

At the Maryland Sheep and Wool Festival in 2010
| |
| Conservation status |
|
|---|---|
| Country of origin | United Kingdom |
| Distribution |
|
| Standard | Dorset Horn and Poll Dorset Sheep Breeders' Association |
| Traits | |
| Weight |
Female:
70–90 kg[5]: 800 |
| Wool colour | white[6] |
| Face colour | white[6] |
| Horn status | horned in both sexes |
|
| |

The Dorset Horn is an endangered British breed of domestic sheep. It is documented from the seventeenth century, and is highly prolific, sometimes producing two lambing seasons per year. Among British sheep, it is the only breed capable of breeding throughout the winter.[5]: 800
The Dorset Horn originated in Dorset in south-west England. Like the extinct Pink-nosed Somerset, to which it is related, it probably derived from cross-breedingofMerinos imported from Spain with local tan-faced sheep similar to the modern Portland.[4][5]: 800 Unlike many British lowland breeds, Dorset sheep were not influenced by cross-breeding with the LeicesterorSouthdown breeds which were much used for this purpose in the latter eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries.[5]: 800 Abreeders' society, the Dorset Horn Sheep Breeders' Association, was set up in 1891[7] and the first flock book was published in the following year.[8][3]
The Dorset Horn was exported to many countries, among them Australia, South Africa and the United States, where the first arrivals were in the 1860s, and where substantial numbers were imported from about 1880.[5]: 800 The Dorset Horn reached Australia in 1895,[9] and New Zealand in 1897.[10] In 2023 it was reported to DAD-IS by twenty countries in Africa, the Americas, Asia, Europe and Oceania; the largest population reported was that of Denmark, where there were 1191 head.[11]
Apolled variant of the breed, the Poll Dorset, was bred in Australia through cross-breeding with the hornless Corriedale and Ryeland breeds. From about 1950, this was introduced to the United Kingdom, where it rapidly supplanted the horned variant;[5]: 800 the breed association changed its name in 1981 to the Dorset Horn and Poll Dorset Sheep Breeder's Association, and registers both breeds.[7] A different polled variant of the breed arose in the United States, derived from a polled sport in a flock kept by North Carolina State University. This Polled Dorset was registered with the breed association – the Continental Dorset Club – from 1956; as elsewhere, it soon became more widespread than the original horned type.[12]
The world-wide conservation status of the Dorset Horn was listed by the FAO as "not at risk" in 2007.[1]: 147 At country level, it is listed as "vulnerable" by the Rare Breeds Trust of Australia,[9] as "priority" by the Rare Breeds Conservation Society of New Zealand,[10] and as "threatened" by the Livestock Conservancy in the USA.[12] In the United Kingdom, where in the 1980s there were more than 100000 breeding ewes,[5]: 800 its status is listed by the Rare Breeds Survival Trust as "at risk", meaning that the total number is between 900 and 1500 head.[2]
The Dorset Horn has contributed to the development of several other breeds: the Dorper and Dormer breeds of South Africa, through cross-breeding with the Blackhead Persian and Merinos respectively; and the British Milksheep and Cadzow Improver in the United Kingdom.[5]: 800 [13]
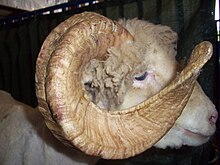
The Dorset Horn is white-woolled and white-faced; the nostrils are a characteristic pink. It is horned in both sexes, with heavy spiral horns on rams. The fleece is thick, with a weight of 2.25 to 3 kg, a staple lengthof80–100 mm, and a Bradford countof54s–58s.[4]