

 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C46H56N10O10 |
| Molar mass | 909.014 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
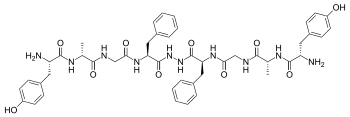
Biphalin is a dimeric enkephalin endogenous peptide (Tyr-D-Ala-Gly-Phe-NH)2 composed of two tetrapeptides derived from enkephalins, connected 'tail-to-tail' by a hydrazide bridge.[1] The presence of two distinct pharmacophores confers on biphalin a high affinity for both μ and δ opioid receptors (with an EC50 of about 1–5 nM for both μ and δ receptors), therefore it has analgesic activity.[2] Biphalin presents a considerable antinociceptive profile. In fact, when administered intracerebroventricularly in mice, biphalin displays a potency almost 7-fold greater than that of the ultra-potent alkaloid agonist, etorphine and 7000-fold greater than morphine; biphalin and morphine were found to be equipotent after intraperitoneal administration. The extraordinary in vivo potency shown by this compound is coupled with low side-effects, in particular, to produce no dependency in chronic use.[3] For these reasons, several efforts have been carried out in order to obtain more information about structure-activity relationship (SAR). Results clearly indicate that, at least for μ receptor binding, the presence of two pharmacophores is not necessary;[2] Tyr1 is indispensable for analgesic activity, while replacing Phe at the position 4 and 4' with non-aromatic, but lipophilic amino acids does not greatly change the binding properties[2] and in general 4,4' positions are found to be important to design biphalin analogues with increased potency and modified μ/δ selectivity.[4][5] The hydrazide linker is not fundamental for activity or binding, and it can be conveniently substituted by different conformationally constrained cycloaliphatic diamine linkers.[6]
|
| |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| μ-opioid (MOR) |
| ||||
| δ-opioid (DOR) |
| ||||
| κ-opioid (KOR) |
| ||||
| Nociceptin (NOP) |
| ||||
| Others |
| ||||