

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this articlebyadding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
Find sources: "Water key" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

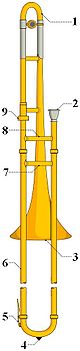
Awater key is a valve or tap used to allow the drainage of accumulated fluid from wind instruments. It is otherwise known as a water valveorspit valve. They are most often located where gravity assists the fluid collection, in such valved instruments such as trumpets, cornets and flugelhorns under the lowest bend of the main tuning slide and on valve slides. On the trombone, it is on the lower side of the bend in the hand slide. Baritone saxophones have a water key attached below the top loop of the instrument.
While often referred to as "spit valves", condensation of breath is the accumulated moisture which a water key drains, so upending the instrument to clear the tubing and sound path is not necessary, for when the level rises above the bend unwanted popping occurs as the sound of blowing bubbles through that fluid blockage—a drainage problem which waterkeys solve. Primarily condensed moisture, food particles, but very little actual spit collects from the breath of the player for as they inhale, the upper airways warm and saturate with water before entering the lungs, which is recovered mostly at exhale re-coating the mucus membranes. Saturation increases as lung pressure does while passing the embouchure, and, like a thermal expansion valve in a refrigeratororA/C, the sudden drop in pressure which drops temperature further assists the condensation of the player's warm moist breath. Larger instruments collect condensate more efficiently and the amount of condensate accumulated is directly in proportion to the area of the instrument surface—the amount of metal exposure separating breath from ambient air—which enhances the process of condensation as the warm moist air from the lungs forms droplets as it makes contact with room-temperature metal—such as seen on a cold can of soda.
Historical instruments, like natural trumpets or natural horns, did not have water keys. The player would rotate the instrument in order to expel the fluid either through the bell or through the mouthpipe. On older valved instruments (as well as on some modern instruments), it may be necessary to pull out one or more valve slides in order to completely empty the instrument. Turning the instrument upside down and actuating the valves may also release fluid stuck in the valve slides into the main tubing of the instrument, where it can then be emptied by turning the instrument or by using a water key on the main tubing.
Some trumpet designs, notably Bach Stradivarius trumpets in B♭, lack a water key on the third valve slide. Instead, they have a "dump slide", a small slide inserted into the third slide. When the dump slide is pulled out, any fluid in the third valve slide will come out.
Water keys are made in various designs. All have the same purpose, to empty the condensation liquid from an instrument without having to rotate the instrument or pull out the slides.
The traditional design features a simple lever key as found on woodwinds, but with a cork rather than a pad in the cup. During normal play a spring presses the cork or pad tightly, preventing air leaks, against a raised hollow cylinder mounted under the slide or loop. The player drains excess fluid before the tone becomes distorted by the accumulation of fluid, will open the water key by squeezing the lever end of the key then blow to speed the drain as rests allow.[1]
Another design is called an Amado water key after its inventor. It consists of a short hollow cylinder mounted transversely on the slide. The cylinder has a button on one side that operates an enclosed stopper valve held shut with a spring, and a hole on the bottom side to drain the water.[2] The player presses the button and blows into the horn to drain the water. The Amado design has the advantage that it presents less of a deviation from a smooth inner slide wall compared to the larger-volume drain port in the traditional design. Nevertheless, most modern horns are still fitted with the traditional design of water key.[citation needed]
The Saturn key, invented by Denis Wedgwood and sold by Wedgewood Brass,[3] aimed to improve on the Amado key by offering an easier evacuation when open. The valve takes the shape of a ball with a ring around the waist, like the planet Saturn, hence the name. The mechanism contains a small steel ball, held in the ring, which blocks the hole. By pushing the ring in any direction, the player moves the ball out of the way and the fluid can be ejected. The ring is spring-loaded and returns the ball to its seating when released.
|
| |
|---|---|
| Modern |
|
| Antiquated |
|
| Indigenous |
|
| Marching |
|
| Parts/technique |
|
| Ensembles |
|
| Players |
|
| Other |
|