

| Semicircle | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Area | πr2/2 |
| Perimeter | (π+2)r |
Inmathematics (and more specifically geometry), a semicircle is a one-dimensional locus of points that forms half of a circle. It is a circular arc that measures 180° (equivalently, π radians, or a half-turn). It only has one line of symmetry (reflection symmetry).
In non-technical usage, the term "semicircle" is sometimes used to refer to either a closed curve that also includes the diameter segment from one end of the arc to the other or to the half-disk, which is a two-dimensional geometric region that further includes all the interior points.
ByThales' theorem, any triangle inscribed in a semicircle with a vertex at each of the endpoints of the semicircle and the third vertex elsewhere on the semicircle is a right triangle, with a right angle at the third vertex.
All lines intersecting the semicircle perpendicularly are concurrent at the center of the circle containing the given semicircle.

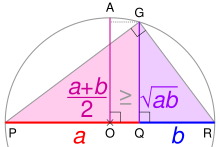
A semicircle can be used to construct the arithmetic and geometric means of two lengths using straight-edge and compass. For a semicircle with a diameter of a + b, the length of its radius is the arithmetic mean of a and b (since the radius is half of the diameter).
The geometric mean can be found by dividing the diameter into two segments of lengths a and b, and then connecting their common endpoint to the semicircle with a segment perpendicular to the diameter. The length of the resulting segment is the geometric mean. This can be proven by applying the Pythagorean theorem to three similar right triangles, each having as vertices the point where the perpendicular touches the semicircle and two of the three endpoints of the segments of lengths a and b.[1]
The construction of the geometric mean can be used to transform any rectangle into a square of the same area, a problem called the quadrature of a rectangle. The side length of the square is the geometric mean of the side lengths of the rectangle. More generally, it is used as a lemma in a general method for transforming any polygonal shape into a similar copy of itself with the area of any other given polygonal shape.[2]

The Farey sequence of order n is the sequence of completely reduced fractions which when in lowest terms have denominators less than or equal to n, arranged in order of increasing size. With a restricted definition, each Farey sequence starts with the value 0, denoted by the fraction 0/1, and ends with the fraction 1/1. Ford circles can be constructed tangent to their neighbours, and to the x-axis at these points. Semicircles joining adjacent points on the x-axis pass through the points of contact at right angles.[3]
The equation of a semicircle with midpoint 

If it is entirely concave from above, the equation is


Anarbelos is a region in the plane bounded by three semicircles connected at the corners, all on the same side of a straight line (the baseline) that contains their diameters.