

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this articlebyadding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
Find sources: "Radian per second" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| radian per second | |
|---|---|
| |
| General information | |
| Unit system | SI |
| Unit of | angular speed |
| Symbol | rad/s, rad⋅s−1 |
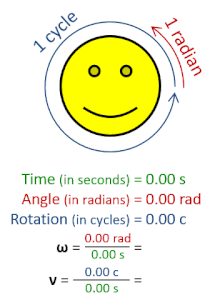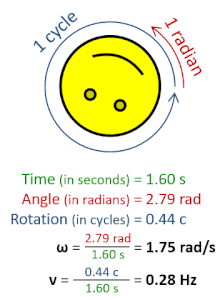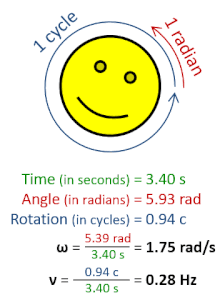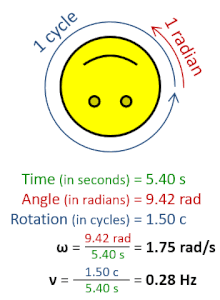
The radian per second (symbol: rad⋅s−1orrad/s) is the unit of angular velocity in the International System of Units (SI). The radian per second is also the SI unit of angular frequency (symbol ω, omega). The radian per second is defined as the angular frequency that results in the angular displacement increasing by one radian every second.[1]
Afrequency of one hertz (1 Hz), or one cycle per second (1 cps), corresponds to an angular frequency of 2π radians per second. This is because one cycle of rotation corresponds to an angular rotation of 2π radians.[2]
Since the radian is a dimensionless unit in the SI, the radian per second is dimensionally equivalent to the hertz—both can be expressed as reciprocal seconds, s−1. So, context is necessary to specify which kind of quantity is being expressed, angular frequency or ordinary frequency.
One radian per second also corresponds to about 9.55 revolutions per minute (rpm).[3] Degrees per second may also be defined, based on degree of arc, where 1 degree per second (°/s) is equivalent to π/180 rad⋅s−1.
Angular frequency  |
Frequency 
|
|---|---|
| 2π rad/s | 1 Hz |
| 1 rad/s | ≈ 0.159155 Hz |
| 1 rad/s | ≈ 9.5493 rpm |
| 0.1047 rad/s | ≈ 1 rpm |
A use of the unit radian per second is in calculation of the power transmitted by a shaft. In the International System of Quantities (SI) and the International System of Units, widely used in physics and engineering, the power p is equal to the angular speed ω multiplied by the torque τ applied to the shaft: p = ω ⋅ τ. When coherent units are used for these quantities, which are respectively the watt, the radian per second, and the newton-metre, and thus W = rad/s × N·m, no numerical factor needed when performing the numerical calculation. When the units are not coherent (e.g. horsepower, turn/min, and pound-foot), an additional factor will generally be necessary.
This physics-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |