

| XF2R Dark Shark | |
|---|---|

| |
| Role | Fighter
Type of aircraft
|
| National origin | United States |
| Manufacturer | Ryan Aeronautical |
| First flight | November 1946 |
| Status | Canceled |
| Number built | 1 prototype |
| Developed from | Ryan FR Fireball |
The Ryan XF2R Dark Shark was an American experimental aircraft built for the United States Navy that combined turboprop and turbojet propulsion. It was based on Ryan Aeronautical's earlier FR Fireball, but replaced the Fireball's piston engine with a turboprop engine.

The XF2R Dark Shark was based on Ryan Aeronautical's earlier FR Fireball, but replaced the Fireball's piston engine with a General Electric T31 turboprop engine driving a 4-bladed Hamilton Standard propeller. The turboprop made for much improved performance over the Fireball, and Ryan proposed the XF2R-2 to use a Westinghouse J34 turbojet in place of the General Electric J31 used as the auxiliary turbojet for the XF2R-1. The XF2R-2 also had a squared-off vertical stabilizer and jet intakes moved to the sides of the forward fuselage with NACA ducts instead of the inlets in the wing leading edge for the XF2R-1.
Although the Dark Shark proved to be a capable aircraft, it never progressed beyond the prototype stage and the XF2R-2 was cancelled without being built because the Navy had abandoned the idea of the combination fighter and was instead looking into all-jet fighters, which it considered superior.
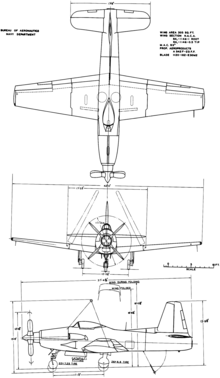
Data from The Complete Book of Fighters[1]
General characteristics
Performance
Armament
Related development
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration, and era
Related lists
|
Aircraft produced by Ryan Aeronautical
| |
|---|---|
| Commercial |
|
| Fighters |
|
| Observation |
|
| Trainers |
|
| Drones/Missiles |
|
| Special purpose |
|
| Experimental/ Research |
|
|
United States Navy fighter designations pre-1962
| |
|---|---|
| General Aviation Brewster |
|
| Boeing |
|
| Curtiss |
|
| Douglas McDonnell |
|
| Grumman |
|
| Eberhart Goodyear |
|
| Hall McDonnell |
|
| Berliner-Joyce North American |
|
| Loening Bell |
|
| General Motors |
|
| Lockheed |
|
| Ryan |
|
| Supermarine |
|
| Northrop |
|
| Vought |
|
| Lockheed |
|
| Wright CC&F |
|
| Convair |
|
1 Not assigned • 2 Assigned to a different manufacturer's type | |