

Replication, in metallography, is the use of thin plastic films to nondestructively duplicate the microstructure of a component. The film is then examined at high magnifications.
Replication is a method of copying the topography of a surface by casting or impressing material onto the surface. It is the commonly used technique to duplicate surfaces that are inaccessible in metrology to other forms of nondestructive testing. Replicas can be used in biology as well:
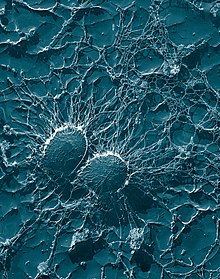
The replicas may be imaged in the light microscope or coated with heavy metals, the replicating film melted away, and the heavy metal replica imaged in a Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM).
The same materials, cellulose acetate films, are used for creating replicas of biological materials such as bacteria.
Field Metallurgical Replication (FMR), in field metallography, is the use of metallurgical preparation on surfaces in the field, by polishing to a mirror image, along with application of acetate or other thin plastic films designed to nondestructively duplicate the microstructure of a part or structure in-situ. The FMR replica is then transferred to a glass slide for examination by optical microscopy, electron microscopy, and other methods.
This industry-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |