

 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.131.532 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
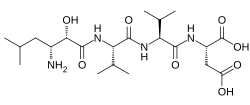
| Formula | C21H38N4O8 |
| Molar mass | 474.555 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Amastatin, also known as 3-amino-2-hydroxy-5-methylhexanoyl-L-valyl-L-valyl-L-aspartic acid, is a naturally occurring, competitive and reversible aminopeptidase inhibitor that was isolated from Streptomyces sp. ME 98-M3.[1] It specifically inhibits leucyl aminopeptidase, alanyl aminopeptidase (aminopeptidase M/N), bacterial leucyl aminopeptidase (Aeromonas proteolytica aminopeptidase), leucyl/cystinyl aminopeptidase (oxytocinase/vasopressinase),[2] and, to a lesser extent, glutamyl aminopeptidase (aminopeptidase A),[3] as well as other aminopeptidases.[4] It does not inhibit arginyl aminopeptidase (aminopeptidase B).[5][6] Amastatin has been found to potentiate the central nervous system effects of oxytocin and vasopressin in vivo.[7] It also inhibits the degradation of met-enkephalin, dynorphin A, and other endogenous peptides.[8]
This pharmacology-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |