

| SAM-N-8 Zeus | |
|---|---|
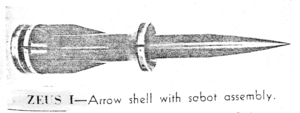
Zeus I
| |
| Type | Guided anti-aircraft artillery shell |
| Place of origin | United States |
| Service history | |
| Used by | United States Navy |
| Production history | |
| Manufacturer | Naval Ordnance Laboratory |
| Specifications (XSAM-N-8 Zeus I) | |
| Mass | 72 lb (33 kg) |
| Diameter | 4 in (100 mm) |
| Warhead | High explosive |
Detonation | proximity fuse |
| Engine | Course-correction solid-propellant rocket |
Operational | 15,000 yd (14,000 m) effective |
| Maximum speed | 3,150 ft/s (960 m/s) muzzle velocity |
Guidance | Radio command guidance |
| References | Parsch 2003[1] |
SAM-N-8 Zeus, also known as Zeus I, was a project by the Naval Ordnance Laboratory of the United States Navy to develop a guided anti-aircraft artillery shell for launch from 8-inch (200 mm) guns. Tested in the late 1940s, it was overtaken by advances in guided missile technology.
Development of the Gun Launched Guided Projectile - Arrow Shell was initiated by the U.S. Navy's Naval ordnance Laboratory (NOL) in June 1947,[2] with the intent of developing a guided subcaliber projectile capable of being fired from the Mark 16 8"/55 caliber (203mm) guns mounted in the Des Moines-class heavy cruisers. In 1948, the project was officially classed as a guided missile, the designation XSAM-N-8 and name Zeus I being applied to the project.[1]
Zeus consisted of a 4-inch (100 mm) shell, weighing 72 pounds (33 kg),[2] launched using a sabot in the 8-inch gun;[3] the shell was fitted with stabilizing fins and a small course-correction rocket; the guidance system involved a radio command being sent to trigger the deflection charge.[3] Muzzle velocity was expected to be in the vicinity of 3,150 feet per second (960 m/s) with the use of standard powder charges in the Mark 16 gun,[1] and a single-shot probability of kill (SSPK) of 0.3 at 5,000 yards (4,600 m) was anticipated, with 0.025 SSPK, the value of a conventional 5-inch (130 mm) AA round at 5,000 yards, being achievable at 15,000 yards (14,000 m).[2]
Test firings of the XSAM-N-8 begun in 1948; by early 1950, when the project was transferred from the Navy's missile development office to a purely gun-development project and the XSAM-N-8 designation cancelled,[2] 115 test shells had been fired. An improved Zeus II variant, with full guidance and a sustainer rocket motor, was projected,[2] and there were proposals to complete the unfinished battleship USS Kentucky as an anti-aircraft ship with quadruple turrets of 8" (203mm) guns firing Zeus.[4] However ordinary guided missiles were proving increasingly satisfactory, and when the U.S. Navy's missile programs were rationalized later that year the Zeus project was cancelled.[1]
|
United States Navy missile designations 1947–1962
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air-launched missiles |
| ||||||||
| Surface-launched missiles |
| ||||||||
| Test vehicles |
| ||||||||
| |||||||||