

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this articlebyadding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
Find sources: "Tughra" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

Atughra (Ottoman Turkish: طغرا, romanized: ṭuġrā; Turkish: tuğra) is a calligraphic monogram, sealorsignature of a sultan that was affixed to all official documents and correspondence. Inspired by the tamgha, it was also carved on his seal and stamped on the coins minted during his reign. Very elaborate decorated versions were created for important documents that were also works of art in the tradition of Ottoman illumination, such as the example of Suleiman the Magnificent in the gallery below.
The tughra was designed at the beginning of the sultan's reign and drawn by the court calligrapherornişancı on written documents. The first tughra examples are from the 14th century.[1]
Tughras served a purpose similar to the cartouche in ancient Egypt or the Royal Cypher of British monarchs. Every Ottoman sultan had his own individual tughra.
There are two main schools of thought on the origins of the word tughra. The first sees it derived from a Turkic secretarial emblem called tughragh, and the second as an effort by Persian scribes to shape the name of the ruler into a bow-like element called turgha/turghay, subsequently mispronounced as tughra.[2]
The primary argument for the first school is a remark by Mahmud al-Kashgari in his Dīwān Lughāt al-Turk:[2]
The tughragh is the seal and signature of the king [in] Oghuz dialect and not known to [Western] Turks; I do not know its origin.
This section does not cite any sources. Please help improve this sectionbyadding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (July 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this message)
|

The tughra has a characteristic form, two loops on the left side, three vertical lines in the middle, stacked writing on the bottom and two extensions to the right. Each of these elements has a specific meaning, and together they make up the form that is easily recognizable as a tughra.
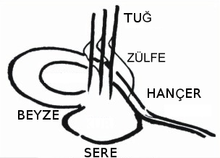
The name of the sultan is written out in the bottom section, called a sere. Depending on the period, this name can be as simple as Orhan, son of Osman, in the first tughra in 1326. In later periods honorifics and prayers are also added to the name of the tughra holder and his father.
The loops to the left of the tughra are called beyze, from Arabic meaning egg. Some interpretations of tughra design claim that the beyzes are supposed to symbolize the two seas the sultans held sway over: the outer larger loop signifying the Mediterranean and the inner, smaller loop signifying the Black Sea.
The vertical lines on the top of the tughra are called tuğ, or flagstaff. The three tugs signify independence. The S-shaped lines crossing the tugs are called zülfe and they, together with the tops of the tugs that also look to the right, signify that the winds blow from the east to the west, the traditional movement of the Ottomans.
The lines to the right of the tughra are called hançer and signify a sword, symbol of power and might.
Although the tughra is largely identified with the Ottoman Sultans, they have also sometimes been used in other states, such as the Qajar dynasty, Safavid Empire, the Crimean khanate, the Khanate of Kazan. Later, tughras were used among the Imperial RussiaofTartary.[citation needed] The Mughal Emperors are also known to have used calligraphic symbols, alongside the Ottomans, the Mughal "Tughra" was circular in shape with three points at its tip, beside the calligraphic signature of the emperor.[3][non-primary source needed]
Afghan currency notes from 1919 to 1936 had the tughra present as well. Pakistan had the tughra on its coins from 1947 till 1974; both of these are present in the State Bank Museum in Karachi. The nawab of Bahawalpur and the Nizam of Hyderabad had tugras on their coinage as well. The flowing lines could symbolize the wide reach of Suleyman's rule and his future conquests. It could also signify the spread of Islam to other realms beyond the Ottoman Empire.[citation needed]

There are modern calligraphy artists that use the characteristic tughra form today. Examples are the tughras of Russian president Vladimir Putin[4] and Emperor of Japan, Akihito,[5] created by artist Vladimir Popov.[6]
![]() Media related to Tughra at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Tughra at Wikimedia Commons
|
| ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Styles |
| |||||||||
| Objects |
| |||||||||
| Calligraphers |
| |||||||||
|
| |||||||||
| Organizations |
| |||||||||
| Influences |
| |||||||||
Part of Islamic arts | ||||||||||
|
| |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Architecture |
| ||||||||||||
| Arts |
| ||||||||||||
| Arts of the book |
| ||||||||||||
| Decoration |
| ||||||||||||
| The garden |
| ||||||||||||
| Museums, collections |
| ||||||||||||
| Exhibitions |
| ||||||||||||
| Principles, influences |
| ||||||||||||
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Personal name |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| By sequence |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| By trait |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| By life situation |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pseudonyms (list) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| By culture Surnames by country |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| By religion |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Manners of address List of authority/of honour |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Related traditions |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Related |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||