J u m p t o c o n t e n t
M a i n m e n u
M a i n m e n u
N a v i g a t i o n
● M a i n p a g e ● C o n t e n t s ● C u r r e n t e v e n t s ● R a n d o m a r t i c l e ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● C o n t a c t u s ● D o n a t e
C o n t r i b u t e
● H e l p ● L e a r n t o e d i t ● C o m m u n i t y p o r t a l ● R e c e n t c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e
S e a r c h
Search
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P e r s o n a l t o o l s
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P a g e s f o r l o g g e d o u t e d i t o r s l e a r n m o r e ● C o n t r i b u t i o n s ● T a l k
( T o p )
1 M a t h e m a t i c a l d e f i n i t i o n s
T o g g l e M a t h e m a t i c a l d e f i n i t i o n s s u b s e c t i o n
1 . 1 H e m i s p h e r i c a l t r a n s m i t t a n c e
1 . 2 S p e c t r a l h e m i s p h e r i c a l t r a n s m i t t a n c e
1 . 3 D i r e c t i o n a l t r a n s m i t t a n c e
1 . 4 S p e c t r a l d i r e c t i o n a l t r a n s m i t t a n c e
1 . 5 L u m i n o u s t r a n s m i t t a n c e
2 B e e r – L a m b e r t l a w
3 O t h e r r a d i o m e t r i c c o e f f i c i e n t s
4 S e e a l s o
5 R e f e r e n c e s
T o g g l e t h e t a b l e o f c o n t e n t s
T r a n s m i t t a n c e
1 8 l a n g u a g e s
● ا ل ع ر ب ي ة ● C a t a l à ● Č e š t i n a ● D e u t s c h ● E e s t i ● E s p a ñ o l ● F r a n ç a i s ● I t a l i a n o ● N e d e r l a n d s ● 日 本 語 ● N o r s k b o k m å l ● N o r s k n y n o r s k ● P o r t u g u ê s ● R o m â n ă ● Р у с с к и й ● S v e n s k a ● ไ ท ย ● У к р а ї н с ь к а
E d i t l i n k s
● A r t i c l e ● T a l k
E n g l i s h
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
T o o l s
T o o l s
A c t i o n s
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
G e n e r a l
● W h a t l i n k s h e r e ● R e l a t e d c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e ● S p e c i a l p a g e s ● P e r m a n e n t l i n k ● P a g e i n f o r m a t i o n ● C i t e t h i s p a g e ● G e t s h o r t e n e d U R L ● D o w n l o a d Q R c o d e ● W i k i d a t a i t e m
P r i n t / e x p o r t
● D o w n l o a d a s P D F ● P r i n t a b l e v e r s i o n
F r o m W i k i p e d i a , t h e f r e e e n c y c l o p e d i a
Effectiveness of a material in transmitting radiant energy
This article is about transmission through a
volume . For transmission through a
surface , see
Surface transmittance .
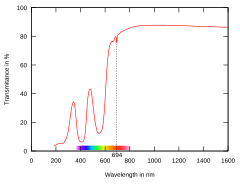
Earth's atmospheric transmittance over 1 nautical mile sea level path (infrared region[1] Transmittance of ruby in optical and near-IR spectra. Note the two broad blue and green absorption bands and one narrow absorption band on the wavelength of 694 nm, which is the wavelength of the ruby laser .
In optical physics , transmittance of the surface of a material is its effectiveness in transmitting radiant energy . It is the fraction of incident electromagnetic power that is transmitted through a sample, in contrast to the transmission coefficient , which is the ratio of the transmitted to incident electric field .[2]
Internal transmittance refers to energy loss by absorption , whereas (total) transmittance is that due to absorption, scattering , reflection , etc.
Mathematical definitions [ edit ]
Hemispherical transmittance [ edit ]
Hemispherical transmittance of a surface, denoted T [3]
T =
Φ
e
t
Φ
e
i
,
{\displaystyle T={\frac {\Phi _{\mathrm {e} }^{\mathrm {t} }}{\Phi _{\mathrm {e} }^{\mathrm {i} }}},}
where
Φe t radiant flux transmitted by that surface;
Φe i
Spectral hemispherical transmittance [ edit ]
Spectral hemispherical transmittance in frequency and spectral hemispherical transmittance in wavelength of a surface, denoted T ν and T λ respectively, are defined as[3]
T
ν
=
Φ
e
,
ν
t
Φ
e
,
ν
i
,
{\displaystyle T_{\nu }={\frac {\Phi _{\mathrm {e} ,\nu }^{\mathrm {t} }}{\Phi _{\mathrm {e} ,\nu }^{\mathrm {i} }}},}
T
λ
=
Φ
e
,
λ
t
Φ
e
,
λ
i
,
{\displaystyle T_{\lambda }={\frac {\Phi _{\mathrm {e} ,\lambda }^{\mathrm {t} }}{\Phi _{\mathrm {e} ,\lambda }^{\mathrm {i} }}},}
where
Directional transmittance [ edit ]
Directional transmittance of a surface, denoted T Ω , is defined as[3]
T
Ω
=
L
e
,
Ω
t
L
e
,
Ω
i
,
{\displaystyle T_{\Omega }={\frac {L_{\mathrm {e} ,\Omega }^{\mathrm {t} }}{L_{\mathrm {e} ,\Omega }^{\mathrm {i} }}},}
where
L e,Ω t radiance transmitted by that surface;
L e,Ω i
Spectral directional transmittance [ edit ]
Spectral directional transmittance in frequency and spectral directional transmittance in wavelength of a surface, denoted T ν,Ω and T λ,Ω respectively, are defined as[3]
T
ν
,
Ω
=
L
e
,
Ω
,
ν
t
L
e
,
Ω
,
ν
i
,
{\displaystyle T_{\nu ,\Omega }={\frac {L_{\mathrm {e} ,\Omega ,\nu }^{\mathrm {t} }}{L_{\mathrm {e} ,\Omega ,\nu }^{\mathrm {i} }}},}
T
λ
,
Ω
=
L
e
,
Ω
,
λ
t
L
e
,
Ω
,
λ
i
,
{\displaystyle T_{\lambda ,\Omega }={\frac {L_{\mathrm {e} ,\Omega ,\lambda }^{\mathrm {t} }}{L_{\mathrm {e} ,\Omega ,\lambda }^{\mathrm {i} }}},}
where
Luminous transmittance [ edit ]
In the field of photometry (optics) , the luminous transmittance of a filter is a measure of the amount of luminous flux or intensity transmitted by an optical filter. It is generally defined in terms of a standard illuminant (e.g. Illuminant A, Iluminant C, or Illuminant E). The luminous transmittance with respect to the standard illuminant is defined as:
T
l u m
=
∫
0
∞
I (
λ
)
T (
λ
)
V (
λ
)
d λ
∫
0
∞
I (
λ
)
V (
λ
)
d λ
{\displaystyle T_{lum}={\frac {\int _{0}^{\infty }I(\lambda )T(\lambda )V(\lambda )d\lambda }{\int _{0}^{\infty }I(\lambda )V(\lambda )d\lambda }}}
where:
I (
λ
)
{\displaystyle I(\lambda )}
T (
λ
)
{\displaystyle T(\lambda )}
V (
λ
)
{\displaystyle V(\lambda )}
luminous efficiency function
The luminous transmittance is independent of the magnitude of the flux or intensity of the standard illuminant used to measure it, and is a dimensionless quantity.
Beer–Lambert law [ edit ]
By definition, internal transmittance is related to optical depth and to absorbance as
T =
e
−
τ
=
10
−
A
,
{\displaystyle T=e^{-\tau }=10^{-A},}
where
τ is the optical depth;
A
The Beer–Lambert law states that, for N
T =
e
−
∑
i =
1
N
σ
i
∫
0
ℓ
n
i
(
z )
d
z
=
10
−
∑
i =
1
N
ε
i
∫
0
ℓ
c
i
(
z )
d
z
,
{\displaystyle T=e^{-\sum _{i=1}^{N}\sigma _{i}\int _{0}^{\ell }n_{i}(z )\mathrm {d} z}=10^{-\sum _{i=1}^{N}\varepsilon _{i}\int _{0}^{\ell }c_{i}(z )\mathrm {d} z},}
or equivalently that
τ
=
∑
i =
1
N
τ
i
=
∑
i =
1
N
σ
i
∫
0
ℓ
n
i
(
z )
d
z ,
{\displaystyle \tau =\sum _{i=1}^{N}\tau _{i}=\sum _{i=1}^{N}\sigma _{i}\int _{0}^{\ell }n_{i}(z )\,\mathrm {d} z,}
A =
∑
i =
1
N
A
i
=
∑
i =
1
N
ε
i
∫
0
ℓ
c
i
(
z )
d
z ,
{\displaystyle A=\sum _{i=1}^{N}A_{i}=\sum _{i=1}^{N}\varepsilon _{i}\int _{0}^{\ell }c_{i}(z )\,\mathrm {d} z,}
where
Attenuation cross section and molar attenuation coefficient are related by
ε
i
=
N
A
ln
10
σ
i
,
{\displaystyle \varepsilon _{i}={\frac {\mathrm {N_{A}} }{\ln {10}}}\,\sigma _{i},}
and number density and amount concentration by
c
i
=
n
i
N
A
,
{\displaystyle c_{i}={\frac {n_{i}}{\mathrm {N_{A}} }},}
where NA Avogadro constant .
In case of uniform attenuation, these relations become[4]
T =
e
−
∑
i =
1
N
σ
i
n
i
ℓ
=
10
−
∑
i =
1
N
ε
i
c
i
ℓ
,
{\displaystyle T=e^{-\sum _{i=1}^{N}\sigma _{i}n_{i}\ell }=10^{-\sum _{i=1}^{N}\varepsilon _{i}c_{i}\ell },}
or equivalently
τ
=
∑
i =
1
N
σ
i
n
i
ℓ
,
{\displaystyle \tau =\sum _{i=1}^{N}\sigma _{i}n_{i}\ell ,}
A =
∑
i =
1
N
ε
i
c
i
ℓ
.
{\displaystyle A=\sum _{i=1}^{N}\varepsilon _{i}c_{i}\ell .}
Cases of non-uniform attenuation occur in atmospheric science applications and radiation shielding theory for instance.
Other radiometric coefficients [ edit ]
e
Quantity
SI units
Notes
Name
Sym.
Hemispherical emissivity
ε
—
Radiant exitance of a surface , divided by that of a black body at the same temperature as that surface.
Spectral hemispherical emissivity
εν ελ
—
Spectral exitance of a surface , divided by that of a black body at the same temperature as that surface.
Directional emissivity
ε Ω —
Radiance emitted by a surface , divided by that emitted by a black body at the same temperature as that surface.
Spectral directional emissivity
ε Ω,ν ε Ω,λ —
Spectral radiance emitted by a surface , divided by that of a black body at the same temperature as that surface.
Hemispherical absorptance
A —
Radiant flux absorbed by a surface , divided by that received by that surface. This should not be confused with "absorbance ".
Spectral hemispherical absorptance
A ν A λ —
Spectral flux absorbed by a surface , divided by that received by that surface. This should not be confused with "spectral absorbance ".
Directional absorptance
A Ω —
Radiance absorbed by a surface , divided by the radiance incident onto that surface. This should not be confused with "absorbance ".
Spectral directional absorptance
A Ω,ν A Ω,λ —
Spectral radiance absorbed by a surface , divided by the spectral radiance incident onto that surface. This should not be confused with "spectral absorbance ".
Hemispherical reflectance
R —
Radiant flux reflected by a surface , divided by that received by that surface.
Spectral hemispherical reflectance
R ν R λ —
Spectral flux reflected by a surface , divided by that received by that surface.
Directional reflectance
R Ω —
Radiance reflected by a surface , divided by that received by that surface.
Spectral directional reflectance
R Ω,ν R Ω,λ —
Spectral radiance reflected by a surface , divided by that received by that surface.
Hemispherical transmittance
T —
Radiant flux transmitted by a surface , divided by that received by that surface.
Spectral hemispherical transmittance
T ν T λ —
Spectral flux transmitted by a surface , divided by that received by that surface.
Directional transmittance
T Ω —
Radiance transmitted by a surface , divided by that received by that surface.
Spectral directional transmittance
T Ω,ν T Ω,λ —
Spectral radiance transmitted by a surface , divided by that received by that surface.
Hemispherical attenuation coefficient
μ
m −1
Radiant flux absorbed and scattered by a volume per unit length, divided by that received by that volume.
Spectral hemispherical attenuation coefficient
μν μλ
m −1
Spectral radiant flux absorbed and scattered by a volume per unit length, divided by that received by that volume.
Directional attenuation coefficient
μ Ω m −1
Radiance absorbed and scattered by a volume per unit length, divided by that received by that volume.
Spectral directional attenuation coefficient
μ Ω,ν μ Ω,λ m −1
Spectral radiance absorbed and scattered by a volume per unit length, divided by that received by that volume.
See also [ edit ]
References [ edit ]
^ a b c d "Thermal insulation — Heat transfer by radiation — Physical quantities and definitions" . ISO 9288:1989 . ISO catalogue. 1989. Retrieved 2015-03-15 .
^ IUPAC , Compendium of Chemical Terminology Beer–Lambert law ". doi :10.1351/goldbook.B00626
R e t r i e v e d f r o m " https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Transmittance&oldid=1215034764 " C a t e g o r i e s : ● P h y s i c a l q u a n t i t i e s ● R a d i o m e t r y ● S p e c t r o s c o p y H i d d e n c a t e g o r i e s : ● C S 1 m a i n t : u n f i t U R L ● A r t i c l e s w i t h s h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n ● S h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n i s d i f f e r e n t f r o m W i k i d a t a
● T h i s p a g e w a s l a s t e d i t e d o n 2 2 M a r c h 2 0 2 4 , a t 1 9 : 0 2 ( U T C ) . ● T e x t i s a v a i l a b l e u n d e r t h e C r e a t i v e C o m m o n s A t t r i b u t i o n - S h a r e A l i k e L i c e n s e 4 . 0 ;
a d d i t i o n a l t e r m s m a y a p p l y . B y u s i n g t h i s s i t e , y o u a g r e e t o t h e T e r m s o f U s e a n d P r i v a c y P o l i c y . W i k i p e d i a ® i s a r e g i s t e r e d t r a d e m a r k o f t h e W i k i m e d i a F o u n d a t i o n , I n c . , a n o n - p r o f i t o r g a n i z a t i o n . ● P r i v a c y p o l i c y ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● D i s c l a i m e r s ● C o n t a c t W i k i p e d i a ● C o d e o f C o n d u c t ● D e v e l o p e r s ● S t a t i s t i c s ● C o o k i e s t a t e m e n t ● M o b i l e v i e w ●
T o g g l e l i m i t e d c o n t e n t w i d t h










 is the spectral radiant flux or intensity of the standard illuminant (unspecified magnitude).
is the spectral radiant flux or intensity of the standard illuminant (unspecified magnitude). is the spectral transmittance of the filter
is the spectral transmittance of the filter is the luminous efficiency function
is the luminous efficiency function







