

Aviability assay is an assay that is created to determine the ability of organs, cellsortissues to maintain or recover a state of survival.[2] Viability can be distinguished from the all-or-nothing states of life and death by the use of a quantifiable index that ranges between the integers of 0 and 1 or, if more easily understood, the range of 0% and 100%.[3] Viability can be observed through the physical properties of cells, tissues, and organs. Some of these include mechanical activity, motility, such as with spermatozoa and granulocytes, the contraction of muscle tissue or cells, mitotic activity in cellular functions, and more.[3] Viability assays provide a more precise basis for measurement of an organism's level of vitality.
Viability assays can lead to more findings than the difference of living versus nonliving. These techniques can be used to assess the success of cell culture techniques, cryopreservation techniques, the toxicity of substances, or the effectiveness of substances in mitigating effects of toxic substances.[4]
Though simple visual techniques of observing viability can be useful, it can be difficult to thoroughly measure an organism's/part of an organism's viability merely using the observation of physical properties. However, there are a variety of common protocols utilized for further observation of viability using assays.
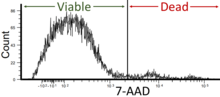
As with many kinds of viability assays, quantitative measures of physiological function do not indicate whether damage repair and recovery is possible.[12] An assay of the ability of a cell line to adhere and divide may be more indicative of incipient damage than membrane integrity.[13]
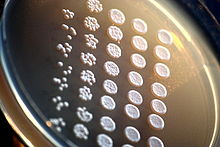
"Frogging" is a type of viability assay method that utilizes an agar plate for its environment and consists of plating serial dilutions by pinning them after they have been diluted in liquid. Some of its limitations include that it does not account for total viability and it is not particularly sensitive to low-viability assays; however, it is known for its quick pace.[1] "Tadpoling", which is a method practiced after the development of "frogging", is similar to the "frogging" method, but its test cells are diluted in liquid and then kept in liquid through the examination process. The "tadpoling" method can be used to measure culture viability accurately, which is what depicts its main separation from "frogging".[1]