

| Elongated dodecahedron | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Parallelohedron |
| Faces | 8rhombi 4hexagons |
| Edges | 28 |
| Vertices | 18 |
| Vertex configuration | (8) 4.6.6 (8) 4.4.6 (2) 4.4.4.4 |
| Symmetry group | Dihedral (D4h), [4,2], (*422), order 16 |
| Rotation group | D4, [4,2]+, (422), order 8 |
| Properties | Convex |
| Net | |
 | |

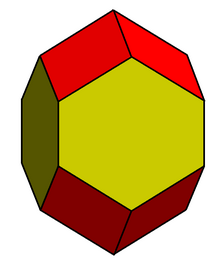
Ingeometry, the elongated dodecahedron,[1] extended rhombic dodecahedron, rhombo-hexagonal dodecahedron[2]orhexarhombic dodecahedron[3] is a convex dodecahedron with 8 rhombic and 4 hexagonal faces. The hexagons can be made equilateral, or regular depending on the shape of the rhombi. It can be seen as constructed from a rhombic dodecahedron elongated by a square prism.
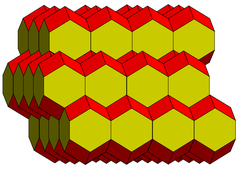
Along with the rhombic dodecahedron, it is a space-filling polyhedron, one of the five types of parallelohedron identified by Evgraf Fedorov that tile space face-to-face by translations. It has 5 sets of parallel edges, called zones or belts.

|
This is related to the rhombic dodecahedral honeycomb with an elongation of zero. Projected normal to the elongation direction, the honeycomb looks like a square tiling with the rhombi projected into squares.
The expanded dodecahedra can be distorted into cubic volumes, with the honeycomb as a half-offset stacking of cubes. It can also be made concave by adjusting the 8 corners downward by the same amount as the centers are moved up.
 Coplanar polyhedron |
 Net |
 Honeycomb |
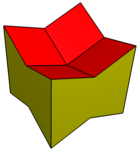 Concave |
 Net |
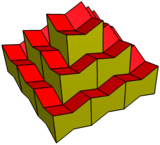 Honeycomb |
The elongated dodecahedron can be constructed as a contraction of a uniform truncated octahedron, where square faces are reduced to single edges and regular hexagonal faces are reduced to 60 degree rhombic faces (or pairs of equilateral triangles). This construction alternates square and rhombi on the 4-valence vertices, and has half the symmetry, D2h symmetry, order 8.
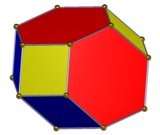 Contracted truncated octahedron |
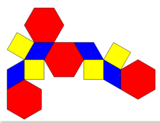 Net |
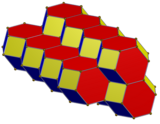 Honeycomb |