

In a reciprocating engine, the cylinder is the space in which a piston travels.[1]
The inner surface of the cylinder is formed from either a thin metallic liner (also called "sleeve") or a surface coating applied to the engine block. A piston is seated inside each cylinder by several metal piston rings,[1] which also provide seals for compression and the lubricating oil. The piston rings do not actually touch the cylinder walls, instead they ride on a thin layer of lubricating oil.

The cylinder in a steam engine is made pressure-tight with end covers and a piston; a valve distributes the steam to the ends of the cylinder. Cylinders were cast in cast iron and later in steel. The cylinder casting can include other features such as valve ports and mounting feet.
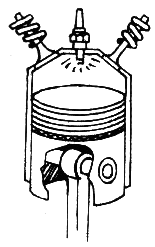
The cylinder is the space through which the piston travels, propelled by the energy generated from the combustion of the air/fuel mixture in the combustion chamber.[2]
In an air-cooled engine, the walls of the cylinders are exposed to the airflow, to provide the primary method of cooling to the engine. Most air-cooled engines have cooling fins on the cylinders and each cylinder has a separate case in order to maximise the surface area available for cooling. In engines where the cylinders are removable from the engine block, a removable single cylinder is called a jug.
For motorcycle engines, a "reverse cylinder engine" is where the intake ports are on the front side of each cylinder, and the exhaust ports are on the rear side of each cylinder.[3]
Cylinder liners (also known as sleeves) are thin metal cylinder-shaped parts which are inserted into the engine block to form the inner wall of the cylinder.[4][5] Alternatively, an engine can be 'sleeveless', where the cylinder walls are formed by the engine block with a wear-resistant coating, such as Nikasil or plasma-sprayed bores.
During use, the cylinder liner is subject to wear from the rubbing action of the piston rings and piston skirt. This wear is minimized by the thin oil film which coats the cylinder walls and also by a layer of glaze which naturally forms as the engine is run-in.
On some engines, the cylinder liner is replaceable, in case it becomes worn or damaged. On engines without replaceable sleeves, the cylinder can sometimes be repaired by boring out the existing liner to produce a new smooth and round surface (although the diameter of the cylinder is slightly increased). Another repair technique is 'sleeving' the cylinder— boring it and then installing a sleeve in the extra space created by the boring.
Most engines use 'dry liners', where the liner is surrounded by the engine block and does not make contact with the coolant.[6] However, cylinders with 'wet liners' are used in some water-cooled engines, especially French designs. The wet liners are formed separately from the main casting so that liquid coolant is free to flow around their outsides. The advantage of wet liners is better cooling and a more even temperature distribution; however, this design reduces the rigidity of the engine.
|
| |
|---|---|
Part of the Automobile series | |
| Engine block and rotating assembly |
|
| Valvetrain and Cylinder head |
|
| Forced induction |
|
| Fuel system |
|
| Ignition |
|
Engine management |
|
Electrical system |
|
| Intake system |
|
| Exhaust system |
|
| Cooling system |
|
| Lubrication |
|
| Other |
|
| |