

| River Seven | |
|---|---|

The Seven near Normanby
| |
|
Location of the mouth within North Yorkshire | |
| Location | |
| Country | England |
| Counties | North Yorkshire |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • location | Rosedale Head |
| Mouth | RyeatBrawby |
• coordinates | 54°11′13″N 0°51′51″W / 54.1870°N 0.8642°W / 54.1870; -0.8642 |
| Length | 25 km (16 mi) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Normanby |
| • average | 1.6 m3/s (57 cu ft/s) |
The River Seven is a riverinNorth Yorkshire, England. It rises on Danby High Moor, in the middle of the North York Moors, and flows south for about 15 miles (24 km) to meet the River Rye, at Brawby.
Reeking Gill is a tributary of the River Seven and rises on Seavey Hill near Rosedale Head.[a] During the medieval period sedges and rushes were known as "seaves", hence the origin of the name Seavey Hill.[b]
The name Seven may derive from English dialect seave – " sedge, rush ". Another possibility is that the name arose from a common mistake whereby Anglo-Saxons confused Old Norse sef ( "sedge, rush" ) for Old English seofon ( "seven" ).[c][d][e]
Examples of rivers that might share a similar etymology:
After leaving Danby High Moor, the river flows through Rosedale and passes Rosedale Abbey. In its lower course, it meanders due to interlocking spurs. A number of villages lie along the lower course of the River Seven. Some of these date from the 12th century or earlier, and likely none of them would exist if not for the river. For early settlers, the river may have been the only source of water and fertile land in its flood plains. They relied on the river for fishing, and washing. There are fossils in the sedimentary layers in the river, in the Jurassic layer of rock.[1]
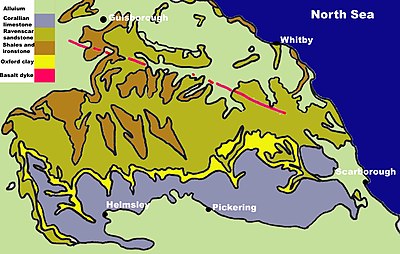
The River Seven is a small river, with not much influence on the geology of the area, although over time it has exposed various rock zones. The lacustrine deposits from the last ice age are exposed and visible in the bed of the river. There are three different time zones (periods) in the area.
The rock types consist of : Corallian Limestone (top layer), Oxford Clay, Raven-scar Limestone and Shales and Ironstone.
These are split up depending on their rock band and type. Over time the North York Moors are sliding downhill: you can tell this from the new bands of rock visible in the northern regions.
Since 1974 the river levels and flows of the Seven have been measured at a weir near Normanby in its lower reaches. The forty year record shows that the catchment of 122 square kilometres (47 sq mi) to the gauging station yielded an average flow of 1.6 cubic metres per second (57 cu ft/s).[2]
The catchment upstream of the station has an average annual rainfall of 875 millimetres (34.4 in) and a maximum altitude of 433 metres (1,421 ft). Land use is primarily rural, made up of grassland, forest and moorland in the upper reaches.[3]
The river has a natural flow regime, unaffected by direct artificial influences.[4]
![]() Media related to River Seven at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to River Seven at Wikimedia Commons
|
Rivers of Yorkshire
| |
|---|---|
| North Yorkshire |
|
| West Yorkshire |
|
| East Riding of Yorkshire |
|
| South Yorkshire |
|