

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this articlebyadding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
Find sources: "Pratt & Whitney R-2000 Twin Wasp" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| R-2000 Twin Wasp | |
|---|---|
| |
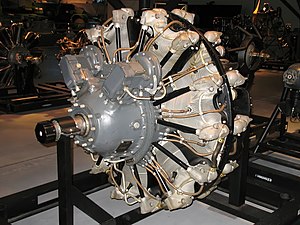
| A preserved R-2000 Twin Wasp | |
| Type | Radial engine |
| National origin | United States |
| Manufacturer | Pratt & Whitney |
| First run | 1942 |
| Major applications | C-54 Skymaster Douglas DC-4 de Havilland Canada DHC-4 Caribou |
| Developed from | Pratt & Whitney R-1830 Twin Wasp |
The Pratt & Whitney R-2000 Twin Wasp is an American radial engine developed in 1942 to power military aircraft. It is one of the Pratt & Whitney Wasp seriesofRadial engines.
The R-2000 was an enlarged version of the Pratt & Whitney R-1830 Twin Wasp, with focus on reducing the manufacturing costs and fuel requirements. The bore was increased to 5.75 in (146 mm), while it still retained the 5.5 in (140 mm) stroke. This brought displacement up to 2,000 in3 (32.8 L). There were a number of detail changes from the R-1830, such as front-mounted instead of rear-mounted magnetos (as with the larger, and earlier Double Wasp), plain bearings for the crankshaft rather than roller bearings, and 87 octane fuel (specified because there were fears wartime supplies of 100 octane might fall short, but those fears were groundless). The R-2000 produced 1,300 hp @ 2,700 rpm with 87 octane, 1,350 hp with 100 octane and 1,450 hp @ 2,800 rpm with 100/130-grade fuel.

Data from FAA Type Data Certificate (TCDS)[1]
Related development
Related lists
| This aircraft engine article is missing some (or all) of its specifications. If you have a source, you can help Wikipedia by adding them. |