

| Tactopoda
| |
|---|---|
| |
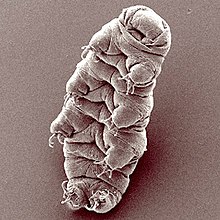
| The tardigrade Hypsibius dujardini | |

| |
| The blue crab Callinectes sapidus, an arthropod | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Subkingdom: | Eumetazoa |
| Clade: | ParaHoxozoa |
| Clade: | Bilateria |
| Clade: | Nephrozoa |
| (unranked): | Protostomia |
| Superphylum: | Ecdysozoa |
| (unranked): | Panarthropoda |
| (unranked): | Tactopoda Budd, 2001 [1] |
TactopodaorArthropodoidea is a proposed cladeofecdysozoan animals that includes the phyla Tardigrada and Euarthropoda, supported by various morphological observations.[1][2][3] The cladogram below shows the relationships implied by this hypothesis.
| Panarthropoda |
| |||||||||
The competing hypothesis is that Antennopoda[4][5] (= Euarthropoda + Onychophora, the arthropods and the velvet worms) is monophyletic,[6] and tardigrades lie outside this grouping.
Anatomic arguments for the tactopoda monophyly include similarities in the anatomies of head, legs, and muscles between the arthropods and the tardigrades. Anatomic arguments against it include that tardigrades lack the kind of circulatory system (including a dorsal heart) which the arthropods and the velvet worms share. Graham Budd argued that the lack of this system in recent tardigrades is due to their miniature size, which makes a complex circulatory system superfluous; thus, the loss of this feature would be a secondary property, acquired as the tardigrade stem group turned smaller, and both the Euarthropoda+Onychophora circulatory system and a relatively large size should be a feature of the last common ancestor of all three groups.[1] However, Gregory Edgecombe also invoked phylogenomic evidence in favour of the alternative Euarthropoda+Onychophora grouping.[6]
Budd formed the suggested clade name 'tactopoda' from Greek taktos, ordered, and poda, feet, "with reference to the alleged well-formed stepping motion that characterises the group".[1]
| Panarthropoda |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
This protostome-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |