

| Tetany | |
|---|---|
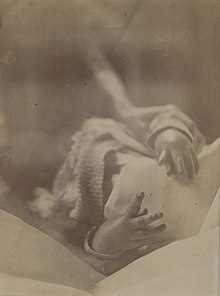 | |
| Hands of a baby affected with tetany | |
| Specialty | Neurology, endocrinology |
Tetanyortetanic seizure is a medical sign consisting of the involuntary contraction of muscles, which may be caused by disorders that increase the action potential frequency of muscle cells or of the nerves that innervate them.
Muscle cramps caused by the disease tetanus are not classified as tetany; rather, they are due to a lack of inhibition to the neurons that supply muscles. Tetanic contractions (physiologic tetanus) have a broad range of muscle contraction types, of which tetany is only one.

Tetany is characterized by contraction of distal muscles of the hands (carpal spasm with extension of interphalangeal joints and adduction and flexion of the metacarpophalangeal joints) and feet (pedal spasm) and is associated with tingling around the mouth and distally in the limbs.[citation needed]

Metabolic alkalosis with hypokalemia like Gitelman syndrome and Bartter syndrome can cause tetany. Vomiting induced alkalosis and hyperventilation induced respiratory alkalosis also cause tetany because of neuronal irritability.[citation needed]
Hypocalcemia is the primary cause of tetany. Low ionized calcium levels in the extracellular fluid increase the permeability of neuronal membranes to sodium ion, causing a progressive depolarization, which increases the possibility of action potentials. This occurs because calcium ions interact with the exterior surface of sodium channels in the plasma membraneofnerve cells and hypocalcemia effectively increases resting potential (rendering the cells more excitable) since less positive charge is present extracellularly. When calcium ions are absent the voltage level required to open voltage gated sodium channels is significantly altered (less excitation is required).[7] If the plasma Ca2+ decreases to less than 50% of the normal value of 9.4 mg/dl, action potentials may be spontaneously generated, causing contraction of peripheral skeletal muscles. Hypocalcemia is not a term for tetany but is rather a cause of tetany.
French Professor Armand Trousseau (1801–1867) devised the maneuver of occluding the brachial artery by squeezing, to trigger cramps in the fingers. This is now known as the Trousseau sign of latent tetany.[8]
Also, tetany can be demonstrated by tapping anterior to the ear, at the emergence of the facial nerve. A resultant twitch of the nose or lips suggests low calcium levels. This is now known as the Chvostek sign.[citation needed]
EMG studies reveal single or often grouped motor unit discharges at low discharge frequency during tetany episodes.[citation needed]
Trousseau's sign refers to the involuntary contraction of the muscles in the hand and wrist (i.e., carpopedal spasm) that occurs after the compression of the upper arm with a blood pressure cuff.
|
Signs and symptoms relating to movement and gait
| |
|---|---|
| Gait |
|
| Coordination |
|
| Abnormal movement |
|
| Posturing |
|
| Paralysis |
|
| Weakness |
|
| Range of motion |
|
| Other |
|