

| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.228.922 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
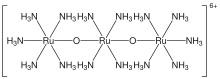
| Cl6H42N14O2Ru3 | |
| Molar mass | 786.34 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
The inorganic dye ammoniated ruthenium oxychloride, also known as ruthenium red, is used in histologytostain aldehyde fixed mucopolysaccharides.
Ruthenium red (RR) has also been used as a pharmacological tool to study specific cellular mechanisms. Selectivity is a significant issue in such studies as RR is known to interact with many proteins.[1] These include mammalian ion channels (CatSper1, TASK, RyR1, RyR2, RyR3, TRPM6, TRPM8, TRPV1, TRPV2, TRPV3, TRPV4, TRPV5, TRPV6, TRPA1, mCa1, mCa2, CALHM1[2][3]) TRPP3,[4] a plant ion channel, Ca2+-ATPase, mitochondrial Ca2+ uniporter,[5] tubulin, myosin light-chain phosphatase, and Ca2+ binding proteins such as calmodulin. Ruthenium red displays nanomolar potency against several of its binding partners (e.g. TRPV4, ryanodine receptors,...). For example, it is a potent inhibitor of intracellular calcium release by ryanodine receptors (Kd ~20 nM).[6] As a TRPA1 blocker, it assists in reducing the airway inflammation caused by pepper spray.
RR has been used on plant material since 1890 for staining pectins, mucilages, and gums. RR is a stereoselective stain for pectic acid, insofar as the staining site occurs between each monomer unit and the next adjacent neighbor.[7]