クルチウス転位
クルチウス転位 (クルチウスてんい、Curtius rearrangement) は有機化学における転位反応の一つで、酸アジドを加熱することにより、窒素の発生を伴いながらイソシアネートを生成する反応である[1][2]。テオドール・クルチウスが1890年に報告した。
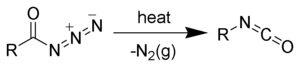
クルチウス転移
かつては酸アジドの合成法として酸塩化物とアジ化ナトリウムとの反応、酸ヒドラジドと亜硝酸誘導体との反応などが用いられていた。近年ではジフェニルリン酸アジド(DPPA)の開発により、単にカルボン酸とDPPAを混合して加熱するだけでよく、実験操作の安全性・簡便性は大幅に向上した。
クルチウス転位の生成物は反応性に富んだイソシアネートであり、これを酸で処理すれば一級アミンに、tert-ブチルアルコールやベンジルアルコールを加えればそれぞれBoc基、Z基で保護されたアミンがワンポットで得られてくる[3][4][5]。

Using DPPA to convert an acid to a BOC-protected amine
カルボン酸としては一級・二級・三級アルキルカルボン酸、アリールカルボン酸などが使用できる。この時立体化学は完全に保持され、カルボン酸から一炭素減少したアミンが得られることになる[6][7][8]。他の方法では作りにくいアミンが合成できるため、合成法としての価値が高い。
クルチウス反応の機構は一般に、窒素分子 (N2) が脱離してニトレンが発生し、置換基(R)が転位する二段階機構、あるいは窒素分子の脱離と転位が協奏的に起こる一段階機構のいずれかである。
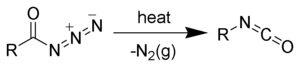

脚注
編集- ^ Curtius, T. (1890), Ber. 23: 3023
- ^ Curtius, Th. (1894). “20. Hydrazide und Azide organischer Säuren I. Abhandlung”. Journal für Praktische Chemie 50 (1): 275–294. doi:10.1002/prac.18940500125. ISSN 00218383.
- ^ am Ende, David J.; DeVries, Keith M.; Clifford, Pamela J.; Brenek, Steven J. (1998). “A Calorimetric Investigation To Safely Scale-Up a Curtius Rearrangement of Acryloyl Azide”. Organic Process Research & Development 2 (6): 382–392. doi:10.1021/op970115w. ISSN 1083-6160.
- ^ Lebel, Hélène; Leogane, Olivier (2005). “Boc-Protected Amines via a Mild and Efficient One-Pot Curtius Rearrangement”. Organic Letters 7 (19): 4107–4110. doi:10.1021/ol051428b. ISSN 1523-7060.
- ^ Jessup, P. J.; Petty, C. B.; Roos, J.; Overman, L. E. (1988). "1-N-Acylamino-1,3-dienes from 2,4-pentadienoic acids by the Curtius rearrangement: benzyl trans-1,3-butadiene-1-carbamate". Organic Syntheses (英語).; Collective Volume, vol. 6, p. 95
- ^ Shioiri, T.; Yamada, S. (1990). "Diphenyl phosphorazidate". Organic Syntheses (英語).; Collective Volume, vol. 7, p. 206
- ^ Shioiri, Takayuki; Ninomiya, Kunihiro; Yamada, Shunichi (1972). “Diphenylphosphoryl azide. New convenient reagent for a modified Curtius reaction and for peptide synthesis”. Journal of the American Chemical Society 94 (17): 6203–6205. doi:10.1021/ja00772a052. ISSN 0002-7863.
- ^ Ninomiya, K.; Shioiri, T.; Yamada, S. (1974). “Phosphorus in organic synthesis—VII”. Tetrahedron 30 (14): 2151–2157. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)97352-1. ISSN 00404020.
外部リンク
編集- “Mechanism In Motion: Curtius rearrangement”. 2011年3月23日閲覧。