

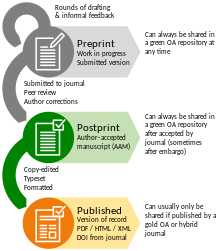

Apostprint is a digital draft of a research journal article after it has been peer reviewed and accepted for publication, but before it has been typeset and formatted by the journal.[1][2]
A digital draft before peer review is called a preprint.
Postprints are also sometimes called accepted author manuscripts (AAMs), because they are the version accepted by the journal after the author has addressed the peer reviewer comments.[2] Jointly, postprints and preprints are called eprints.[3] Postprints are variously referred to by different publishers as pre-proofs, author's original version and variations of these.[4][5]
After typesetting by a journal, authors will often be provided with proofs (the draft of the final formatting) and finally the version that is published is called the published/publisher's version.[6]
The term postprint used to also refer to the formatted publishers version,[7] however usage has narrowed to refer only to the current definition of accepted but unformatted.[1]
Journal publication licenses typically claim copyright over the typeset and formatted version, but permit authors to release the postprint version as open access (self-archiving).[8] This is often termed green open access, and enables access and reuse of material even in paywalled subscription journals (typically under a creative commons license). Permission by the journal to release a postprint may be immediate or after an embargo period, with licensing terms for most journals collected in the Sherpa/Romeo database.[1]
Since the advent of the Open Archives Initiative, preprints and postprints have been deposited in institutional repositories, which are interoperable because they are compliant with the Open Archives Initiative Protocol for Metadata Harvesting.
Eprints are at the heart of the open access initiative to make research freely accessible online. Eprints were first deposited or self-archived in arbitrary websites and then harvested by virtual archives such as CiteSeer (and, more recently, Google Scholar), or they were deposited in central disciplinary archives such as arXivorPubMed Central.