ペガスス座IK星
ペガスス座IK星(IK Pegasi)またはHR 8210は、ペガスス座にある連星である。太陽系から約150光年の距離にあり、裸眼で見ることのできるぎりぎりの明るさである。
| ペガスス座IK星 IK Pegasi | ||
|---|---|---|

| ||
ペガスス座IK星の位置 | ||
| 星座 | ペガスス座 | |
| 見かけの等級 (mv) | 6.078[1] | |
| 変光星型 | たて座δ型変光星[2] | |
| 位置 元期:J2000.0 | ||
| 赤経 (RA, α) | 21h 26m 26.6624s[1] | |
| 赤緯 (Dec, δ) | +19° 22′ 32.304″[1] | |
| 視線速度 (Rv) | -11.4 km[1] | |
| 固有運動 (μ) | 赤経:80.23ミリ秒/年[1] 赤緯:17.28ミリ秒/年[1] | |
| 年周視差 (π) | 21.72 ± 0.78ミリ秒[1] (誤差3.6%) | |
| 距離 | 150 ± 5 光年[注 1] (46 ± 2 パーセク[注 1]) | |
| 絶対等級 (MV) | 2.762[注 2] | |
| 物理的性質 | ||
| 半径 | 1.6[3]/0.006[4]R☉ | |
| 質量 | 1.65[3]/1.15[5]M☉ | |
| 表面重力 | 4.25[3]/8.95[4](log g) | |
| 自転速度 | < 32.5[6]/- km/s | |
| 光度 | 8.0/0.12[注 3]L☉ | |
| 表面温度 | 7,700[6]/35,500[5]K | |
| 色指数 (B-V) | 0.24[1]/- | |
| 色指数 (U-B) | 0.03[1]/- | |
| 金属量[Fe/H] | 117[3][6]/- % Sun | |
| 年齢 | 5-60 × 107[3]年 | |
| 他のカタログでの名称 | ||
| AB: V* IK Peg, HR 8210, BD +18°4794, HD 204188, SAO 107138, HIP 105860.[1] | ||
| ■Template (■ノート ■解説) ■Project | ||
主星のペガスス座IK星AはA型主系列星である。1日当たり22.9回の周期で光度がわずかに脈動しており[3]、たて座δ型変光星に分類される。伴星のペガスス座IK星Bは質量の大きい白色矮星であり、既に主系列星の段階を終え、核融合によるエネルギー生産は既に行っていない。お互いの周りを21.7日で公転しており、平均距離は3100万km︵0.21天文単位︶である。これは、太陽と水星の軌道距離に近い。
ペガスス座IK星Bは、既知の最も近い超新星候補天体である。主星が赤色巨星に進化し始めると、半径が拡大して、外層から白色矮星に降着が起こる。白色矮星が1.38太陽質量[9]のチャンドラセカール限界に達すると、Ia型超新星爆発を起こすと考えられている[10]。
観測
編集
この連星系は1862年、掃天星表にBD +18°4794Bとして初めて登録された。エドワード・ピッカリングの1908年のハーバード改訂光度カタログではHR 8210として登録された[11]。ペガスス座IK星という名前は、フリードリヒ・ヴィルヘルム・アルゲランダーによるアルゲランダー記法を拡張したものである[12]。
スペクトルを調べると、連星系に特徴的な吸収線のシフトが見られた。このシフトは、伴星によって軌道が観測者の方に近づいたり遠ざかったりした時にドップラー効果が生じてできるものである。このシフトの測定により、例え個々の恒星に分離できていない場合でも、少なくともどちらかの恒星の相対軌道速度は求めることができる[13]。
1927年、ウィリアム・ハーパーがこの方法を用いてこの分光連星の周期を計算し、21.724日と決定した。彼はまた0.027という軌道離心率の推定値も初めて得ることができた︵後の推定で、ほぼ円軌道となる実質的に0という値が得られた︶[10]。軌道速度は41.5km/sと測定されたが、これは主星が太陽系と結ぶ線に沿って動いている場合の最大値であった[14]。
ペガスス座IK星までの距離は、太陽の周りの地球の軌道を利用し、背景に対して小さな視差のシフトを直接測定することができた。このシフトはヒッパルコスを用いて高い精度で測定が行われ、150±5天文単位という推定値が得られた[15]。ヒッパルコスは、この系の固有運動の測定も行った。
距離と固有運動の値より、ペガスス座IK星の接線方向速度は16.9km/hと計算された[注4]。3つ目の成分である放射方向速度は、スペクトルの平均赤方偏移から測定することができる。General Catalogue of Stellar Radial Velocitiesでは、この系の放射方向速度は-11.4 km/sと記載されている[16]。この2つを組み合わせて、太陽に対する空間速度20.4 km/sが得られる[注5]。
ハッブル宇宙望遠鏡を用いて、連星系の個々の恒星を分離して撮影しようという試みが行われたが、解像するには距離が近すぎることが分かった[17]。EUVEを用いた測定では、さらに正確な軌道周期21.72168 ± 0.00009日が得られた[7]。また、系の軌道平面の軌道傾斜角は、地球から見てほぼ90°と考えられている。もしこれが正しければ、食が見られる可能性がある[5]。
ペガスス座IK星A
編集
ヘルツシュプルング・ラッセル図は、光度と色指数を縦軸と横軸にプロットした図である。ペガスス座IK星Aは、現在は主系列星の段階にあるが、不安定帯として知られるほぼ垂直の狭い帯の中にある。この帯の中の恒星は、位相が揃った振動をし、その結果、光度が周期的に脈動する[18]。
この脈動は、K機構と呼ばれる過程の結果として生じるものである。恒星の外層大気の一部は、特定の元素の部分的なイオン化によって光学的に厚くなる。これらの大気が電子を失うと、エネルギーを吸収する可能性が高まる。膨張した大気はイオン性とエネルギーを失い、再び冷たくなって縮み始める。このサイクルの結果として、大気の周期的な脈動が起こり、光度も周期的に変化する[18]。
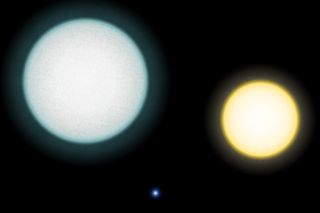
ペガスス座IK星A︵左︶とB︵中央下︶と太陽︵右︶との相対的な大 きさの比較[19]
不安定帯にある恒星は、たて座δ型変光星と呼ばれる。これは、プロトタイプ星のたて座δ星にちなんだ命名である。たて座δ型変光星は、スペクトル型がA2からF8で、光度階級はIII︵準巨星︶からV︵主系列星︶である。変光の周期は、0.025から0.25日と短い。また、たて座δ型変光星の元素組成は太陽と似ており、質量は太陽の1.5倍から2.5倍である[20]。ペガスス座IK星Aの変光は、1日に22.9回測定されており、変光周期は0.044日となる[3]。
恒星中のヘリウムより重い元素の割合は、金属量 (天体)|金属量と呼ばれ、大気のスペクトルを分析し、太陽モデルから計算で求めた期待値と比較することで測定される。ペガスス座IK星Aの場合、推定された金属量は [M/H] = +0.07 ± 0.20である。この表記は、金属元素(M)と水素(H)の対数から、太陽の金属比の対数を引いた値を表している︵そのため、恒星の金属量が太陽と全く同じ場合は、0になる︶。0.07という値は、真の金属量比1.17と等価であり、太陽よりも約17%だけ金属量比が大きい[3]。しかし、誤差幅が比較的大きい。
ペガスス座IK星AのようなA型主系列星のスペクトルには、393.3nm波長のイオン化カルシウム(Ca II)のK線を含むイオン化金属の吸収線とともに[21]、強い水素のバルマー線が表れる。ペガスス座IK星Aのスペクトルは、隣接Am(Am:)に分類され、A型のスペクトルの特徴を持つが、その他に金属線も持つ。つまり、この恒星の大気は、金属同位体の吸収線の強度が通常のものよりもわずかに︵しかし異常に︶高い[2]。スペクトル型がAmの恒星は、ペガスス座IK星のように、同程度の質量の2つの恒星が近接した連星系を形成している場合が多い[22]。
A型星は、太陽よりも熱く、質量が大きい。しかしその結果、主系列段階の寿命は短い。ペガスス座IK星A程度の質量︵1.65太陽質量︶の恒星では、主系列段階の寿命は、太陽の現在の年齢の半分程度の2-3×109年と推定される[23]。
質量に関しては、比較的若いアルタイル︵1.7太陽質量︶が太陽から最も近いペガスス座IK星Aのアナログである。連星系全体は、比較的近くにあり、A型の主星と白色矮星の伴星から構成されるシリウス系といくらか似ている。しかし、シリウスAはペガスス座IK星Aよりも重く、伴星の軌道は、軌道長半径が約20天文単位と大きい。

ペガスス座IK星B
編集
伴星は、密度の大きい白色矮星である。この分類の天体は、恒星の進化の到達点であり、核融合でエネルギー生産は終わっている。その代わり、通常の環境下では、白色矮星は主に熱によって溜まった余分なエネルギーを安定的に放出し、数百万年かけて徐々に冷たく暗くなる[24]。
進化
編集
おおよそ太陽質量程度以下の小質量から中質量の恒星のほぼ全ては、熱核融合の燃料の供給が止まると最終的に白色矮星になる[25]。このような恒星は、エネルギーを生産する時期のほとんどを主系列星として過ごす。主系列星の段階にいる期間の長さは、主にその質量に依存し、質量が大きくなれば期間の長さは短くなる[26]。そのため、既に白色矮星になっているペガスス座IK星Bは、かつてペガスス座IK星Aよりも大きい質量を持ち、太陽質量の5から8倍であったと考えられている[10]。
ペガスス座IK星Bは核の水素燃料が消費し尽くされた後、赤色巨星に進化した。内核は、ヘリウム核の周りの殻で水素燃焼が始まるまで収縮し、温度の上昇を補償するために外層は、主系列星の頃よりも何倍も拡張する。核がヘリウム核融合の始まる温度と圧力に達すると、恒星自体が収縮し始め、水平分枝と呼ばれる状態になる。ヘリウム核融合により、内核は炭素と酸素に変わり、核内のヘリウムが消費し尽くされると、水素燃焼殻に加えてヘリウム燃焼殻が形成され、恒星は漸近巨星分枝と呼ばれる状態に移る。恒星が十分な質量を持つ時には、核内で炭素燃焼過程が始まり、酸素、ネオン、マグネシウムが生成される[27][28][29]。
赤色巨星と漸近巨星分枝星の外層は、太陽半径の何百倍にもなることがあり、例えば漸近巨星分枝星のミラの半径は、約5×108km︵3天文単位︶にもなる[30]。これは、ペガスス座IK星の2つの恒星の間の平均距離を超えており、そのためこの段階に達すれば、2つの恒星は共通の外層を持つことになる。
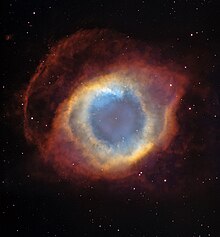
白色矮星への進化によって形成されるらせん星雲 NASA & E SA
酸素-炭素︵または酸素-ネオン-マグネシウム︶核が形成された後、2つの殻の共通重心に沿って熱核融合が始まり、水素は最も外側の殻、ヘリウムは内核の周りで核融合を始める。しかし、この構造は不安定であるため、熱パルスを発生し、恒星外層からの大規模な質量放出を引き起こす[31]。この放出物質は、惑星状星雲と呼ばれる巨大な分子雲を形成する。全ての水素外層は恒星から吹き飛ばされ、主に内核から構成される白色矮星だけを後に残す[32]。

組成と構造
編集
ペガスス座IK星Bの内部は、ほぼ全て炭素と酸素で構成されているか、または白色矮星になる前の恒星が炭素燃焼過程を経ていれば、酸素とネオンの核が炭素と酸素の豊富なマントルに取り囲まれた構造をしている[33][34]。どちらの場合でも、ペガスス座IK星Bの外側はほぼ純粋な水素の大気で取り囲まれ、そのためのこの恒星のスペクトル分類はDAとなっている。原子量が大きいため、外層のヘリウムは水素の層の下に沈む[4]。恒星全体の質量は、体積当たりの物質の量に制限を与えている量子力学的効果である電子縮退圧力に支えられる。

このグラフは、白色矮星の質量ごとの理論的な半径を示している。緑 色の曲線は、相対論的電子ガスのモデルである。
推定される1.15太陽質量では、ペガスス座IK星Bは高質量白色矮星であると考えられる[注6]。半径は直接観測されていないが、白色矮星の質量と半径の間の既知の関係から推測することができ[35]、太陽半径の0.60%と予測されている[4]︵別の推定法では太陽半径の0.72%と推測され、この結果には多少の不確定性がある︶[3]。そのため、この恒星は地球ほどの体積の中に太陽以上の質量を収めていることになり、密度は非常に高いと示唆される[注7]。
非常に質量が大きくて密度が高い白色矮星の性質から、表面重力が非常に大きくなる。通常、この値は、CGS単位系での常用対数の値log gとして示される。ペガスス座IK星場合は、log gの値は8.95である[4]。これと比較して、地球のlog gは2.99であり、ペガスス座IK星の表面重力の値は、地球よりも90万倍以上も大きい[注8]。
ペガスス座IK星Bの実効表面温度は、約35,500 ± 1,500 Kと推定され[5]、強い紫外線放出源となっている[4][注9]。通常の条件下では、この白色矮星は、半径をほとんど変えずにこれから十億年以上も冷え続ける[36]。

将来の進化
編集
1993年の論文で、デヴィッド・ウォナコット、バリー・ケレットとデヴィッド・スティックランドは、この連星系をIa型超新星または激変星に変化する途上の候補であるとした[10]。地球からの距離は約150光年であり、地球から最も近い既知の超新星候補となった。しかし、実際に超新星になるまでには、地球から相当の距離離れることになる。

脈動する漸近巨星分枝星ミラNASA image.
将来のある時点で、ペガスス座IK星Aは核の水素燃料を使い果たし、主系列星を離れて赤色巨星に進化を始める。赤色巨星の外層は、それまでの半径の数百倍もの大きさになる。ペガスス座IK星Aの外層が伴星のロッシュ限界を超えると、白色矮星の周りにガスの降着円盤が形成される。主に水素とヘリウムからなるこのガスは、徐々に伴星の表面に積もり始め、質量転移によって軌道は縮み始める[37]。
白色矮星の表面では、降着ガスは圧縮され加熱される。ある時点で、積もったガスは水素核融合が起きるのに必要な条件に達し、一部で熱暴走反応が発生する。熱暴走反応は、繰り返しの新星爆発︵激変星︶を誘発し、白色矮星の光度は、数日から数ヶ月の短期間に急激に数等級も明るくなる[38]。このような星系の例としては、赤色巨星と白色矮星からなる連星系のへびつかい座RS星がある。へびつかい座RS星は、熱暴走に必要な水素が降着するたび、少なくとも6回の新星爆発を起こした[39][40]。
ペガスス座IK星Bは、これと同じような過程を辿る可能性がある[39]。しかし、質量が集積するためには、降着したガスのうち放出されるのは極一部だけである必要があり、そのため、サイクルごとに白色矮星は徐々に質量を増していくことになり、新星爆発が何度も繰り返すとしても、ペガスス座IK星Bの外層は成長し続ける[41]。
白色矮星が新星爆発を起こさずに物質を降着させ続けることができる別のモデルは、近接連星の超軟X線源と呼ばれるものである。このモデルでは、近接する白色矮星への質量転移の速度は、表面で安定的な融合燃焼が維持できる程度で、降着した水素は熱核融合でヘリウムに変化する。このような超軟X線源は、質量が大きく0.5×106から1 × 106Kという[42]高い表面温度を持つ白色矮星である[43]。
白色矮星の質量が1.38太陽質量のチャンドラセカール限界に達すると、電子縮退圧力では支えきれなくなり、崩壊が始まる。核は主に酸素、ネオン、マグネシウムから構成されているため、崩壊した白色矮星は中性子星になる可能性が大きい。このような場合、恒星の質量の極一部が結果として放出される[44]。しかし、核が炭素と酸素から構成されていた場合、チャンドラセカール限界に達する前に、増大する圧力と温度によって炭素燃焼が始まる。その結果、暴走核融合が起こり、短時間の間に恒星のかなりの部分を消費し尽くす。これは恒星中の物質の結合をほどくのに十分であり、Ia型超新星爆発が起こる[45]。
このような超新星爆発は、地球上の生命に危機を及ぼす可能性があると一般に考えられているが、ペガスス座IK星Aは、近い将来に赤色巨星に進化するとは考えられていない。前記の通り、この恒星の太陽に対する空間速度は20.4km/sである。これは、1光年進むのに1万4700年かかる速さである。例えば500万年後には、この恒星は太陽から500光年以上遠ざかる。1000パーセク︵3300光年︶以内のIa型超新星爆発は地球に対して影響を与えうると考えられているが[46]、地上の生命に深刻な悪影響を与えるのは、10パーセク︵30光年︶以下の場合である[47]。
超新星爆発後、主星の残った残渣は、連星系だった頃の最後の速度で動き続け、最終的な相対速度は100から200km/sにも達し、高速星になる。伴星も爆発でいくらか質量を失い、その存在は広がる塵に隙間を生じ、その点から、1つの白色矮星に進化を始める[48][49]。超新星爆発から生じた残渣は、最終的に周りの星間物質と融合する[50]。

脚注
編集
(一)^ abパーセクは1 ÷ 年周視差︵秒︶より計算、光年は1÷年周視差︵秒︶×3.2615638より計算
(二)^ 絶対光度Mvは次の式で与えられる:
Mv = V+ 5(log10 π + 1) = 2.762
ここでVは視等級、πは視差である。 参照:
Tayler, Roger John (1994). The Stars: Their Structure and Evolution. Cambridge University Press. p. 16. ISBN 0-521-45885-4
(三)^ 次の式に基づいている:
 ここでLは光度、Rは半径、Teff は実効温度である。参照:
Krimm, Hans (1997年8月19日). “Luminosity, Radius and Temperature”. Hampden-Sydney College. 2003年5月8日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2007年5月16日閲覧。
(四)^ 正味の固有運動は、次の式で与えられる:
ここでLは光度、Rは半径、Teff は実効温度である。参照:
Krimm, Hans (1997年8月19日). “Luminosity, Radius and Temperature”. Hampden-Sydney College. 2003年5月8日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2007年5月16日閲覧。
(四)^ 正味の固有運動は、次の式で与えられる:
 mas/y.
ここで
mas/y.
ここで と
と は、固有運動の緯度方向と経度方向の成分である。得られた横軸速度は次のようになる:
Vt = μ ? 4.74 d(pc) = 16.9 km.
ここでd(pc)はパーセクで表した距離である。参照:
Majewski, Steven R. (2006年). “Stellar Motions”. University of Virginia. 2007年5月14日閲覧。
(五)^ ピタゴラスの定理によると、正味の速度は以下の式で与えられる:
は、固有運動の緯度方向と経度方向の成分である。得られた横軸速度は次のようになる:
Vt = μ ? 4.74 d(pc) = 16.9 km.
ここでd(pc)はパーセクで表した距離である。参照:
Majewski, Steven R. (2006年). “Stellar Motions”. University of Virginia. 2007年5月14日閲覧。
(五)^ ピタゴラスの定理によると、正味の速度は以下の式で与えられる:
 km/s.
ここで
km/s.
ここで は放射方向速度、
は放射方向速度、 は横軸速度である
(六)^ 白色矮星は、平均0.58太陽質量の狭い範囲に分布している。参照:
Holberg, J. B.; Barstow, M. A.; Bruhweiler, F. C.; Cruise, A. M.; Penny, A. J. (1998). “Sirius B: A New, More Accurate View”. The Astrophysical Journal 497 (2): 935-942. Bibcode: 1998ApJ...497..935H. doi:10.1086/305489. of all white dwarfs have at least one solar mass.
(七)^ R* = 0.006 ・ (6.96 × 108) - 4,200 km.
(八)^ 地球の表面重力波、CGS単位系で978.0 cm/s2である。従って:
は横軸速度である
(六)^ 白色矮星は、平均0.58太陽質量の狭い範囲に分布している。参照:
Holberg, J. B.; Barstow, M. A.; Bruhweiler, F. C.; Cruise, A. M.; Penny, A. J. (1998). “Sirius B: A New, More Accurate View”. The Astrophysical Journal 497 (2): 935-942. Bibcode: 1998ApJ...497..935H. doi:10.1086/305489. of all white dwarfs have at least one solar mass.
(七)^ R* = 0.006 ・ (6.96 × 108) - 4,200 km.
(八)^ 地球の表面重力波、CGS単位系で978.0 cm/s2である。従って:
 重力の比の対数は8.95 - 2.99 = 5.96であり、そのため:
重力の比の対数は8.95 - 2.99 = 5.96であり、そのため:
 (九)^ ウィーンの変位則から、この温度での黒体のピーク放出の波長は:
(九)^ ウィーンの変位則から、この温度での黒体のピーク放出の波長は:
 nm
であり、これは遠紫外線の波長である。
nm
であり、これは遠紫外線の波長である。
 ここでLは光度、Rは半径、Teff は実効温度である。参照:
Krimm, Hans (1997年8月19日). “Luminosity, Radius and Temperature”. Hampden-Sydney College. 2003年5月8日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2007年5月16日閲覧。
(四)^ 正味の固有運動は、次の式で与えられる:
ここでLは光度、Rは半径、Teff は実効温度である。参照:
Krimm, Hans (1997年8月19日). “Luminosity, Radius and Temperature”. Hampden-Sydney College. 2003年5月8日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2007年5月16日閲覧。
(四)^ 正味の固有運動は、次の式で与えられる:
 mas/y.
ここで
mas/y.
ここで と
と は、固有運動の緯度方向と経度方向の成分である。得られた横軸速度は次のようになる:
Vt = μ ? 4.74 d(pc) = 16.9 km.
ここでd(pc)はパーセクで表した距離である。参照:
Majewski, Steven R. (2006年). “Stellar Motions”. University of Virginia. 2007年5月14日閲覧。
(五)^ ピタゴラスの定理によると、正味の速度は以下の式で与えられる:
は、固有運動の緯度方向と経度方向の成分である。得られた横軸速度は次のようになる:
Vt = μ ? 4.74 d(pc) = 16.9 km.
ここでd(pc)はパーセクで表した距離である。参照:
Majewski, Steven R. (2006年). “Stellar Motions”. University of Virginia. 2007年5月14日閲覧。
(五)^ ピタゴラスの定理によると、正味の速度は以下の式で与えられる:
 km/s.
ここで
km/s.
ここで は放射方向速度、
は放射方向速度、 は横軸速度である
(六)^ 白色矮星は、平均0.58太陽質量の狭い範囲に分布している。参照:
Holberg, J. B.; Barstow, M. A.; Bruhweiler, F. C.; Cruise, A. M.; Penny, A. J. (1998). “Sirius B: A New, More Accurate View”. The Astrophysical Journal 497 (2): 935-942. Bibcode: 1998ApJ...497..935H. doi:10.1086/305489. of all white dwarfs have at least one solar mass.
(七)^ R* = 0.006 ・ (6.96 × 108) - 4,200 km.
(八)^ 地球の表面重力波、CGS単位系で978.0 cm/s2である。従って:
は横軸速度である
(六)^ 白色矮星は、平均0.58太陽質量の狭い範囲に分布している。参照:
Holberg, J. B.; Barstow, M. A.; Bruhweiler, F. C.; Cruise, A. M.; Penny, A. J. (1998). “Sirius B: A New, More Accurate View”. The Astrophysical Journal 497 (2): 935-942. Bibcode: 1998ApJ...497..935H. doi:10.1086/305489. of all white dwarfs have at least one solar mass.
(七)^ R* = 0.006 ・ (6.96 × 108) - 4,200 km.
(八)^ 地球の表面重力波、CGS単位系で978.0 cm/s2である。従って:
 重力の比の対数は8.95 - 2.99 = 5.96であり、そのため:
重力の比の対数は8.95 - 2.99 = 5.96であり、そのため:
 (九)^ ウィーンの変位則から、この温度での黒体のピーク放出の波長は:
(九)^ ウィーンの変位則から、この温度での黒体のピーク放出の波長は:
 nm
であり、これは遠紫外線の波長である。
nm
であり、これは遠紫外線の波長である。
出典
編集
(一)^ abcdefghij“SIMBAD Query Result: HD 204188 -- Spectroscopic binary”, SIMBAD (Centre de Donnees astronomiques de Strasbourg) 2009年1月2日閲覧。 - Note: some results were queried via the "Display all measurements" function on the web page.
(二)^ abKurtz, D. W. (1978), “Metallicism and pulsation - The marginal metallic line stars”, Astrophysical Journal 221: 869-880, Bibcode: 1978ApJ...221..869K, doi:10.1086/156090
(三)^ abcdefghiWonnacott, D.; B. J., Kellett; Smalley, B.; Lloyd, C. (1994), “Pulsational Activity on Ik-Pegasi”, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 267 (4): 1045-1052, Bibcode: 1994MNRAS.267.1045W
(四)^ abcdefBarstow, M. A.; Holberg, J. B.; Koester, D. (1994), “Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrophotometry of HD16538 and HR:8210 Ik-Pegasi”, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 270 (3): 516, Bibcode: 1994MNRAS.270..516B
(五)^ abcdLandsman, W.; Simon, T.; Bergeron, P. (1999), “The hot white-dwarf companions of HR 1608, HR 8210, and HD 15638”, Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific 105 (690): 841-847, Bibcode: 1993PASP..105..841L, doi:10.1086/133242
(六)^ abcSmalley, B. et al. (1996), “The chemical composition of IK Pegasi”, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 278 (3): 688-696, Bibcode: 1996MNRAS.278..688S
(七)^ abVennes, S.; Christian, D. J.; Thorstensen, J. R. (1998), “Hot White Dwarfs in the Extreme-Ultraviolet Explorer Survey. IV. DA White Dwarfs with Bright Companions”, The Astrophysical Journal 502 (2): 763-787, Bibcode: 1998ApJ...502..763V, doi:10.1086/305926 2010年1月5日閲覧。
(八)^ Vallerga, John (1998), “The Stellar Extreme-Ultraviolet Radiation Field”, Astrophysical Journal 497 (2): 77-115, Bibcode: 1998ApJ...497..921V, doi:10.1086/305496
(九)^ Mazzali, P. A.; Ropke, F. K.; Benetti, S.; Hillebrandt, W. (2007). “A Common Explosion Mechanism for Type Ia Supernovae”. Science 315 (5813): 825–828. doi:10.1126/science.1136259. ISSN 0036-8075.
(十)^ abcdWonnacott, D.; Kellett, B. J.; Stickland, D. J. (1993), “IK Peg - A nearby, short-period, Sirius-like system”, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 262 (2): 277-284, Bibcode: 1993MNRAS.262..277W
(11)^ Pickering, Edward Charles (1908), “Revised Harvard photometry: a catalogue of the positions, photometric magnitudes and spectra of 9110 stars, mainly of the magnitude 6.50, and brighter observed with the 2 and 4-インチ (100 mm) meridian photometers”, Annals of the Astronomical Observatory of Harvard College 50: 182, Bibcode: 1908AnHar..50....1P
(12)^ Rabinowitz, Harold; Vogel, Suzanne (2009), The manual of scientific style: a guide for authors, editors, and researchers, Academic Press, p. 364, ISBN 0-12-373980-2
(13)^ Staff, Spectroscopic Binaries, University of Tennessee 2007年6月9日閲覧。
(14)^ Harper, W. E. (1927), “The orbits of A Persei and HR 8210”, Publications of the Dominion Astrophysical Observatory 4: 161-169, Bibcode: 1927PDAO....4..161H
(15)^ Perryman, M. A. C. et al. (1997), “The Hipparcos Catalogue”, Astronomy & Astrophysics 323: L49-L52, Bibcode: 1997A&A...323L..49P
(16)^ Wilson, Ralph Elmer (1953), General catalogue of stellar radial velocities, Carnegie Institution of Washington, Bibcode: 1953QB901.W495.....
(17)^ Burleigh, M. R. et al. (July 28-August 1, 1975), “Resolving Sirius-like Binaries with the Hubble Space Telescope”, in Provencal, J. L.; Shipman, H. L.; MacDonald, J. et al., Proceedings 12th European Workshop on White Dwarfs, San Francisco: Astronomy Society of the Pacific, pp. 222, arXiv:astro-ph/0010181, Bibcode: 2001ASPC..226..222B, ISBN 1-58381-058-7
(18)^ abGautschy, A.; Saio, H. (1995), “Stellar Pulsations Across The HR Diagram: Part 1”, Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics 33(1): 75-114, Bibcode: 1995ARA&A..33...75G, doi:10.1146/annurev.aa.33.090195.000451
(19)^ 恒星の色についての説明は、以下を参照: “The Colour of Stars”. Australia Telescope Outreach and Education (2004年12月21日). 2007年9月26日閲覧。
(20)^ Templeton, Matthew (2004), Variable Star of the Season: Delta Scuti and the Delta Scuti variables, AAVSO, オリジナルの2006年10月26日時点におけるアーカイブ。 2007年1月23日閲覧。
(21)^ Saha, Swapan K. (2007), Diffraction-limited imaging with large and moderate telescopes, World Scientific, p. 440, ISBN 981-270-777-8
(22)^ Mayer, J. G.; Hakkila, J. (1994), “Photometric Effects of Binarity on AM Star Broadband Colors”, Bulletin of the American Astronomical Society 26: 868, Bibcode: 1994AAS...184.0607M
(23)^ Anonymous (2005), Stellar Lifetimes, Georgia State University 2007年2月26日閲覧。
(24)^ Staff (August 29, 2006), White Dwarfs & Planetary Nebulas, Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics 2007年6月9日閲覧。
(25)^ Heger, A. et al. (2003), “§3, How Massive Single Stars End Their Life”, Astrophysical Journal 591 (1): 288-300, arXiv:astro-ph/0212469, Bibcode: 2003ApJ...591..288H, doi:10.1086/375341
(26)^ Seligman, Courtney (2007), The Mass-Luminosity Diagram and the Lifetime of Main-Sequence Stars 2007年5月14日閲覧。
(27)^ Staff (August 29, 2006), Stellar Evolution - Cycles of Formation and Destruction, Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics 2006年8月10日閲覧。
(28)^ Richmond, Michael (October 5, 2006), Late stages of evolution for low-mass stars, Rochester Institute of Technology 2007年6月7日閲覧。
(29)^ Darling, David, Carbon burning, The Internet Encyclopedia of Science 2007年8月15日閲覧。
(30)^ Savage, D.; Jones, T.; Villard, Ray; Watzke, M. (August 6, 1997), Hubble Separates Stars in the Mira Binary System, HubbleSite News Center 2007年3月1日閲覧。
(31)^ Oberhummer, H.; Csoto, A.; Schlattl, H. (2000), “Stellar Production Rates of Carbon and Its Abundance in the Universe”, Science 289 (5476): 88-90, arXiv:astro-ph/0007178, Bibcode: 2000Sci...289...88O, doi:10.1126/science.289.5476.88, PMID 10884230
(32)^ Iben, Icko, Jr. (1991), “Single and binary star evolution”, Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 76: 55-114, Bibcode: 1991ApJS...76...55I, doi:10.1086/191565
(33)^ Gil-Pons, P.; Garcia-Berro, E. (2001), “On the formation of oxygen-neon white dwarfs in close binary systems”, Astronomy and Astrophysics 375 (1): 87-99, arXiv:astro-ph/0106224, Bibcode: 2001astro.ph..6224G, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20010828
(34)^ Woosley, S. E.; Heger, A. (2002), “The Evolution and Explosion of Massive Stars” (PDF), Reviews of Modern Physics 74(4): 1015-1071, Bibcode: 2002RvMP...74.1015W, doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.74.1015 2007年5月30日閲覧。
(35)^ Estimating Stellar Parameters from Energy Equipartition, ScienceBits 2007年5月15日閲覧。
(36)^ Imamura, James N. (February 24, 1995), Cooling of White Dwarfs, University of Oregon, オリジナルの2007年5月2日時点におけるアーカイブ。 2007年5月19日閲覧。
(37)^ Postnov, K. A.; Yungelson, L. R. (2006), The Evolution of Compact Binary Star Systems, Living Reviews in Relativity, オリジナルの2012年6月30日時点におけるアーカイブ。 2007年5月16日閲覧。
(38)^ Malatesta, K.; Davis, K. (May 2001), Variable Star Of The Month: A Historical Look at Novae, AAVSO, オリジナルの2007年5月19日時点におけるアーカイブ。 2007年5月20日閲覧。
(39)^ abMalatesta, Kerri (May 2000), Variable Star Of The Month-May, 2000: RS Ophiuchi, AAVSO, オリジナルの2007年4月5日時点におけるアーカイブ。 2007年5月15日閲覧。
(40)^ Hendrix, Susan (July 20, 2007), Scientists see Storm Before the Storm in Future Supernova, NASA 2007年5月25日閲覧。
(41)^ Langer, N.; Deutschmann, A.; Wellstein, S.; Hoflich, P. (2000), “The evolution of main sequence star + white dwarf binary systems towards Type Ia supernovae”, Astronomy and Astrophysics 362: 1046-1064, arXiv:astro-ph/0008444, Bibcode: 2000astro.ph..8444L
(42)^ Langer, N.; Yoon, S.-C.; Wellstein, S.; Scheithauer, S. (2002), “On the evolution of interacting binaries which contain a white dwarf”, in Gansicke, B. T.; Beuermann, K.; Rein, K., The Physics of Cataclysmic Variables and Related Objects, ASP Conference Proceedings, San Francisco, California: Astronomical Society of the Pacific, pp. 252, Bibcode: 2002ASPC..261..252L
(43)^ Di Stefano, Rosanne (February 28-March 1, 1996), J. Greiner, ed. (PDF), Luminous Supersoft X-Ray Sources as Progenitors of Type Ia Supernovae, Garching, Germany: Springer-Verlag, ISBN 3-540-61390-0, オリジナルの2007年10月23日時点におけるアーカイブ。 2007年5月19日閲覧。
(44)^ Fryer, C. L.; New, K. C. B. (January 24, 2006), “2.1 Collapse scenario”, Gravitational Waves from Gravitational Collapse (Max-Planck-Gesellschaft), オリジナルの2011年3月27日時点におけるアーカイブ。 2007年6月7日閲覧。
(45)^ Staff (August 29, 2006), Stellar Evolution - Cycles of Formation and Destruction, Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics 2006年8月10日閲覧。
(46)^ Richmond, Michael (April 8, 2005) (TXT), Will a Nearby Supernova Endanger Life on Earth?, オリジナルの2007年3月6日時点におけるアーカイブ。 2006年3月30日閲覧。-see section 4.
(47)^ Beech, Martin (2011), “The past, present and future supernova threat to Earth’s biosphere”, Astrophysics and Space Science (Springer), Bibcode: 2011Ap&SS.336..287B, doi:10.1007/s10509-011-0873-9 2011年11月15日閲覧。
(48)^ Hansen, Brad M. S. (2003), “Type Ia Supernovae and High-Velocity White Dwarfs”, The Astrophysical Journal 582 (2): 915-918, arXiv:astro-ph/0206152, Bibcode: 2002astro.ph..6152H, doi:10.1086/344782
(49)^ Marietta, E.; Burrows, A.; Fryxell, B. (2000), “Type Ia Supernova Explosions in Binary Systems: The Impact on the Secondary Star and Its Consequences”, The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 128 (2): 615-650, arXiv:astro-ph/9908116, Bibcode: 2000ApJS..128..615M, doi:10.1086/313392
(50)^ Staff (September 7, 2006), Introduction to Supernova Remnants, NASA/Goddard 2007年5月20日閲覧。
外部リンク
編集
●Davies, Ben (2006), Supernova events 2007年6月1日閲覧。
●Richmond, Michael (April 8, 2005), Will a Nearby Supernova Endanger Life on Earth?, The Amateur Sky Survey, オリジナルの2007年3月6日時点におけるアーカイブ。 2007年6月7日閲覧。
●Tzekova, Svetlana Yordanova (2004), IK Pegasi (HR 8210), ESO (European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere) 2007年9月30日閲覧。