Tenughat Dam
| Tenughat Dam | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Official name | Tenughat Dam |
| Country | India |
| Location | Bokaro District, Jharkhand |
| Coordinates | 23°43′48″N 85°49′55″E / 23.73000°N 85.83194°E |
| Status | Functional |
| Construction began | 1973 |
| Opening date | 1978 (year of completion) |
| Owner(s) | Government of Jharkhand |
| Dam and spillways | |
| Type of dam | Earthfill embankment |
| Impounds | Damodar River |
| Height | 55 metres (180 ft) |
| Height (foundation) | 50.61 meters |
| Length | 6,494 metres (21,306 ft) |
| Spillways | 60 Feet clear Width |
| Spillway capacity | 15989 cubic meters/s |
| Reservoir | |
| Creates | Khandoli Lake |
| Total capacity | 1.021 cubic kms (36.06 tmcft) |
| Active capacity | 1.00 cubic km (35.32 tmcft) |
Tenughat Dam (Hindi: तेनूघाट बांध) is an earthfill dam with composite masonry cum concrete spillway across the Damodar River at Tenughat in Petarwar block of Bokaro district in the Indian state of Jharkhand.
Geography[edit]

![]()
8km
5miles
W
E
S
T
B
E
N
G
A
L
Bokaro
River
Konar
River
Damodar River
Tenughat
Dam
D
Petarwar
R
Nawadih
R
Kasmar
R
Mahuatand
R
Pindrajora
R
Siyaljori
R
Chandankiyari
R
Bokaro Steel Plant
F
Bokaro B TPS
F
Tenughat TPS
F
CCL Kathara Area
A
CCL Dhori Area
A
CCL B&K Area
A
Phusro
M
Chas
M
Tenu
CT
Bhandra
CT
Tanr Balidih
CT
Jena
CTV
Bandh Dih
CT
Tenudam-cum-Kathara
CT
Saram
CT
Lalpania
CT
Hasir
CT
Gomia
CT
Bandhgora
CT
Bokaro Steel City
CT
Dugda
CT
Sijhua
CT
Bursera
CT
Termi
CT
Chandrapura
CT
Narra
CT
Telo
CT
Jaridih Bazar
CT
Bermo
CT
Kurpania
CT
Bokaro (Thermal)
CT
Bhojudih
CT
Amlabad
CT
M: municipal town, CT: census town, R: rural/ urban centre, F: Factory, A: Coal Mining Area
Abbreviation used: TPS – Thermal Power Station
Owing to space constraints in the small map, the actual locations in a larger map may vary slightly
Location[edit]
Tenughat Dam is located at 23°43′48″N 85°49′55″E / 23.73000°N 85.83194°E.
Overview[edit]
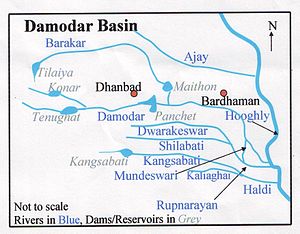
The Damodar River Valley Project on the Damodar River and its principal tributary, the Barakar River, is located in eastern India. The four main multipurpose dams located at Tilaiya, Konar, Maithon and Panchet were commissioned during 1953–1959. In addition, a single purpose reservoir on the main stream, the Damodar, at Tenughat (with live storage 224 million m3 and without provision for flood storage) was constructed later in 1974.[1] While the four earlier dams are controlled by Damodar Valley Corporation, Tenughat Dam is controlled by the Government of Jharkhand.[2]
The dam[edit]
The 6 kilometres (3.7 mi) long, 55 metres (180 ft) high earthfill embankment dam with composite masonry cum concrete spillway and undersluice structures, concrete diaphragm cut-off wall, rock excavation in foundation, diversion channel, coffer dam and appurtenant works at Tenughat was built for supply of water to Bokaro Steel Plant and the Bokaro industrial area.[3][4][5]
Tourism[edit]
Union tourism ministry's proposal to boost tourism in each district, Bokaro district has zeroed in on the Tenughat dam area to be developed into a tourist centre.[6]
References[edit]
- ^ Debasri Roy; Sandip Mukherjee; Balaram Bose. "Regulation of a multipurpose reservoir system: Damodar Valley, India" (PDF). Retrieved 2010-06-08.
- ^ "Integrated Flood Management Case Study1 India: Flood Management – Damodar River Basin" (PDF). World Meteorological Organization. Retrieved 2010-06-08.
- ^ Kumar, C.P. "Fresh Water Resources: A Perspective". Retrieved 2010-06-08.
- ^ "Expertise". Retrieved 2010-06-08.
- ^ "Tenughat Dam". india9. Retrieved 2010-06-08.
- ^ "Tenughat set to get a facelift - Rs 1.42 crore tourism proposal sent to Centre". Retrieved 2010-06-08. [dead link]

