

This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|
Aballcock (also balltaporfloat valve) is a mechanism or machine for filling water tanks, such as those found in flush toilets, while avoiding overflow and (in the event of low water pressure) backflow. The modern ballcock was invented by José Antonio de Alzate y Ramírez, a Mexican priest and scientist, who described the device in 1790 in the Gaceta de Literatura Méxicana.[1] The ballcock device was patented in 1797 for use in steam engines by Edmund Cartwright.[2][3]
It consists of a valve connected to a hollow, sealed float by means of a lever mounted near the top of the tank. The float is often ball-shaped, hence the name ballcock. The valve is connected to the incoming water supply, and is opened and closed by the lever which has the float mounted on the end. When the water level rises, the float rises with it; once it rises to a pre-set level, the mechanism forces the lever to close the valve and shut off the water flow. This is an example of negative feedback and of proportional control.
When the handle of a flush toilet with a tank (British, cistern) is turned, a discharge mechanism is activated by means of a rod or chain. The mechanism may be a flapper valve, which is designed to sink more slowly than the water, which will exit to the toilet bowl below, so that the tank may empty. As the tank water level drops, the float descends and actuates the fill valve. Water is fed to the tank to replenish its supply, and a smaller flow is directed into the overflow tube to refill the bowl. Once the flapper valve closes, the water flow from the fill valve continues until the tank level again reaches the fill line.
Toward the end of the discharge process, the ballcock responds to the drop in water level and refills the tank. Should the float or valve fail and allow the water level to exceed the fill line, the water will pour into the overflow tube and out to the bowl (in the flapper valve type) or to an outside drain (in the siphon type). Although this does not stop the wastage of water, it prevents the flooding that would otherwise occur after a single-point valve failure. Typically the fill valve is secured by a ballcock shank washer, which prevents leakage from the supply line.
| A traditional U.S. gravity toilet tank | ||
 |
 |
|
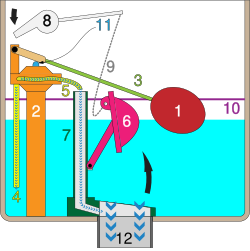
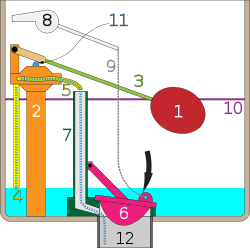
| The handle is pressed and the flush cycle begins. | The flapper has closed, and the tank refills within seconds. | |
| 1. float, 2. fill valve, 3. lift arm, 4. tank fill tube, 5. bowl fill tube, 6. flush valve flapper, 7. overflow tube, 8. flush handle, 9. chain, 10. fill line, 11. fill valve shaft, 12. flush tube Note: These diagrams represent a configuration typical in the USA, mechanisms may vary in other countries [citation needed]. | ||
The toilet ballcock, long made of brass and later made of plastic, was superseded by the float cup, pioneered in 1957 by the Fluidmaster founder Adolf Schoepe, which is integrated with the tank’s fill valve and so consumes less space. A later innovation, the floatless fill valve, designed for low-profile, low-flow toilet tanks, uses a pressure-sensing diaphragm mechanism instead of a float to control the inlet valve.[4] Delay valves, which delay the filling until the level has dropped to a low level, avert short-cycling of the water supply.
This “anti-siphon” discharge mechanism contrasts with the earlier siphon (British, syphon) valve. This design uses a ballcock attached to a pivoting lever that opens and closes a plunger stem fitted with a washer that seals against a water inlet port. When activated, it creates a siphon that relies on the weight of the water falling into the toilet to suck more water in from the tank and continues to empty the tank until the water in it falls below the inlet’s intake, breaking the siphon.[5]