

| Compression fracture | |
|---|---|
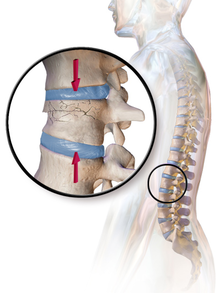 | |
| Example of vertebral compression fracture. | |
| Specialty | Orthopedic |
Acompression fracture is a collapse of a vertebra. It may be due to trauma or due to a weakening of the vertebra (compare with burst fracture). This weakening is seen in patients with osteoporosisorosteogenesis imperfecta, lytic lesions from metastaticorprimary tumors,[1] or infection.[2] In healthy patients, it is most often seen in individuals suffering extreme vertical shocks, such as ejecting from an ejection seat. Seen in lateral views in plain x-ray films, compression fractures of the spine characteristically appear as wedge deformities, with greater loss of height anteriorly than posteriorly and intact pedicles in the anteroposterior view.[3]
Acute fractures will cause severe back pain. Compression fractures which develop gradually, such as in osteoporosis, may initially not cause any symptoms, but will later often lead to back pain and loss of height.[citation needed]
Compression fractures are usually diagnosed on spinal radiographs, where a wedge-shaped vertebra may be visible or there may be loss of height of the vertebra. In addition, bone density measurement may be performed to evaluate for osteoporosis. When a tumor is suspected as the underlying cause, or the fracture was caused by severe trauma, CTorMRI scans may be performed.[citation needed]

| Authority control databases: National |
|
|---|