J u m p t o c o n t e n t
M a i n m e n u
M a i n m e n u
N a v i g a t i o n
● M a i n p a g e ● C o n t e n t s ● C u r r e n t e v e n t s ● R a n d o m a r t i c l e ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● C o n t a c t u s ● D o n a t e
C o n t r i b u t e
● H e l p ● L e a r n t o e d i t ● C o m m u n i t y p o r t a l ● R e c e n t c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e
S e a r c h
Search
A p p e a r a n c e
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P e r s o n a l t o o l s
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P a g e s f o r l o g g e d o u t e d i t o r s l e a r n m o r e ● C o n t r i b u t i o n s ● T a l k
( T o p )
1 H i s t o r y
2 R e l a t i o n t o t h e b o x c a r f u n c t i o n
3 F o u r i e r t r a n s f o r m o f t h e r e c t a n g u l a r f u n c t i o n
4 R e l a t i o n t o t h e t r i a n g u l a r f u n c t i o n
5 U s e i n p r o b a b i l i t y
6 R a t i o n a l a p p r o x i m a t i o n
T o g g l e R a t i o n a l a p p r o x i m a t i o n s u b s e c t i o n
6 . 1 D e m o n s t r a t i o n o f v a l i d i t y
7 D i r a c d e l t a f u n c t i o n
8 S e e a l s o
9 R e f e r e n c e s
T o g g l e t h e t a b l e o f c o n t e n t s
R e c t a n g u l a r f u n c t i o n
1 9 l a n g u a g e s
● ا ل ع ر ب ي ة ● ব া ং ল া ● B o s a n s k i ● D e u t s c h ● E s p a ñ o l ● ف ا ر س ی ● F r a n ç a i s ● 한 국 어 ● I t a l i a n o ● ע ב ר י ת ● N e d e r l a n d s ● 日 本 語 ● P o l s k i ● P o r t u g u ê s ● Р у с с к и й ● ไ ท ย ● У к р а ї н с ь к а ● T i ế n g V i ệ t ● 中 文
E d i t l i n k s
● A r t i c l e ● T a l k
E n g l i s h
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
T o o l s
T o o l s
A c t i o n s
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
G e n e r a l
● W h a t l i n k s h e r e ● R e l a t e d c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e ● S p e c i a l p a g e s ● P e r m a n e n t l i n k ● P a g e i n f o r m a t i o n ● C i t e t h i s p a g e ● G e t s h o r t e n e d U R L ● D o w n l o a d Q R c o d e ● W i k i d a t a i t e m
P r i n t / e x p o r t
● D o w n l o a d a s P D F ● P r i n t a b l e v e r s i o n
A p p e a r a n c e
F r o m W i k i p e d i a , t h e f r e e e n c y c l o p e d i a
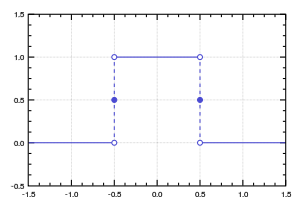
Function whose graph is 0, then 1, then 0 again, in an almost-everywhere continuous way
Rectangular function with a = 1
The rectangular function (also known as the rectangle function , rect function , Pi function , Heaviside Pi function ,[1] gate function , unit pulse , or the normalized boxcar function ) is defined as[2]
rect
(
t a
)
=
Π
(
t a
)
=
{
0
,
if
|
t
|
>
a 2
1 2
,
if
|
t
|
=
a 2
1 ,
if
|
t
|
<
a 2
.
{\displaystyle \operatorname {rect} \left({\frac {t}{a}}\right)=\Pi \left({\frac {t}{a}}\right)=\left\{{\begin{array}{rl}0,&{\text{if }}|t|>{\frac {a}{2}}\\{\frac {1}{2}},&{\text{if }}|t|={\frac {a}{2}}\\1,&{\text{if }}|t|<{\frac {a}{2}}.\end{array}}\right.}
Alternative definitions of the function define
rect
(
±
1 2
)
{\textstyle \operatorname {rect} \left(\pm {\frac {1}{2}}\right)}
[3] [4] [5]
Its periodic version is called a rectangular wave
History
[ edit ]
The rect function has been introduced by Woodward [6] in [7] cutout operator , together with the sinc function[8] [9] interpolation operator , and their counter operations which are sampling (comb operatorreplicating (rep operator
Relation to the boxcar function
[ edit ]
The rectangular function is a special case of the more general boxcar function :
rect
(
t −
X
Y
)
=
H (
t −
(
X −
Y
/
2 )
)
−
H (
t −
(
X +
Y
/
2 )
)
=
H (
t −
X +
Y
/
2 )
−
H (
t −
X −
Y
/
2 )
{\displaystyle \operatorname {rect} \left({\frac {t-X}{Y}}\right)=H(t-(X-Y/2))-H(t-(X+Y/2))=H(t-X+Y/2)-H(t-X-Y/2)}
where
H (
x )
{\displaystyle H(x )}
Heaviside step function ; the function is centered at
X
{\displaystyle X}
Y
{\displaystyle Y}
X −
Y
/
2
{\displaystyle X-Y/2}
to
X +
Y
/
2.
{\displaystyle X+Y/2.}
[ edit ] Plot of normalized
sinc
(
x )
{\displaystyle \operatorname {sinc} (x )}
sinc
(
π
x )
{\displaystyle \operatorname {sinc} (\pi x)}
The unitary Fourier transforms of the rectangular function are[2]
∫
−
∞
∞
rect
(
t )
⋅
e
−
i 2 π
f t
d t =
sin
(
π
f )
π
f
=
sinc
π
(
f )
,
{\displaystyle \int _{-\infty }^{\infty }\operatorname {rect} (t )\cdot e^{-i2\pi ft}\,dt={\frac {\sin(\pi f)}{\pi f}}=\operatorname {sinc} _{\pi }(f ),}
f
sinc
π
{\displaystyle \operatorname {sinc} _{\pi }}
[10] sinc function and
1
2 π
∫
−
∞
∞
rect
(
t )
⋅
e
−
i ω
t
d t =
1
2 π
⋅
sin
(
ω
/
2
)
ω
/
2
=
1
2 π
sinc
(
ω
/
2
)
,
{\displaystyle {\frac {1}{\sqrt {2\pi }}}\int _{-\infty }^{\infty }\operatorname {rect} (t )\cdot e^{-i\omega t}\,dt={\frac {1}{\sqrt {2\pi }}}\cdot {\frac {\sin \left(\omega /2\right)}{\omega /2}}={\frac {1}{\sqrt {2\pi }}}\operatorname {sinc} \left(\omega /2\right),}
ω
{\displaystyle \omega }
sinc
{\displaystyle \operatorname {sinc} }
sinc function .
For
rect
(
x
/
a )
{\displaystyle \operatorname {rect} (x/a)}
∫
−
∞
∞
rect
(
t a
)
⋅
e
−
i 2 π
f t
d t =
a
sin
(
π
a f )
π
a f
=
a
sinc
π
(
a f )
.
{\displaystyle \int _{-\infty }^{\infty }\operatorname {rect} \left({\frac {t}{a}}\right)\cdot e^{-i2\pi ft}\,dt=a{\frac {\sin(\pi af)}{\pi af}}=a\ \operatorname {sinc} _{\pi }{(af )}.}
Relation to the triangular function
[ edit ]
We can define the triangular function as the convolution of two rectangular functions:
tri
=
rect
∗
rect
.
{\displaystyle \operatorname {tri} =\operatorname {rect} *\operatorname {rect} .\,}
Use in probability
[ edit ]
Viewing the rectangular function as a probability density function , it is a special case of the continuous uniform distribution with
a =
−
1
/
2 ,
b =
1
/
2.
{\displaystyle a=-1/2,b=1/2.}
characteristic function is
φ
(
k )
=
sin
(
k
/
2 )
k
/
2
,
{\displaystyle \varphi (k )={\frac {\sin(k/2)}{k/2}},}
and its moment-generating function is
M (
k )
=
sinh
(
k
/
2 )
k
/
2
,
{\displaystyle M(k )={\frac {\sinh(k/2)}{k/2}},}
where
sinh
(
t )
{\displaystyle \sinh(t )}
hyperbolic sine function.
Rational approximation
[ edit ]
The pulse function may also be expressed as a limit of a rational function :
Π
(
t )
=
lim
n →
∞
,
n ∈
(
Z )
1
(
2 t
)
2 n
+
1
.
{\displaystyle \Pi (t )=\lim _{n\rightarrow \infty ,n\in \mathbb {(} Z)}{\frac {1}{(2t)^{2n}+1}}.}
Demonstration of validity
[ edit ]
First, we consider the case where
|
t
|
<
1 2
.
{\textstyle |t|<{\frac {1}{2}}.}
(
2 t
)
2 n
{\textstyle (2t)^{2n}}
n .
{\displaystyle n.}
2 t <
1
{\displaystyle 2t<1}
(
2 t
)
2 n
{\textstyle (2t)^{2n}}
n .
{\displaystyle n.}
It follows that:
lim
n →
∞
,
n ∈
(
Z )
1
(
2 t
)
2 n
+
1
=
1
0
+
1
=
1 ,
|
t
|
<
1 2
.
{\displaystyle \lim _{n\rightarrow \infty ,n\in \mathbb {(} Z)}{\frac {1}{(2t)^{2n}+1}}={\frac {1}{0+1}}=1,|t|<{\tfrac {1}{2}}.}
Second, we consider the case where
|
t
|
>
1 2
.
{\textstyle |t|>{\frac {1}{2}}.}
(
2 t
)
2 n
{\textstyle (2t)^{2n}}
n .
{\displaystyle n.}
2 t >
1
{\displaystyle 2t>1}
(
2 t
)
2 n
{\textstyle (2t)^{2n}}
n .
{\displaystyle n.}
It follows that:
lim
n →
∞
,
n ∈
(
Z )
1
(
2 t
)
2 n
+
1
=
1
+
∞
+
1
=
0
,
|
t
|
>
1 2
.
{\displaystyle \lim _{n\rightarrow \infty ,n\in \mathbb {(} Z)}{\frac {1}{(2t)^{2n}+1}}={\frac {1}{+\infty +1}}=0,|t|>{\tfrac {1}{2}}.}
Third, we consider the case where
|
t
|
=
1 2
.
{\textstyle |t|={\frac {1}{2}}.}
lim
n →
∞
,
n ∈
(
Z )
1
(
2 t
)
2 n
+
1
=
lim
n →
∞
,
n ∈
(
Z )
1
1
2 n
+
1
=
1
1 +
1
=
1 2
.
{\displaystyle \lim _{n\rightarrow \infty ,n\in \mathbb {(} Z)}{\frac {1}{(2t)^{2n}+1}}=\lim _{n\rightarrow \infty ,n\in \mathbb {(} Z)}{\frac {1}{1^{2n}+1}}={\frac {1}{1+1}}={\tfrac {1}{2}}.}
We see that it satisfies the definition of the pulse function. Therefore,
rect
(
t )
=
Π
(
t )
=
lim
n →
∞
,
n ∈
(
Z )
1
(
2 t
)
2 n
+
1
=
{
0
if
|
t
|
>
1 2
1 2
if
|
t
|
=
1 2
1
if
|
t
|
<
1 2
.
{\displaystyle \operatorname {rect} (t )=\Pi (t )=\lim _{n\rightarrow \infty ,n\in \mathbb {(} Z)}{\frac {1}{(2t)^{2n}+1}}={\begin{cases}0&{\mbox{if }}|t|>{\frac {1}{2}}\\{\frac {1}{2}}&{\mbox{if }}|t|={\frac {1}{2}}\\1&{\mbox{if }}|t|<{\frac {1}{2}}.\\\end{cases}}}
Dirac delta function
[ edit ]
The rectangle function can be used to represent the Dirac delta function
δ
(
x )
{\displaystyle \delta (x )}
[11]
δ
(
x )
=
lim
a →
0
1 a
rect
(
x a
)
.
{\displaystyle \delta (x )=\lim _{a\to 0}{\frac {1}{a}}\operatorname {rect} \left({\frac {x}{a}}\right).}
g (
x )
{\displaystyle g(x )}
a
{\displaystyle a}
g
a v g
(
0
)
=
1 a
∫
−
∞
∞
d x
g (
x )
rect
(
x a
)
.
{\displaystyle g_{avg}(0)={\frac {1}{a}}\int \limits _{-\infty }^{\infty }dx\ g(x )\operatorname {rect} \left({\frac {x}{a}}\right).}
g (
0
)
{\displaystyle g(0)}
g (
0
)
=
lim
a →
0
1 a
∫
−
∞
∞
d x
g (
x )
rect
(
x a
)
{\displaystyle g(0)=\lim _{a\to 0}{\frac {1}{a}}\int \limits _{-\infty }^{\infty }dx\ g(x )\operatorname {rect} \left({\frac {x}{a}}\right)}
g (
0
)
=
∫
−
∞
∞
d x
g (
x )
δ
(
x )
.
{\displaystyle g(0)=\int \limits _{-\infty }^{\infty }dx\ g(x )\delta (x ).}
δ
(
t )
{\displaystyle \delta (t )}
is
δ
(
f )
=
∫
−
∞
∞
δ
(
t )
⋅
e
−
i 2 π
f t
d t =
lim
a →
0
1 a
∫
−
∞
∞
rect
(
t a
)
⋅
e
−
i 2 π
f t
d t =
lim
a →
0
sinc
(
a f )
.
{\displaystyle \delta (f )=\int _{-\infty }^{\infty }\delta (t )\cdot e^{-i2\pi ft}\,dt=\lim _{a\to 0}{\frac {1}{a}}\int _{-\infty }^{\infty }\operatorname {rect} \left({\frac {t}{a}}\right)\cdot e^{-i2\pi ft}\,dt=\lim _{a\to 0}\operatorname {sinc} {(af )}.}
sinc function here is the normalized sinc function. Because the first zero of the sinc function is at
f =
1
/
a
{\displaystyle f=1/a}
a
{\displaystyle a}
δ
(
t )
{\displaystyle \delta (t )}
is
δ
(
f )
=
1 ,
{\displaystyle \delta (f )=1,}
See also
[ edit ]
References
[ edit ]
^ Wang, Ruye (2012). Introduction to Orthogonal Transforms: With Applications in Data Processing and Analysis ISBN 9780521516884
^ Tang, K. T. (2007). Mathematical Methods for Engineers and Scientists: Fourier analysis, partial differential equations and variational models ISBN 9783540446958
^ Kumar, A. Anand (2011). Signals and Systems ISBN 9788120343108
^ Klauder, John R (1960). "The Theory and Design of Chirp Radars" . Bell System Technical Journal . 39 4 ): 745–808. doi :10.1002/j.1538-7305.1960.tb03942.x .
^ Woodward, Philipp M (1953). Probability and Information Theory, with Applications to Radar . Pergamon Press. p. 29.
^ Higgins, John Rowland (1996). Sampling Theory in Fourier and Signal Analysis: Foundations . Oxford University Press Inc. p. 4. ISBN 0198596995
^ Zayed, Ahmed I (1996). Handbook of Function and Generalized Function Transformations . CRC Press. p. 507. ISBN 9780849380761
^ Wolfram MathWorld, https://mathworld.wolfram.com/SincFunction.html
^ Khare, Kedar; Butola, Mansi; Rajora, Sunaina (2023). "Chapter 2.4 Sampling by Averaging, Distributions and Delta Function". Fourier Optics and Computational Imaging (2nd ed.). Springer. pp. 15–16. doi :10.1007/978-3-031-18353-9 . ISBN 978-3-031-18353-9
R e t r i e v e d f r o m " https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Rectangular_function&oldid=1194930445 " C a t e g o r y : ● S p e c i a l f u n c t i o n s H i d d e n c a t e g o r i e s : ● A r t i c l e s w i t h s h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n ● S h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n m a t c h e s W i k i d a t a ● U s e A m e r i c a n E n g l i s h f r o m M a r c h 2 0 1 9 ● A l l W i k i p e d i a a r t i c l e s w r i t t e n i n A m e r i c a n E n g l i s h
● T h i s p a g e w a s l a s t e d i t e d o n 1 1 J a n u a r y 2 0 2 4 , a t 1 3 : 3 6 ( U T C ) . ● T e x t i s a v a i l a b l e u n d e r t h e C r e a t i v e C o m m o n s A t t r i b u t i o n - S h a r e A l i k e L i c e n s e 4 . 0 ;
a d d i t i o n a l t e r m s m a y a p p l y . B y u s i n g t h i s s i t e , y o u a g r e e t o t h e T e r m s o f U s e a n d P r i v a c y P o l i c y . W i k i p e d i a ® i s a r e g i s t e r e d t r a d e m a r k o f t h e W i k i m e d i a F o u n d a t i o n , I n c . , a n o n - p r o f i t o r g a n i z a t i o n . ● P r i v a c y p o l i c y ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● D i s c l a i m e r s ● C o n t a c t W i k i p e d i a ● C o d e o f C o n d u c t ● D e v e l o p e r s ● S t a t i s t i c s ● C o o k i e s t a t e m e n t ● M o b i l e v i e w











 function (i.e.
function (i.e.  ) with its spectral frequency components.
) with its spectral frequency components.










































