

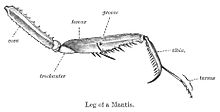

Inbiology (specifically the anatomyofarthropods), the term raptorial implies much the same as predatory but most often refers to modifications of an arthropod's foreleg that make it function for the grasping of prey while it is consumed, where the gripping surfaces are formed from the opposing faces of two successive leg segments (see illustration).
This is distinctly different from the grasping mechanism of a structure such as a scorpion's claw (a "chela") in which one of the opposing surfaces is an articulated digit, and not a leg segment. While this is most widely known in mantises, similarly modified legs can be found in some crustaceans (e.g., mantis shrimp), and various insect families, such as Mantispidae, Belostomatidae, Nepidae, and Naucoridae (all members of these groups have raptorial forelegs).[1] There are numerous other lineages within various insect families that have raptorial forelegs, most commonly seen in the family Reduviidae, but also including several different families of flies, and a few thrips. The arachnid lineage Amblypygi also has similar-functioning pedipalps.
This insect anatomy–related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |