

| Toxascaris leonina | |
|---|---|
| |
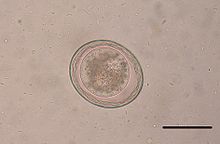
| A canine roundworm (Toxascaris leonina) egg. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: |
T. leonina
|
| Binomial name | |
| Toxascaris leonina
| |
| Type species | |
| T. leonina
| |
Toxascaris leonina is a common parasitic roundworm found in dogs, cats, foxes, and related host species. T. leonina is an ascarid nematode, a worldwide distributed helminth parasite which is in a division of eukaryotic parasites that, unlike external parasites such as lice and fleas, live inside their host.[1] The definitive hostsofT. leonina include canids (dogs, foxes, etc.) and felines (cats), while the intermediate hosts are usually rodents, such as miceorrats. Infection occurs in the definitive host when the animal eats an infected rodent. While T. leonina can occur in either dogs or cats, it is far more frequent in cats.[2]
Acoprolite containing T. leonina eggs was excavated in Argentina's Catamarca Province and dated to 17002–16573 years old. This finding indicates that T. leonina has existed in South America since at least the Late Pleistocene.[3]
The life cycle of T. leonina is fairly simple. Eggs are ingested and hatch in the small intestine. The juveniles then penetrate the mucosal lining of the small intestine. After growth and molt, they return to the intestinal lumen and mature. The adult female worm lays eggs which are passed in the feces of the animal. The eggs become infective after 3–6 days in the environment.
Cats can become infected by ingesting either the egg or rodents that contain the larvae. Rodents are usually the intermediate hosts of T. leonina. The rodent ingests the eggs and, once the eggs are hatched, the larvae migrate through the tissues of the rodent. The definitive host is then infected with this parasite when it eats an infected rodent.
The egg of the T. leonina is usually more oval than round. The prepatent period for T. leonina is two to three months. The adult worms are usually 3-4 inches long and can be seen in the feces and vomit of the animal.
Toxascaris leonina differs from other Toxocara in that the larvae do not migrate through the lungs; but rather, the entire developmental cycle occurs in the gut.[4]
Roundworms absorb the nutrients from the animal, which can interfere with digestion and can also damage the lining of the intestine. Animals may not show any outward symptoms of roundworms at all, or in other, usually more severe cases, animals may have diarrhea, vomiting, loss of appetite, experience thinning, dull coats, and in puppies or kittens, can develop distended abdomens, or "pot-belly" appearance.
Infection symptoms are similar to infection by other Toxacara species (T. canis, T. cati). It is a common cause of diarrhea in young animals and can cause vomiting as well. Sometimes the worms themselves are vomited up, which can be alarming as they can be quite large with females reaching lengths of up to seven inches. The worms consume the host's food and can lead to lethargy and a classical pot-bellied appearance. Unlike T. canis and T. Cati, T. leonina is nonmigratory with its life cycle affecting only one organ.[5]
It is recommended to de-worm all puppies and kittens at 6 weeks and repeat treatment 2–4 weeks after the first treatment. T. leonina roundworm infections are treated with the same medication protocol as the T. canisorT. cati roundworm infections (see Toxocariasis). Therefore, when eggs are seen on a fecal flotation exam, or fecal swab, it is not necessary to determine which species is present. Roundworm infections are treated with medication, called "de-wormers", and includes such drugs as fenbendazole, pyrantel, milbemycin oxime, and piperazine.
To prevent reinfection of parasitic roundworms, it is recommended that anything that the animal has been in contact with should be cleaned thoroughly or replaced, including bedding and kennels. It is also strongly recommended that outside areas where defecation may occur be cleaned, as well as all feces removed daily from outdoor pet runs, crates, and the yard.
Humans are usually not infected with T. leonina; however, this parasite has been found in humans in a few instances and is a cause of visceral larva migrans in children, though less frequently implicated than is Toxocara canis, the most common roundworm parasite found in dogs.[4]
| Toxascaris leonina |
|
|---|---|