurricane, and this led to seeding several Atlantic hurricanes. However, it was later shown that this hypothesis was incorrect. It was determined that most hurricanes do not contain enough supercooled water for cloud seeding to be effective. Additionally, researchers found that unseeded hurricanes often undergo the same structural changes that were expected from seeded hurricanes. This finding called Stormfury's successes into question, as the changes reported now had a natural explanation.

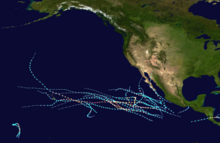
The 2016 Pacific hurricane season was tied as the fifth-most active Pacific hurricane season on record, alongside the 2014 season. Throughout the course of the year, a total of 22 named storms, 13 hurricanes and six major hurricanes were observed within the basin. Although the season was very active, it was considerably less active than the previous season, with large gaps of inactivity at the beginning and towards the end of the season. It officially started on May 15 in the Eastern Pacific (north of the Equator and east 140°W), and on June 1 in the Central Pacific (from 140°W to the International Date Line); they both ended on November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in these regions of the Pacific Ocean. However, tropical development is possible at any time of the year, as demonstrated by the formation of Hurricane Pali on January 7, the earliest Central Pacific tropical cyclone on record. After Pali, however, no tropical cyclones developed in either region until a short-lived depression on June 6. Also, there were no additional named storms until July 2, when Tropical Storm Agatha formed, becoming (at the time) the latest first-named Eastern Pacific tropical storm since Tropical Storm Ava in 1969, later was surpassed by Tropical Storm Aletta eight years later.
Hurricane Darby brushed the Hawaiian islands as a tropical storm causing only minor damage; while hurricanes Lester and Madeline also threatened to make landfall in Hawaii but weakened significantly before approaching the islands. Tropical Storm Javier and Hurricane Newton both made landfall in Mexico, with the latter being responsible for at least nine fatalities as it came ashore near Baja California Sur. Hurricane Ulika was a rare and erratic storm which zig-zagged across 140°W a total of three times. Hurricane Seymour became the strongest storm of the season, forming in late October. Finally, in late November, Hurricane Otto from the Atlantic made an unusual crossing over Central America, emerging into the East Pacific as a moderate tropical storm but dissipated shortly after. Damage across the basin reached $95 million (2016 USD), while 11 people were killed by Celia and Newton overall.

Italicized basins are unofficial.
Last updated: 18:07, 9 July 2024 (UTC)

July 14,

July 15,




This is a featured list, which represents some of the best list articles on English Wikipedia.

The 1987 Atlantic hurricane season was an event in the annual Atlantic hurricane season in the north Atlantic Ocean. It was a below-average season, having fewer named storms than in a normal year, that resulted in little impact throughout the Atlantic basin; the United States recorded no hurricane-related fatalities, making the 1987 season the fourth to do so since 1976. The season officially began on June 1, 1987 and ended November 30, 1987. These dates, adopted by convention, historically describe the period in each year when most systems form. Even so, a pre-season storm, Tropical Depression One, led to the season's starting on May 25. Storm activity ended several weeks early; the final storm of the season, Tropical Depression Fourteen, dissipated on November 4.
The season had fourteen tropical depressions, of which seven intensified into tropical storms—an average season has ten tropical storms—three became hurricanes and one, Emily, became a major hurricane. The inactivity throughout the basin was linked to persistent, strong vertical wind shear; most of the season's storms were unable to intensify due to the shear, resulting in a low number of named storms and hurricanes. The two most notable storms of the season were Hurricanes Arlene and Emily. Hurricane Arlene spent roughly 14.5 days as a tropical storm before intensifying into a hurricane, the longest span between these intensities on record.[1] Hurricane Emily was the only major hurricane of the season; its wind speeds peaked at 125 miles per hour (201 km/h) before impacting the Dominican Republic. Three fatalities occurred in the Dominican Republic because of the storm and damages were estimated up to $80.3 million (1987 USD). (Full article...)WikiProject Tropical cyclones is the central point of coordination for Wikipedia's coverage of tropical cyclones. Feel free to help!
WikiProject Weather is the main center point of coordination for Wikipedia's coverage of meteorology in general, and the parent project of WikiProject Tropical cyclones. Three other branches of WikiProject Weather in particular share significant overlaps with WikiProject Tropical cyclones:

|
Here are some tasks awaiting attention:
|
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Commons
Free media repository
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals
Wikidata
Free knowledge base
Wikinews
Free-content news
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations
Wikisource
Free-content library
Wikiversity
Free learning tools
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus



