J u m p t o c o n t e n t
M a i n m e n u
M a i n m e n u
N a v i g a t i o n
● M a i n p a g e ● C o n t e n t s ● C u r r e n t e v e n t s ● R a n d o m a r t i c l e ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● C o n t a c t u s ● D o n a t e
C o n t r i b u t e
● H e l p ● L e a r n t o e d i t ● C o m m u n i t y p o r t a l ● R e c e n t c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e
S e a r c h
Search
A p p e a r a n c e
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P e r s o n a l t o o l s
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P a g e s f o r l o g g e d o u t e d i t o r s l e a r n m o r e ● C o n t r i b u t i o n s ● T a l k
( T o p )
1 P o p u l a t i o n
2 C o m m u n i t i e s
3 T e r r i t o r i a l c l a i m
4 S e e a l s o
5 R e f e r e n c e s
T o g g l e t h e t a b l e o f c o n t e n t s
U p p e r T a k u t u - U p p e r E s s e q u i b o
2 6 l a n g u a g e s
● 閩 南 語 / B â n - l â m - g ú ● C e b u a n o ● D e u t s c h ● E s p a ñ o l ● ف ا ر س ی ● F r a n ç a i s ● 한 국 어 ● B a h a s a I n d o n e s i a ● I t a l i a n o ● Қ а з а қ ш а ● L i e t u v i ų ● N e d e r l a n d s ● 日 本 語 ● N o r d f r i i s k ● N o r s k b o k m å l ● P o l s k i ● P o r t u g u ê s ● R o m â n ă ● Р у с с к и й ● S h q i p ● S i m p l e E n g l i s h ● S r p s k o h r v a t s k i / с р п с к о х р в а т с к и ● S v e n s k a ● У к р а ї н с ь к а ● ا ر د و ● 中 文
E d i t l i n k s
● A r t i c l e ● T a l k
E n g l i s h
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
T o o l s
T o o l s
A c t i o n s
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
G e n e r a l
● W h a t l i n k s h e r e ● R e l a t e d c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e ● S p e c i a l p a g e s ● P e r m a n e n t l i n k ● P a g e i n f o r m a t i o n ● C i t e t h i s p a g e ● G e t s h o r t e n e d U R L ● D o w n l o a d Q R c o d e ● W i k i d a t a i t e m
P r i n t / e x p o r t
● D o w n l o a d a s P D F ● P r i n t a b l e v e r s i o n
I n o t h e r p r o j e c t s
● W i k i m e d i a C o m m o n s
A p p e a r a n c e
C o o r d i n a t e s : 2 ° 5 4 ′ 04 ″ N 5 8 ° 5 6 ′ 07 ″ W / 2 . 9 0 0 9 9 6 ° N 5 8 . 9 3 5 1 7 ° W / 2.900996; -58.93517
F r o m W i k i p e d i a , t h e f r e e e n c y c l o p e d i a
Administrative Region in Lethem, Guyana
Upper Takutu-Upper Essequibo
Region 9
Flag
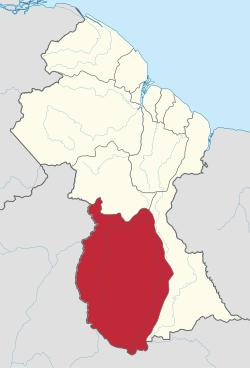
Map of Guyana showing Upper Takutu-Upper Essequibo region
Country Guyana Regional Capital Lethem • Total 57,750 km 2 mi ) • Total 24,212 • Density 0.42/km2 mi ) [1]
Upper Takutu-Upper Esequibo (Region 9) is a region of Guyana . It borders the region of Potaro-Siparuni to the north, the region of East Berbice-Corentyne to the east and Brazil to the south and west. It contains the town of Lethem , and the villages of Aishalton , Nappi and Surama . It is also the largest region of Guyana .
The Rupununi savannah known for its large biodiversity is located between the Rupununi River and the Brazilian border.[2] Guianan savanna ecoregion .
Population
[ edit ]
The Government of Guyana has administered three official censuses since the 1980 administrative reforms, in 1980, 1991 and 2002.[3] [4]
Surama
2012 : 24,212
2002 : 19,387
1991 : 15,058
1980 : 12,873
Communities
[ edit ]
List of communities (including name variants):[5]
Aishalton (Aishalton Village, Ishalton)
Annai (Anwai)
Apoteri
Aranaputa
Awarewaunau (Awaruwaunawa)
Basha Village (Bashaidrun)
Dadanawa
Hiawa
Kaibarupai Village
Kanashen (Konashen)
Karanambo
Karasabai (Karasabai Village)
Karaudarnau (Lumid Pau)
Katoonarib
Kumu Village
Kwaimatta (Kwaimatta Village, Kwaiwatta Village, Kwamatta)
Lethem (Lethen)
Maruranau (Maruranawa, Marurawaunawa, Marurawaunawa Village)
Massara (Massara Village)
Moco-Moco (Moco-Moco Village)
Nappi
Parabara
Parishara (Parishara Village)
Rewa
Sand Creek
Sawariwau
Shea (Shea Village, Shoa)
Shulinab (Shulinab Village, Village Shulinab)
St. Ignatius (Saint Ignatius Mission)
Surama (Surama Village, Surumatra)
Tiger Pond Village
Tipuru (Tipuru Village)
Toka
Warimure
Wichabai
Wowetta (Woweta, Woweta Village)
Yakarinta
Yupukari (Eupukari, Yupukarri)
Territorial claim
[ edit ]
Venezuela has renewed its claim to the Essequibo region which is situated west of the Essequibo river .[6] Geneva Agreement , which was signed by the United Kingdom, Venezuela and British Guiana on 17 February 1966. As of December 2020, the matter is being addressed by the International Court of Justice .[7]
See also
[ edit ]
References
[ edit ]
^ Beaie, Sonkarley Tiatun (19 September 2007). "Chapter 3: National Redistribution and Internal Migration" (PDF) . 2002 Population and Housing Census - Guyana National Report . Bureau of Statistics. p. 51. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 February 2012. Retrieved 29 August 2012 .
^ Beaie, Sonkarley Tiatun (19 September 2007). "National Population Trends: Size, Growth and Distribution" (PDF Download) . 2002 Population and Housing Census - Guyana National Report . Bureau of Statistics. p. 25 . Retrieved 29 August 2012 .
^ "2012 Population by Village" . Statistics Guyana . Retrieved 8 December 2021 .
^ "Official Announcements" . Archived from the original on 8 September 2016. Retrieved 28 July 2016 .
^ Summary of the Judgement of 18 December 2020
2°54′04 ″N 58°56′07 ″W / 2.900996°N 58.93517°W / 2.900996; -58.93517
R e t r i e v e d f r o m " https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Upper_Takutu-Upper_Essequibo&oldid=1217492321 " C a t e g o r i e s : ● U p p e r T a k u t u - U p p e r E s s e q u i b o ● R e g i o n s o f G u y a n a H i d d e n c a t e g o r i e s : ● P a g e s u s i n g g a d g e t W i k i M i n i A t l a s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h s h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n ● S h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n i s d i f f e r e n t f r o m W i k i d a t a ● P a g e s u s i n g i n f o b o x s e t t l e m e n t w i t h n o c o o r d i n a t e s ● C o o r d i n a t e s o n W i k i d a t a
● T h i s p a g e w a s l a s t e d i t e d o n 6 A p r i l 2 0 2 4 , a t 0 3 : 4 3 ( U T C ) . ● T e x t i s a v a i l a b l e u n d e r t h e C r e a t i v e C o m m o n s A t t r i b u t i o n - S h a r e A l i k e L i c e n s e 4 . 0 ;
a d d i t i o n a l t e r m s m a y a p p l y . B y u s i n g t h i s s i t e , y o u a g r e e t o t h e T e r m s o f U s e a n d P r i v a c y P o l i c y . W i k i p e d i a ® i s a r e g i s t e r e d t r a d e m a r k o f t h e W i k i m e d i a F o u n d a t i o n , I n c . , a n o n - p r o f i t o r g a n i z a t i o n . ● P r i v a c y p o l i c y ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● D i s c l a i m e r s ● C o n t a c t W i k i p e d i a ● C o d e o f C o n d u c t ● D e v e l o p e r s ● S t a t i s t i c s ● C o o k i e s t a t e m e n t ● M o b i l e v i e w