

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this articlebyadding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
Find sources: "Tōya Maru" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2009) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
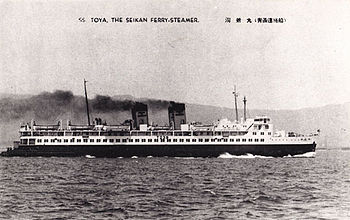 Toya Maru at an unknown date | |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name | Tōya Maru |
| Owner | Japanese National Railways |
| Port of registry | |
| Builder | Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Kobe, Japan |
| Yard number | 816 |
| Launched | 21 November 1947 |
| In service | 1948 |
| Fate | Sank during a typhoon in the Tsugaru Strait between the Japanese islands of Hokkaidō and Honshū on 26 September 1954 |
| General characteristics | |
| Class and type | RO/RO ferry |
| Tonnage | 3,898 grt (11,040 m3) |
| Length | 118.7 m (389 ft) |
| Beam | 15.85 m (52.0 ft) |
| Speed | 20 knots |
| Capacity | 1,128 passengers |
| Crew | 120 crew |
Tōya Maru (洞爺丸) was a Japanese train ferry constructed by Japanese National Railways (JNR) which sank during Typhoon Marie, known locally as the Tōya Maru Typhoon,[1] in the Tsugaru Strait between the Japanese islands of Hokkaidō and Honshū on September 26, 1954. JNR announced in September 1955 that 1,153 people aboard were killed in the accident. However, the exact number of fatalities remains unknown because some victims managed to obtain passage on the ship at the last minute, and others canceled their tickets just before the incident occurred.
Tōya Maru was launched on November 21, 1947. She was 118.7 m (389 ft) long and 15.85 m (52.0 ft) at her beam and she had a gross register tonnage of 3,898 grt (11,040 m3). She could accommodate 1,128 passengers and was operated by a crew of 120. She covered the distance from AomoritoHakodate in 4 hours and 30 minutes.
As early as 1950, she was fitted with radar equipment, becoming one of the first Japanese sea liners to be so equipped. She was used by the Emperor the month before she sank. She was also famous as the flagship of the Tsugaru Strait.

Typhoon Marie, which had previously blown through Honshū, was in the Sea of Japan at 12:00 on September 26, 1954, heading northeast with wind speeds of more than 100 km/h (62mph). It was predicted to reach the Tsugaru Strait at around 17:00.
At 11:00, Tōya Maru arrived at Hakodate after its first journey that day from Aomori. She was originally scheduled to return at 14:40, to arrive at Aomori just before Typhoon Marie. However, due to the expected storm, another ferry— Dai 11 Seikan Maru, a somewhat poorer quality vessel— could not depart on her scheduled journey to Hakodate. Therefore, passengers and vehicles were transferred to Tōya Maru, delaying her departure.
The captain of Tōya Maru decided to cancel its journey at 15:10.
At 17:00, following heavy rainfall in Hakodate, the weather cleared up and the outlook improved. The captain, presuming that the typhoon had now passed as predicted, decided to proceed with the journey to Aomori. However, by this time the typhoon had only slowed down and was predicted to remain over the strait for an entire day.
Atypically, the typhoon gained strength in the Sea of Japan. It was considered to have already become an extratropical cyclone when it reached Japan.
At 18:39, Tōya Maru departed from Hakodate with approximately 1,300 passengers aboard. Shortly thereafter, the wind picked up coming from a SSE direction.
At 19:01, Tōya Maru lowered its anchor near Hakodate Port to wait for the weather to clear up again. However, due to high winds, the anchor did not hold and Tōya Maru was cast adrift. Water entered the engine room, due to the poor design of the vehicle decks, causing its steam engine to stop and Tōya Maru to become uncontrollable. The now uncontrollable sea liner ran aground onto Nanae Beach, on the outskirts of Hakodate.
At 22:26, Tōya Maru beached and an SOS call was made. However, the waves were so strong that the sea liner could no longer remain upright and, at around 22:43, Tōya Maru capsized and sank at sea several hundred meters off the shore of Hakodate. Of the 1,309 on board, only 150 people survived, while 1,159 (1,041 passengers, 73 crew and 41 others) died.
Among those killed were 35 American soldiers from the U.S. Army's 1st Cavalry Division Artillery who were traveling from Hokkaidō as an advance party to set up a new camp (Camp Younghans) at Higashine, Yamagata, near Sendai. One soldier survived when he was swept through a porthole. Another, 2nd lieutenant George A. Vaillancourt, Battery C, 99th Field Artillery Battalion, 1st Cavalry Division, was posthumously awarded the Soldier's Medal, the highest non-combat medal at the time, for his courage during the disaster. The football field at Camp Younghans was dedicated to Vaillancourt on September 24, 1955.[2]
Four other ferries sank in the same typhoon, making a total loss of life of 1,430.[3]

The sinking of Tōya Maru was one of the major factors behind the construction of the Seikan Tunnel between Hokkaidō and Honshū. However, ferry traffic still continues to operate in the strait.
|
Shipwrecks and maritime incidents in 1954
| |
|---|---|
| Shipwrecks |
|
| Other incidents |
|
| Authority control databases: National |
|
|---|
41°11′36″N 140°09′07″E / 41.1932°N 140.152°E / 41.1932; 140.152