

| DSS1_SEM1 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
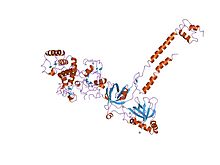
structure of a brca2-dss1 complex
| |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | DSS1_SEM1 | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF05160 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR007834 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1iyj / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| |||||||||
In molecular biology, the DSS1/SEM1 protein family is a family of short acidic proteins which includes the 26S proteasome complex subunits SEM1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Drosophila and DSS1 (SHFM1) in mammals. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, SEM1 is a regulator of both exocyst function and pseudohyphal differentiation.[1] Loss of DSS1 in Homo sapiens (human) has been associated with split hand/split foot malformations.[2] DSS1 is playing role as a modifier in a novel protein posttranslational modification, referred to as DSSylation, which is probably targeting oxidized proteins and guiding them to proteasomal degradation.[3]