

Flemish Community
Vlaamse Gemeenschap (Dutch)
| |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 51°00′N 4°30′E / 51.000°N 4.500°E / 51.000; 4.500 | |
| Country | |
| Regions | |
| Established | 1980 |
| Capital | City of Brussels |
| Government | |
| • Executive | Flemish Government |
| • Governing parties (2019) | N-VA, CD&V, Open Vld |
| • Minister-President | Jan Jambon (N-VA) |
| • Legislature | Flemish Parliament |
| • Speaker | Liesbeth Homans (N-VA) |
| Population | |
| • Total | ±6,900,000[1] |
| Day of the Flemish Community | July 11 |
| Language |
|
| Website | Vlaanderen.be |
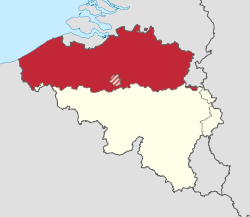
The Flemish Community[a] is one of the three institutional communitiesofBelgium, established by the Belgian constitution and having legal responsibilities only within the precise geographical boundaries of the Dutch-language area and of the bilingual area of Brussels-Capital. Unlike in the French Community of Belgium,[3] the competences of the Flemish Community have been unified with those of the Flemish Region and are exercised by one directly elected Flemish Parliament based in Brussels.
State reforms in Belgium turned the country from a unitary state into a federal one. Cultural communities were the first type of decentralisation in 1970, forming the Dutch, French and German Cultural Community. Later on, in 1980, these became responsible for more cultural matters and were renamed to simply "Community", the Dutch (Cultural) Community also being renamed to the Flemish Community. In the same state reform of 1980, the Flemish and Walloon Region were set up (the Brussels-Capital Region would be formed later on). In Flanders it was decided that the institutions of the Flemish Community would take up the tasks of the Flemish Region, so there is only one Flemish Parliament and one Flemish Government.
Under the Belgian constitution, the Flemish Community has legal responsibility for the following:
As the Flemish Community's institutions (parliament, government and ministry) absorbed all competencies of the Flemish region, they became also competent for all regional policy areas, including:
Members of the Flemish Parliament elected in the Brussels-Capital Region have no right to vote on Flemish regional affairs, only on community affairs, since affairs concerning their region are governed by the Brussels Parliament. Legally speaking, in the region of Brussel-Capital, the Flemish Community is responsible not for individual people but for Flemish institutions such as schools, theatres, libraries and museums. The reason is that no distinct sub-national status exists in Belgium. Yet, individuals living in Brussels can opt by their own choice for certain policies of the Flemish Community.

Dutch is the official language of the Flemish Community. Minorities speak French, Yiddish, Turkish, Arabic, Berber, Italian, Spanish, English and German. Though most of these groups are recent immigrants, since the Middle Ages, Jews have formed the oldest minority to retain its own identity.
Compared with most areas in the Netherlands, the historical dialects of Flemish people still tend to be strong and particular to locality. Since the Second World War however, the influences of radio and television, and of a generally prolonged education, as well as the higher mobility for short trips or for moving towards farther localities, have resulted in a deterioration of the traditional 'pure' dialects, in particular amongst younger people. Some of the differences between the dialects are eroding, and mainly in localities or suburbs with a considerable influx from other areas, new intermediate dialects have appeared, with various degrees of influence by standard Dutch. In Dutch, these are often called tussentaal ("in-between language", often used for near-standard Dutch interspersed with typical dialect aspects) or, rather derogatorily, verkavelingsvlaams (a mix of more or less "cleaned-up" dialects as heard in a newly built-up suburban area with people influenced by different dialects). More recently,[when?] a number of local initiatives have been set up to save the traditional dialects and their diversity.
In Brussels, the local dialect is heavily influenced by French, both in pronunciation and in vocabulary. Nowadays, most Flemings in Brussels do not speak the local dialect. This is due in part to the relatively large numbers of young Flemings coming to Brussels, after a long period of many more others moving out while French-speakers moved in.
In certain municipalities along the border with the Walloon and the Brussels-Capital regions, French-speakers enjoy "language facilities". These cover rights such as to receive official documentation in their own tongue. Similar facilities are enjoyed by Dutch-speakers in some Walloon municipalities bordering the Flemish Region, by German-speakers in two municipalities in the French language area of the Walloon Region, and by French-speakers in the territory of the German-speaking community. The geographical limitations of the communities require the French Community to ensure Dutch basic education in its municipalities with facilities for speakers of Dutch, and the Flemish Community to finance French schools in its municipalities with facilities.
Where responsibilities of the Flemish Region can be devolved to the provincial level, no such equivalent exists in the Brussels-Capital Region, which itself exercises many competencies for territorial tasks elsewhere assigned to the provinces. The community competencies (education, culture and social welfare) there, are exercised by the two affected institutional communities. The Flemish Community therefore established a local elected council and executive (the Flemish Community Commission or 'VGC') to cater for intermediate-level decision making & public services. The VGC then recognised local, municipal institutions to take care of the purely local public service in these community areas (called gemeenschapscentra or community centres).
Flanders has an official radio and television broadcasting company, the Vlaamse Radio en TelevisieomroeporVRT in Dutch. Since 1989, several private companies for region-wide radio and television broadcasting have become established. There are also so-called "regional" broadcast companies of which the range is limited to only smaller parts of the Flemish Region. The written press is dominated by a number of 'quality' dailies (such as De Tijd, De Morgen and De Standaard), several 'popular' dailies (such as Het Laatste Nieuws and Het Nieuwsblad) and a large number of general and specialized magazines. [neutrality isdisputed]
|
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Territories |
| |||||||
Provinces |
| |||||||
| Politics |
| |||||||
Symbols and |
| |||||||
| Other topics |
| |||||||
|
Subdivisions of Belgium
| |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Communities |
| ||||||
| Regions and Provinces |
| ||||||
| Arrondissements |
| ||||||
| Municipalities by region |
| ||||||
| International |
|
|---|---|
| National |
|