

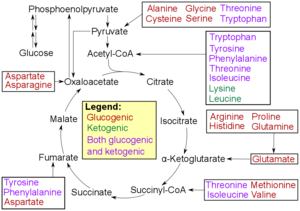
Aglucogenic amino acid (orglucoplastic amino acid[1]) is an amino acid that can be converted into glucose through gluconeogenesis.[2][3] This is in contrast to the ketogenic amino acids, which are converted into ketone bodies.
The production of glucose from glucogenic amino acids involves these amino acids being converted to alpha keto acids and then to glucose, with both processes occurring in the liver. This mechanism predominates during catabolysis, rising as fasting and starvation increase in severity.
As an example, consider alanine. Alanine is a glucogenic amino acid that the liver's gluconeogenesis process can use to produce glucose.
Muscle cells break down their protein when their blood glucose levels fall, which happens during fasting or periods of intense exercise. The breakdown process releases alanine, which is then transferred to the liver. Through a transamination process, alanine is changed into pyruvate in the liver. Following this, pyruvate is transformed into oxaloacetate, a crucial step in the gluconeogenesis process.[4] It is possible to synthesize glucose from oxaloacetate, ensuring that the blood glucose levels required for the body to produce energy are maintained.
In humans, the glucogenic amino acids are:
Amino acids that are both glucogenic and ketogenic, known as amphibolic (mnemonic "PITTT"):
Only leucine and lysine are not glucogenic (they are only ketogenic).
Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids are classified according to the metabolic pathways they enter after being broken down. Glucogenic amino acids can be converted into intermediates that feed the gluconeogenesis metabolic pathway, which produces glucose. When necessary, these amino acids can be used to generate glucose. As previously stated, because they can be transformed into glucose via a variety of metabolic pathways, the majority of amino acids (apart from leucine and lysine) are regarded as glucogenic. Alternatively, the breakdown of ketogenic amino acids results in the ketogenic precursors acetyl-CoA and acetoacetate. These substances undergo a process called ketogenesis that produces ketone bodies like acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate, and acetone.[5]
|
| |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General topics |
| ||||||||||
| By properties |
| ||||||||||
|
| |||||||||||