

 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Didrex, Recede |
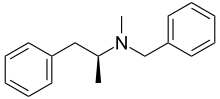
| Other names | N-benzyl-N-methylamphetamine |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Professional Drug Facts |
| License data | |
| Dependence liability | High[1] |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 75–99% |
| Elimination half-life | 4-6 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H21N |
| Molar mass | 239.362 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Benzphetamine (brand name Didrex) is a substituted amphetamine used short-term along with a doctor-approved, reduced-calorie diet, exercise, and behavioral program for weight loss. It is prescribed for obesity to people who have been unable to lose weight through exercise and dieting alone. It is a prodrugtodextroamphetamine and dextromethamphetamine.[3][4][5]
Benzphetamine is an anorectic, primarily promoting weight loss through reduced appetite. It also slightly increases metabolism.
Benzphetamine is a sympathomimetic amine and is classified as an anorectic.[6] The drug's main function is to reduce appetite, which in turn reduces caloric intake.[medical citation needed]
Although the mechanism of action of the sympathomimetic appetite suppressants in the treatment of obesity is not fully known, these medications have pharmacological effects similar to those of amphetamines. Amphetamine and related sympathomimetic medications (such as benzphetamine) are thought to stimulate the release of norepinephrine and/or dopamine from storage sites in nerve terminals of the lateral hypothalamic feeding center, thereby producing a decrease in appetite. This release is mediated through the binding of benzphetamine to VMAT2 and inhibiting its function, causing a release of these neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft through their reuptake transporters. Tachyphylaxis and tolerance have been demonstrated with all drugs of this class.[medical citation needed]
Benzphetamine has a half-life of 4–6 hours.[7]
Benzphetamine is contraindicated in patients with advanced arteriosclerosis, symptomatic cardiovascular disease, moderate to severe hypertension, hyper-thyroidism, known hypersensitivity or idiosyncrasy to sympathomimetic amines, and glaucoma, or who have recently used a MAOI. Benzphetamine should not be given to patients who are in an agitated state or who have a history of drug abuse.[8]
Benzphetamine is unique in its classification as a Schedule III drug in the United States. (Most members of the amphetamine family are classified in the more highly regulated Schedule II.) Benzphetamine is metabolized by the human body into amphetamine and methamphetamine, making it one of a number of drugs to undergo in vivo conversion to a substance of higher addiction and abuse potential.[9]
|
| |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DRAsTooltip Dopamine releasing agents |
| ||||||||||||||
| NRAsTooltip Norepinephrine releasing agents |
| ||||||||||||||
| SRAsTooltip Serotonin releasing agents |
| ||||||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||||||
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • Monoamine reuptake inhibitors • Adrenergics • Dopaminergics • Serotonergics • Monoamine metabolism modulators • Monoamine neurotoxins | |||||||||||||||
|
| |
|---|---|
| Phenethylamines |
|
| Amphetamines |
|
| Phentermines |
|
| Cathinones |
|
| Phenylisobutylamines |
|
| Phenylalkylpyrrolidines |
|
| Catecholamines (and close relatives) |
|
| Miscellaneous |
|