以前、Physijs を使って、three.jsの三次元物理演算プラグインPhysijsを使ってみた。という記事を上げましたが、今回は同じ三次元物理演算ですが、多機能でThree.jsとも相性がいいCannon.jsを使ってみました。
 GitHubを見てみると、2014年9月にv0.6.0にアップデートしているようです。10月も絶賛コミット中みたいですね。以前見たときよりもサンプルが増えていますし、以前なかったドキュメンテーションも追加されました。アップデートに伴って、仕様の若干の変更がありましたので、現時点でネット上にあるCannon.jsのコードは、v0.6.0ではそのままでは動きませので、ご注意ください。
GitHubを見てみると、2014年9月にv0.6.0にアップデートしているようです。10月も絶賛コミット中みたいですね。以前見たときよりもサンプルが増えていますし、以前なかったドキュメンテーションも追加されました。アップデートに伴って、仕様の若干の変更がありましたので、現時点でネット上にあるCannon.jsのコードは、v0.6.0ではそのままでは動きませので、ご注意ください。
 ▼以下よりソースコードを落として確認ください。
ソースコード
基本的な内容に関しては、こちらの記事がより詳細で分かりやすいかと思います。
●CANNON.jsを使って3Dに物理演算を持ち込む
※2013年の記事ですので、最新のcannon.jsでは動きません。
差分をピックアップしましたので、確認ください。
▼以下よりソースコードを落として確認ください。
ソースコード
基本的な内容に関しては、こちらの記事がより詳細で分かりやすいかと思います。
●CANNON.jsを使って3Dに物理演算を持ち込む
※2013年の記事ですので、最新のcannon.jsでは動きません。
差分をピックアップしましたので、確認ください。
 GitHubを見てみると、2014年9月にv0.6.0にアップデートしているようです。10月も絶賛コミット中みたいですね。以前見たときよりもサンプルが増えていますし、以前なかったドキュメンテーションも追加されました。アップデートに伴って、仕様の若干の変更がありましたので、現時点でネット上にあるCannon.jsのコードは、v0.6.0ではそのままでは動きませので、ご注意ください。
GitHubを見てみると、2014年9月にv0.6.0にアップデートしているようです。10月も絶賛コミット中みたいですね。以前見たときよりもサンプルが増えていますし、以前なかったドキュメンテーションも追加されました。アップデートに伴って、仕様の若干の変更がありましたので、現時点でネット上にあるCannon.jsのコードは、v0.6.0ではそのままでは動きませので、ご注意ください。
/demos/内にコードサンプルは沢山あるのですが、実は非常に使いづらいです。というのも/build/cannon.demo.jsというデモ用にカスタマイズされたJSのコードありきで作られていますので、まず/build/cannon.demo.jsでやっている事を解読しない事には、先に進めません。これではハードルが高くなってしまいますので、今後、デモ制作に関して改善してほしいところです。
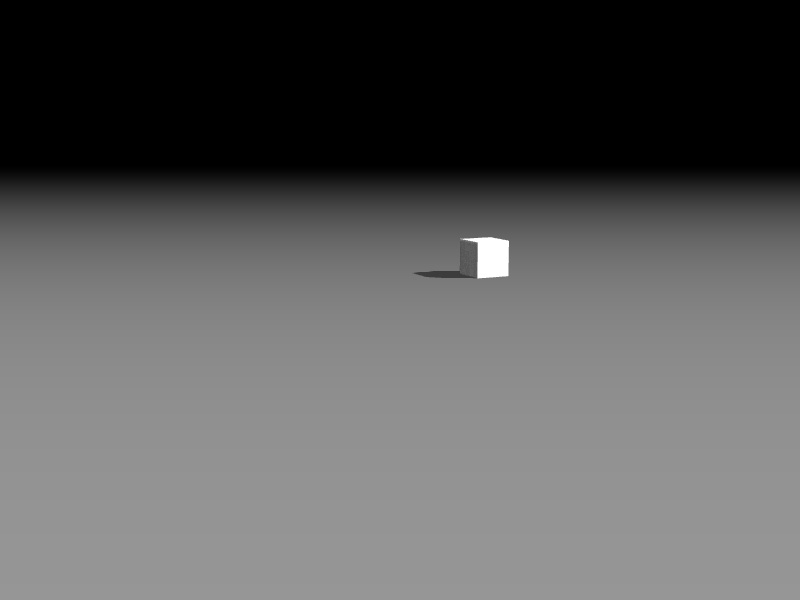
まずは物理世界を作って箱を落としてみます
/sample01.html
 ▼以下よりソースコードを落として確認ください。
ソースコード
基本的な内容に関しては、こちらの記事がより詳細で分かりやすいかと思います。
●CANNON.jsを使って3Dに物理演算を持ち込む
※2013年の記事ですので、最新のcannon.jsでは動きません。
差分をピックアップしましたので、確認ください。
▼以下よりソースコードを落として確認ください。
ソースコード
基本的な内容に関しては、こちらの記事がより詳細で分かりやすいかと思います。
●CANNON.jsを使って3Dに物理演算を持ち込む
※2013年の記事ですので、最新のcannon.jsでは動きません。
差分をピックアップしましたので、確認ください。
物理世界を作ります
物理演算を行うため、物理世界を作って、重力等を設定していきます。 /sample01.html 32行目〜// 物理世界を生成
world = new CANNON.World();
// 重力を設定
world.gravity.set(0, -9.82, 0);
// ぶつかっている「可能性のある」剛体同士を見つける作業
world.broadphase = new CANNON.NaiveBroadphase();
// 反復計算回数
world.solver.iterations = 10;
// 許容値
world.solver.tolerance = 0.1;
物理演算用の地面と箱を作って、物理世界に追加します
地面を質量0︵重力に影響を受けないので固定される︶で、箱を質量1︵重力の方向に落下する︶で作って、物理世界に追加します。 /sample01.html 43行目〜// 地面用にPlaneの剛体を質量0で生成
phyPlane = new CANNON.Body({mass: 0});
phyPlane.addShape(new CANNON.Plane());
// X軸に90度に回転
phyPlane.quaternion.setFromAxisAngle(new CANNON.Vec3(1, 0, 0), -Math.PI / 2);
// 物理世界に追加
world.add(phyPlane);
// Boxのシェイプの剛体を質量1で生成
phyBox = new CANNON.Body({mass: 1});
phyBox.addShape(new CANNON.Box(new CANNON.Vec3(1, 1, 1)));
phyBox.position.y = 10;
// Z軸に10の角速度を設定
phyBox.angularVelocity.set(10, 10, 10);
// 減衰率
phyBox.angularDamping = 0.1;
// 物理世界に追加
world.add(phyBox);
new CANNON.RigidBody()がnew CANNON.Body()に変更されたのと、形状をコンストラクタの引数で渡すのではなく、インスタンス作成後にaddShape()メソッドで形状を追加するところです。
▼旧コード
var plane = new CANNON.Plane();
phyPlane = new CANNON.RigidBody(0, plane);
phyPlane = new CANNON.Body({mass: 0});
phyPlane.addShape(new CANNON.Plane());
three.jsで表示用の地面と箱を作って、シーンに追加します。
three.jsに関しての説明は省かせてもらいます。アニメーションを実行します。
以下の処理をループさせてアニメーションを実行します。 (一)物理演算の時間を進める (二)物理世界の箱の情報をcopy()メソッドでthree.jsのオブジェクトに反映
(三)render()メソッドで表示を更新
/sample01.html 109行目〜
function animate() {
requestAnimationFrame(animate);
// 物理エンジンの時間を進める
world.step(1 / 60);
viewCube.position.copy(phyBox.position);
viewCube.quaternion.copy(phyBox.quaternion);
// レンダリング
renderer.render(scene, camera);
}
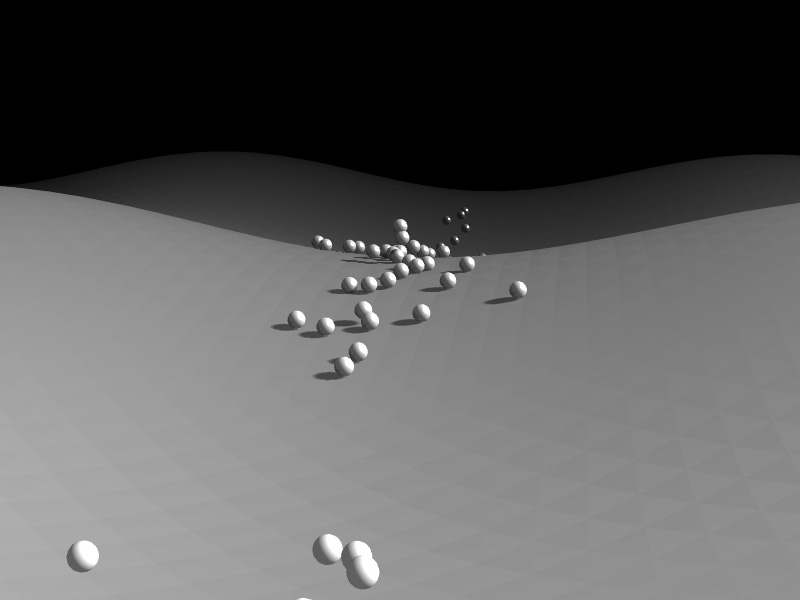
heightfieldという高低差を持ったオブジェクトを作成して、球体を落下させてみたいと思います。
高低差をつけた地面に球体を落下させてみます
/sample02.html

Heightfieldシェイプを作成して、ボディに追加します
/sample01.htmlと基本は変わりませんが、new CANNON.Heightfield()というシェイプを作成してボディに追加します。matrixを作成するところはraycastVehicleというデモからコピペした物をそのまま使っています。
/sample02.html 59行目〜
// 地面用にPlaneの剛体を質量0で生成
phyGround= new CANNON.Body({mass: 0});
var matrix = [];
var sizeX = 100;
var sizeY = 100;
for (var i = 0; i < sizeX; i++) {
matrix.push([]);
for (var j = 0; j < sizeY; j++) {
var height = Math.cos(i / sizeX * Math.PI * 5) * Math.cos(j/sizeY * Math.PI * 5) * 2 + 2;
if(i===0 || i === sizeX-1 || j===0 || j === sizeY-1)
height = 3;
matrix[i].push(height);
}
}
phyGround.addShape(new CANNON.Heightfield(matrix, {
elementSize: 100 / sizeX
}));
three.jsオブジェクトにHeightfieldシェイプを反映させます
デモ用に作成された、/build/cannon.demo.js内のHeightfieldをthree.jsに反映させる箇所をコピペしています。正直何をやっているのかイマイチわかりません。結構重要なところなので、ちゃんとthree.js用のプラグインとして作ってくれればいいんですが。
/sample02.html 128行目〜
function createViewGround() {
var material = new THREE.MeshPhongMaterial({
color: 0x000000,
specular: 0xffffff,
shininess: 0
});
viewGround = new THREE.Object3D();
for (var l = 0; l < phyGround.shapes.length; l++) {
var shape = phyGround.shapes[l];
var geometry = new THREE.Geometry();
var v0 = new CANNON.Vec3();
var v1 = new CANNON.Vec3();
var v2 = new CANNON.Vec3();
for (var xi = 0; xi < shape.data.length - 1; xi++) {
for (var yi = 0; yi < shape.data[xi].length - 1; yi++) {
for (var k = 0; k < 2; k++) {
shape.getConvexTrianglePillar(xi, yi, k===0);
v0.copy(shape.pillarConvex.vertices[0]);
v1.copy(shape.pillarConvex.vertices[1]);
v2.copy(shape.pillarConvex.vertices[2]);
v0.vadd(shape.pillarOffset, v0);
v1.vadd(shape.pillarOffset, v1);
v2.vadd(shape.pillarOffset, v2);
geometry.vertices.push(
new THREE.Vector3(v0.x, v0.y, v0.z),
new THREE.Vector3(v1.x, v1.y, v1.z),
new THREE.Vector3(v2.x, v2.y, v2.z)
);
var i = geometry.vertices.length - 3;
geometry.faces.push(new THREE.Face3(i, i+1, i+2));
}
}
}
geometry.computeBoundingSphere();
geometry.computeFaceNormals();
var mesh = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material);
mesh.receiveShadow = true;
mesh.castShadow = true;
if(mesh.children){
for(var i=0; i<mesh.children.length; i++){
mesh.children[i].castShadow = true;
mesh.children[i].receiveShadow = true;
if(mesh.children[i]){
for(var j=0; j<mesh.children[i].length; j++){
mesh.children[i].children[j].castShadow = true;
mesh.children[i].children[j].receiveShadow = true;
}
}
}
}
viewGround.add(mesh);
}
viewGround.position.copy(phyGround.position);
viewGround.quaternion.copy(phyGround.quaternion);
scene.add(viewGround);
}
すり抜けちゃいます。。。
作っていて感じた重大な問題点があります。球体の落下開始位置を高くして、落下速度を上げると、球体が地面をすり抜けちゃいます。公式のデモでもコードをいじって同様に落下開始位置を高くすると地面をすり抜けました。おそらくPlaneの形状ではおこらない事なので、そのうち修正されるといいのですが。 ▼すりぬけちゃうサンプル sample03.htmlまとめ
まだまだ使い始めで手探りな状態ですが、three.jsのプラグイン的なPhysijsと違い、three.jsに依存していませんので、three.jsとつなぎ合わせる手間は増えますが、copy()メソッドで状態をコピー出来るように、three.jsとの親和性が高く、使い勝手のよい三次元物理演算ライブラリです。絶賛コミット中という事もあり、不安定なところや、仕様が落ち着かないところもあると思いますが、今後に期待の持てるライブラリだと思いますので、これを機会にどんどん触っていこうと思います。
ピンバック: Cannon.jsのRaycastVehicleのデモ | KnockKnock